Throughput in 5G NR is influenced by multiple factors across the end-to-end (E2E) network, including the UE, air interface, gNodeB, transmission network, core, and server nodes. To troubleshoot throughput issues, each node must be optimized separately.
Certain factors impact resource block (RB) allocation and grant size, while others affect modulation and coding scheme (MCS), block error rate (BLER), and rank. Proper analysis of these parameters helps in identifying bottlenecks and improving overall network performance.
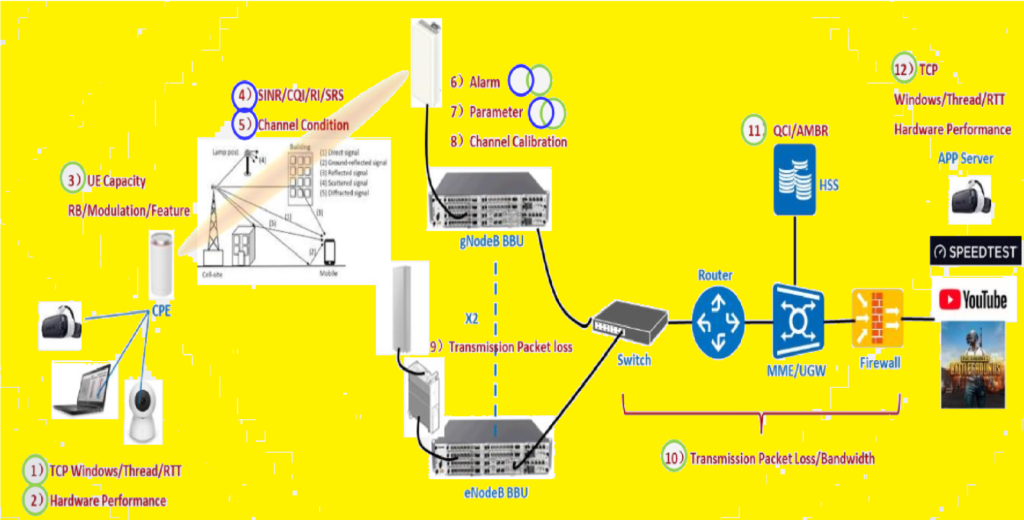
Factors 1,2,3,6,7,9,10,11,12 will be reflected on the Grant and RB, while Factors 4,5,6 and 7 will be reflected on the MCS, BLER and RANK.
Troubleshooting Process Flow on the RAN Side
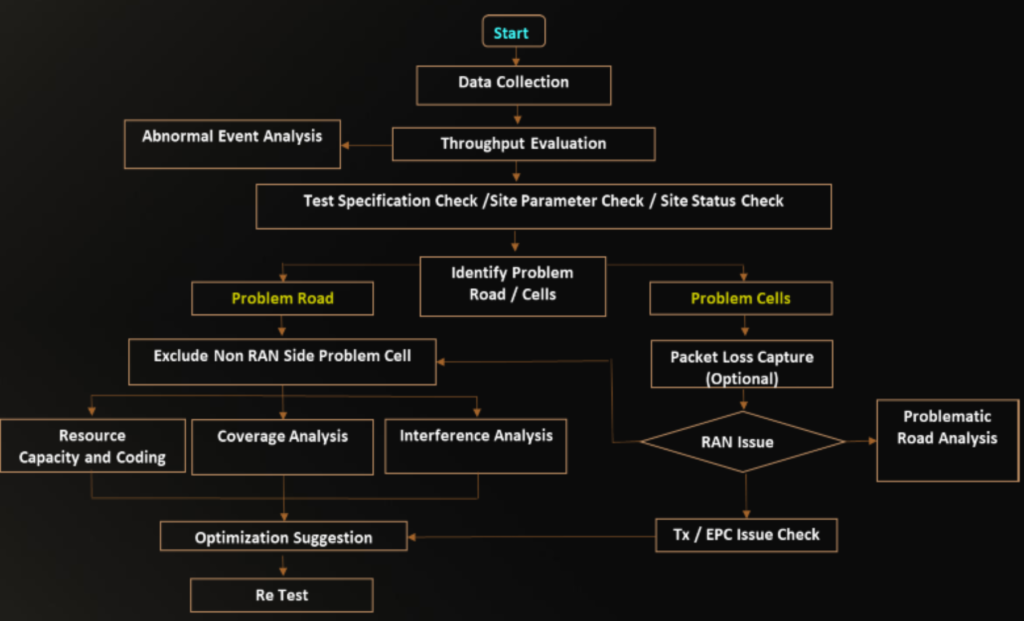
Test Specification Check: Check the test items related to throughput such as UE , Server, Test Software , UE AMBR.
Abnormal Event Analysis: Analyze abnormal events based on DT Log Analysis including Call Drop , frequent PScell Change , Cell Change failure.
Coverage Analysis: Analyze coverage problem if there is missing neighbor , coverage hole, no dominant serving cell, cell change delay.
LTE /NR Site Intermittent: Check both LTE and NR if have major alarm.
Parameter Check: Ensure both LTE and NR Parameters have set accordingly.
Interference Analysis: Analyze interference problem such as overshooting or overlapping issue.
Resource Capacity: Check if resource capacity, scheduling issue, high PRB, High User Number, High CPU Load or problem exist on the RAN Side.
Identify the Packet Loss Issue: Capture the packet loss to identify which domain with fault occurs. Re do packet ping test if is difficult to capture the packet loss and check if RAN side has issue
Test Specification Check
The test specification check for Huawei network optimization includes verifying UE capabilities from the UECapabilityInformation message in drive test logs.
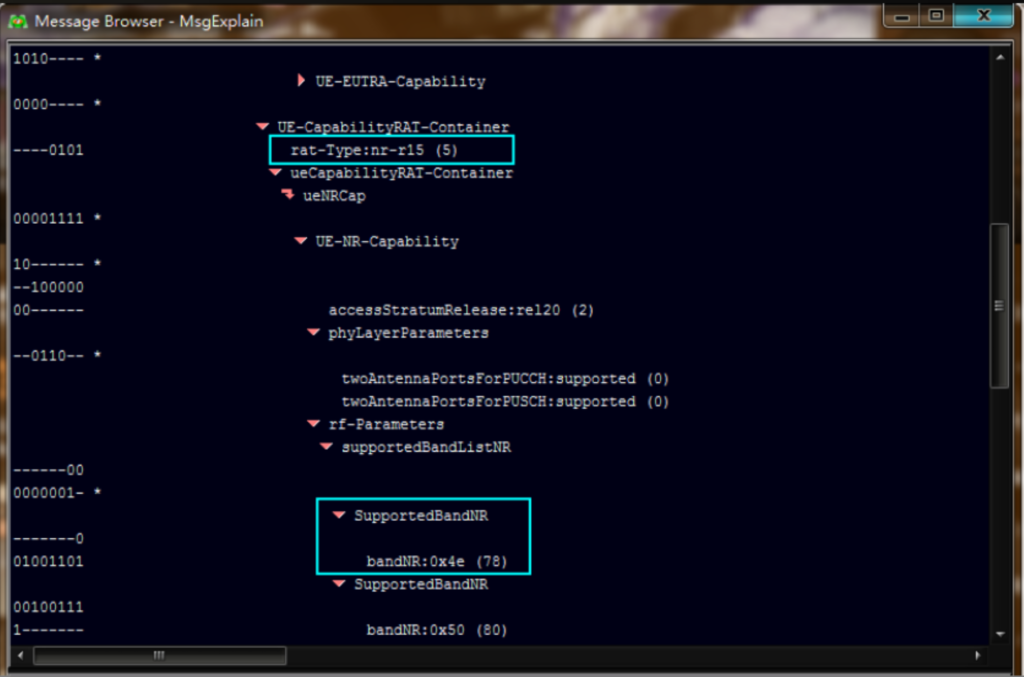
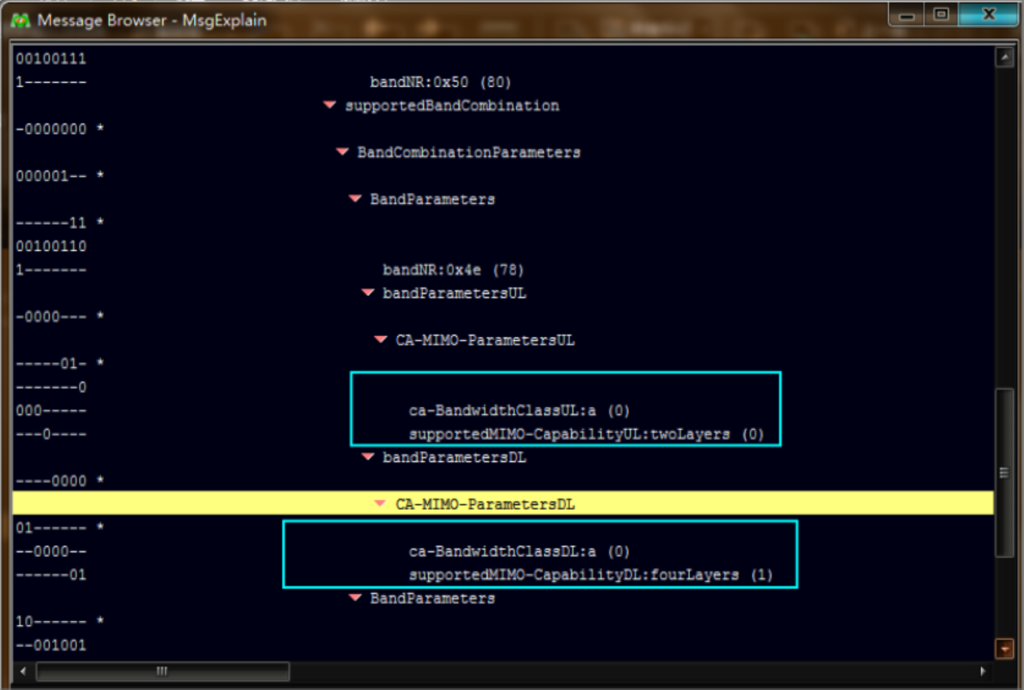
SIM card registration speed is analyzed by checking the UE AMBR in the S1 message.
Laptop performance should meet recommended specifications (e.g., Lenovo X1 Carbon).
Server performance should align with the recommended RH2288 V3 model. For accurate FTP download testing, large files (≥20 GB) with multiple threads should be used to ensure consistent download speeds and prevent performance degradation between file transfers.
Uu Factors Impact Throughput
To Understand the Theoretical formula of DL Throughput Calculation on the RAN Side and the factors that will impact the Throughput.
Downlink throughput = PDCCH DL Grant * PDSCH RE Number per Slot * Bits per RE * Code Rate * Layers * (1-BLER%)
| PDCCH DL Grant | Number of Downlink Scheduling Times. |
| PDSCH RE Number per Slot | Represent the RE Source that can be used by the PDSCH of each timeslot. |
| Bits per RE | 256 QAM = 8bits , 64 QAM=6 bits, 16 QAM = 4 bits , QPSK = 2 bits. |
| Code Rate | Bit Rate of Downlink Data Demodulation determined by MCS index Table , 3GPP 38214 Table 5.1.3.1-2. |
| Layers | RANK; Number of transmission layers on PDSCH. |
| BLER | Target iBLER is 10%. |
Based on the Formula , Throughput can be directly affected by RANK, MCS , BLER , Grant , RB , whereby MCS , BLER and RANK are closely related to Uu Interface factors , while Grant and RB mainly affected by abnormal scheduling or insufficient inbound traffic.
Which factors impacts Uu Interface?
- Number of Grant and RB. [Peak standard: Grant: DL 1600/UL 400 times (4:1&8:2 Frame Structure) RB: 265 RBs (100MHz)]
- Low MCS. [Peak standard: MCS27 (256QAM) /MCS28 (640AM)]
- High IBLER. Peak standard: 0% IBLER
- Rank. [DL/UL Peak Standard: 2T4R (Rank4/2), 4T8R (Rank8/4)].
Below is sample data from other project , to show that Grant, RB,MCS, Rank, BLER can impact the Throughput.
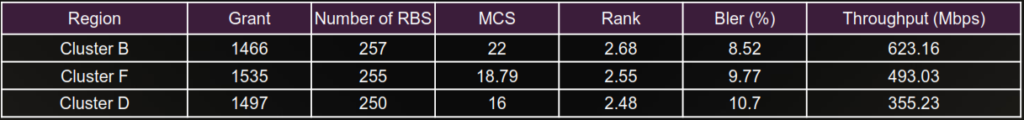
Low Throughput caused by Low Grant
| Problem Details: | Analysis: |
| Low Throughput with Low DL Scheduling Times : XX ( Example < 1400). | The SSB Coverage is good , however the number of scheduling is lower than the threshold. |
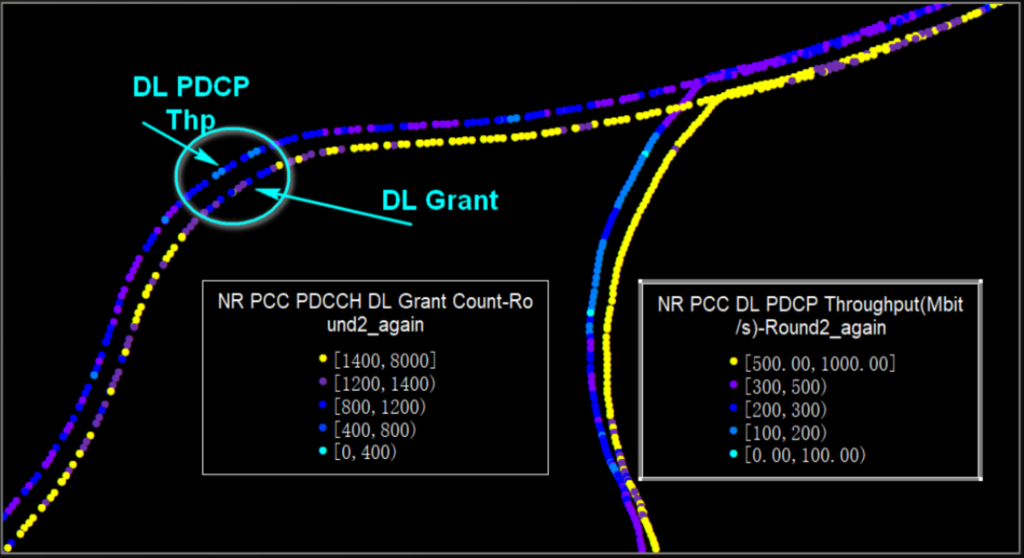
Troubleshooting Suggestion:
1. Terminal Capability
Terminal capability affects 5G NR performance, including maximum achievable data rates. To analyze this, check if the UE is limited by its maximum data rate, which can be verified in the “UECapabilityInformation” message from DT logs. For example, in a 64T64R AAU setup, the UE must support at least RANK 4 for optimal performance. If lower RANKs are observed, it may indicate a capability limitation or suboptimal network conditions affecting throughput.
2. SIM Card Registration Rate
To check if a subscriber’s SIM is limiting throughput, verify the maximum bit rate. For GT SIMs, the commercial SIM max bit rate is 850 Mbps, while normal test SIMs can reach ~2 Gbps. If an abnormal test SIM shows speeds below 100 Mbps, escalate the issue to the Core Team for further investigation. Low speeds on test SIMs may indicate restrictions or misconfigurations affecting network performance.
3. FTP Server Performance and FTP DL file Size
To ensure optimal FTP download speeds, check if the download task is set to multiple threads and that the file size is greater than 20 GB. If the FTP server is functioning properly, verify its performance using a reliable speed test server (e.g., Globe Speed Test Server).
4. Packet Loss
Check if the Upstream packet loss and delay is high on the transmission or core.
5. Abnormal Event Occur
Example frequent handover and etc.
Low 5G Throughput caused by Low DL RB Assigned
| Problem Details: | Analysis: |
| Low Throughput with Low DL RB assigned. | The level and SINR of the primary serving cell are good, the scheduling is good, however the RB assigned is insufficient. |
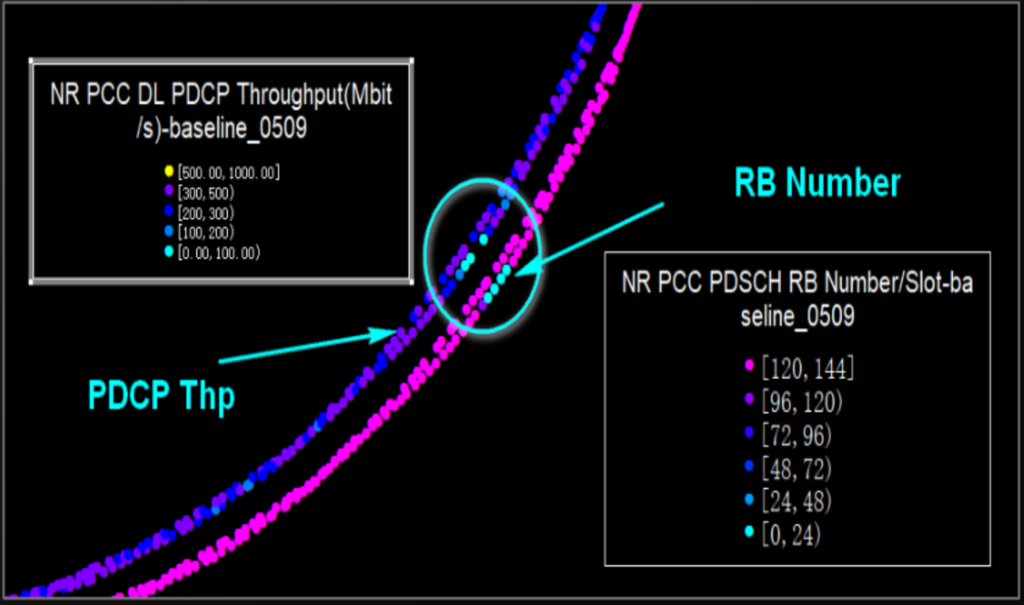
| DL Bandwidth | LST NRDUCELL to check the DLBandwidth. |
| AAU has Excessive High Temperature. | 1. When the operating temperature of the RF unit exceeds the operating range. 2. Alarm is generated, indicating that the RF unit temperature is abnormal. Alarm ID: ALM-26525 |
| RF Unit Input Power is Insufficient. | 1. Alarm is generated when the RF unit detects that the external input power is insufficient. 2. This alarm indicates that the RF unit is derated when this alarm is a minor alarm. As a result, the RB resources are insufficient. Alarm ID: ALM-26546. |
Low 5G Throughput caused by High iBLER
| Problem Details: | Analysis: |
| Low throughput with Average iBLER. | Consecutive samples with high iBLER greater than 15%. |
High iBLER (Instantaneous Block Error Rate) can lead to low throughput and poor network performance. Ideally, the gNodeB adjusts the MCS to maintain an iBLER close to 10%. If iBLER exceeds 15% in consecutive samples.
Troubleshooting Suggestion:
| Downlink Target IBLER. | Troubleshooting should start by verifying the Downlink Target iBLER setting in LST NRDUCELLPDSCH.DlTargetIbler, ensuring it remains at the recommended 10%. Ensure not to set too large. |
| External Interference. | Additionally, check for external interference. |
| Inter Site Interference. | Check if there is any Inter Site Interference, Overlapping. |
Low 5G Throughput caused by Low RANK
Low rank can be RF or Non-RF reason.
| Problem Details: | Analysis: |
| 1. Low throughput with NR PCC Rank Indicator. 2. Low throughput with NR PCC Rank Indicator. | 1. Poor RSRP/SINR causing Low RANK. 2. Good RSRP/SINR, however RANK is low. |
Troubleshooting Suggestion for RF Reason:
| Max Transmit Power | Adjust the Maximum Transmit Power of the Cell if is require. |
| Tilting | Adjust the Mechanical Tilt / Digital Tilt if is require. |
| Azimuth | Adjust the Azimuth if is require. |
Troubleshooting Suggestion for Non RF Reason:
| Channel Calibration | Verify the DSP NRDUCELLCHNCALIB results to ensure successful channel calibration. If calibration fails, request NOC assistance to execute STR NRDUCELLCHNCALIB. |
| Insufficient License | Check the DSP LICINFO command to verify that the allocated license value is sufficient; if not, a “Configuration Data Exceeding Licensed Limit” alarm may appear. |
| Abnormal Event | Check whether there is frequent Handover or There is no handover perform by a strong signal neighbor. |
| RF Unit , CPRI Alarm | 1. Faulty RF Unit will cause cell service capability deteriorate. As a result, the serving cell and neighboring cells are not synchronized, causing severe clock out-of-synchronization and uplink and downlink interference. 2. CPRI alarms or RF intermittent disconnections can degrade RSRP, affecting CSI measurements and throughput performance. |
Low 5G Throughput caused by Low MCS
| Problem Details: | Analysis: |
| Low throughput with Low MCS. | (Example) Poor SINR causing Low MCS. |
Low throughput in a 5G network is often caused by a low Modulation and Coding Scheme (MCS), which directly impacts data transmission efficiency. MCS is determined by the Channel Quality Indicator (CQI), which reflects signal conditions.
Poor Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise Ratio (SINR) degrades CQI, leading to lower MCS selection and smaller Transport Block (TB) sizes, reducing throughput. Poor SINR is usually due to network interference, such as NR intra-RAT neighbor interference, inter-beam interference, or external interference. Addressing these issues helps improve MCS and overall network performance.
Troubleshooting Suggestion:
As since Poor SINR is usually caused by network interference , thus suggest to check
- NR Intra-RAT Neighbor Interference.
- Inter- Beam Interference.
- External Interference.