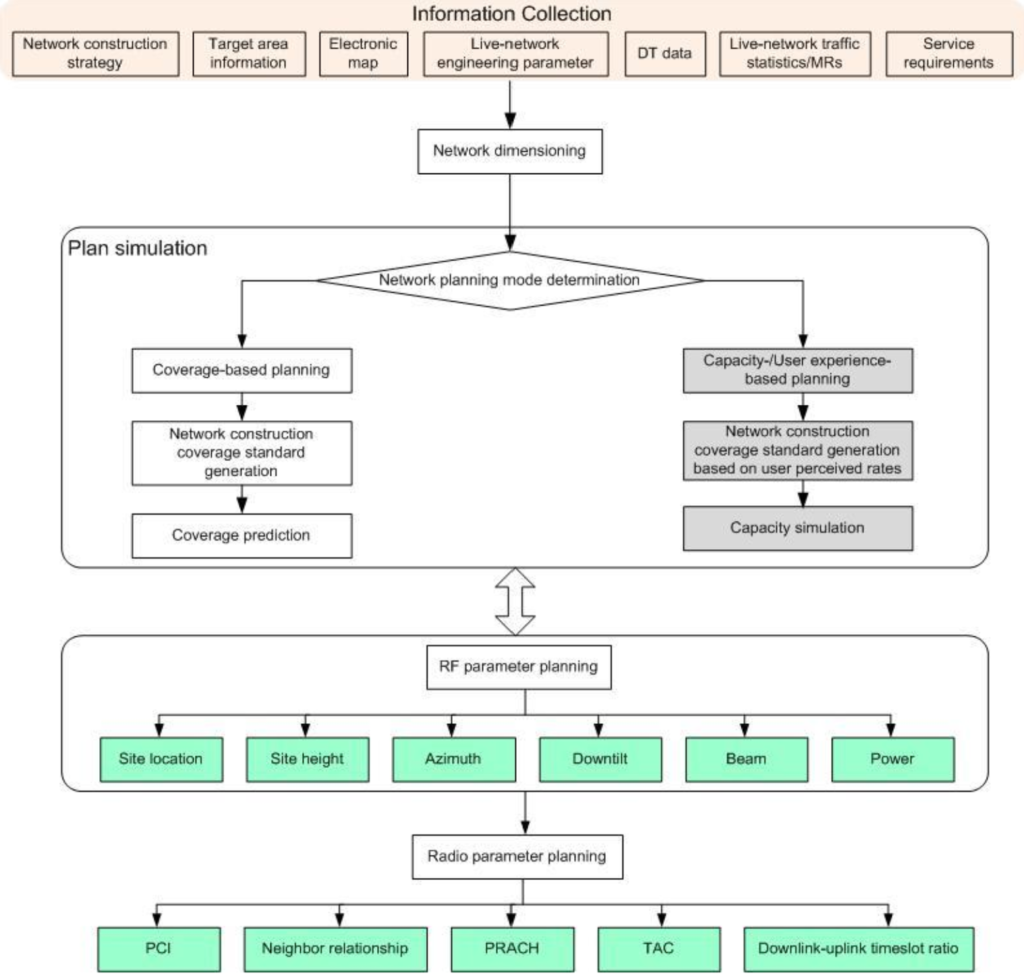
Planning a 5G network involves a systematic approach that begins with collecting relevant information and progresses through dimensioning, detailed planning, simulation, and parameter setting. This procedure ensures that the network meets coverage, capacity, and quality requirements. Below picture shows 5G network planning procedure.
Initial Information Collection
The initial stage of 5G network planning focuses on gathering comprehensive information that serves as the foundation for subsequent planning phases. This includes understanding the 5G network construction policies and objectives set by operators, which outline the strategic goals and performance targets of the network. Frequency band information is crucial to determine the spectrum available for use and its specific characteristics, which impact coverage and capacity planning.
Coverage area information is collected to identify the geographic regions that need to be serviced, while service requirements detail the types of services (e.g., enhanced mobile broadband, ultra-reliable low latency communication, massive IoT) and their performance expectations. Additionally, parameters like coverage probability and signal quality requirements are defined to ensure reliable and high-quality service delivery. Digital maps are used to visualize the planning area and assist in the precise placement of network elements.
For operators with existing 2G/3G/4G networks, legacy network information provides valuable insights. This includes drive test (DT) data, traffic statistics, measurement report (MR) data, site distribution, and engineering parameters. This historical data helps in understanding current network performance and identifying areas for improvement or expansion in the new 5G network.
Network Dimensioning
Network dimensioning is a critical step conducted at the early stages of projects, such as during the bidding and Request for Information (RFI) or Request for Proposal (RFP) phases. The primary goal of dimensioning is to provide a rough plan of the future network to estimate the required site scale and coverage radius. This involves using the collected information to project the size and resources necessary for the network, ensuring that initial plans are aligned with the overall objectives and constraints.
Detailed Planning During Project Delivery
Once the network dimensioning is complete, the detailed planning phase begins, which is typically undertaken during the project delivery phase. This stage focuses on refining the initial plans and determining specific cell parameters related to radio frequency (RF) planning and cell planning.
RF Planning involves defining the engineering parameters such as site location, site height, azimuth, down tilt, and power settings. For 5G networks, RF planning also includes beam configuration, which is essential for optimizing coverage and capacity through advanced beamforming techniques. The settings are verified through simulations to ensure they meet the desired performance criteria and can be used as references for actual network construction.
Simulation and Verification are crucial to validate the planned parameters. Simulation tools help predict network performance under various conditions, allowing planners to identify and rectify potential issues before deployment. The verified settings from simulations provide a reliable basis for constructing the network.
Cell Planning
Cell planning encompasses several tasks essential for the efficient operation of the network. Physical Cell Identifier (PCI) Planning assigns unique PCIs to each cell to prevent collisions and confusion, which are critical for maintaining network integrity and performance. Physical Random Access Channel (PRACH) Root Sequence Planning involves selecting root sequences for initial access by user equipment (UE), facilitating smooth connectivity and access.
Neighboring Cell Planning ensures that cells are correctly configured for seamless handovers by setting up intra-frequency and inter-frequency neighbors, as well as inter-RAT (Radio Access Technology) neighbors. This configuration is vital for maintaining continuous service as users move across different cells. Location Area (LA) Planning, primarily involving tracking area (TA) planning, is crucial for effective mobility management.
TDD Uplink-Downlink Subframe Configuration
For Time Division Duplex (TDD) systems, Uplink-Downlink Subframe Configuration is an important aspect of cell planning. This involves planning the uplink and downlink subframes to balance capacity and latency requirements effectively. Proper configuration ensures that the network can handle varying traffic loads and maintain high performance.
Summary
The 5G network planning procedure is a comprehensive and multi-faceted process that ensures the successful deployment and operation of the network. Starting with thorough information collection and dimensioning, the process moves into detailed RF and cell planning, followed by simulation and parameter verification.
By considering engineering parameters, using network data, and following to service requirements, operators can deploy robust and efficient 5G networks that meet the growing demands of users.
Read Also: Differences Between 4G and 5G Network Planning.