A VoLTE call drop occurs when an ongoing call is abnormally terminated without successful completion. The expected completion involves the exchange of a BYE message and its acknowledgment (200 OK) between the two parties. Drops can arise due to failures in any domain involved in VoLTE, such as LTE, EPC, IMS, or MSS (for ICS or CS fallback calls). Common causes include:
- UE Failures: Loss of radio connection, power failure, or device issues.
- RAN/EPC Triggered: Bearer release initiated by the Radio Access Network or EPC.
- IMS/MSS Triggered: Session termination initiated from the IMS core or MSS node.
- UE-Initiated BYE Failure: Call termination fails after the UE sends the BYE message.
Flow References
- Case 1 and 2: Refer to the detailed bearer release flow during calls (as outlined in specific system references).
- Case 3: Refer to session termination in IMS.
Domains Involved: LTE, EPC, IMS, UDM, and MSS (for CS fallback). Each has unique potential issues impacting the overall call stability.
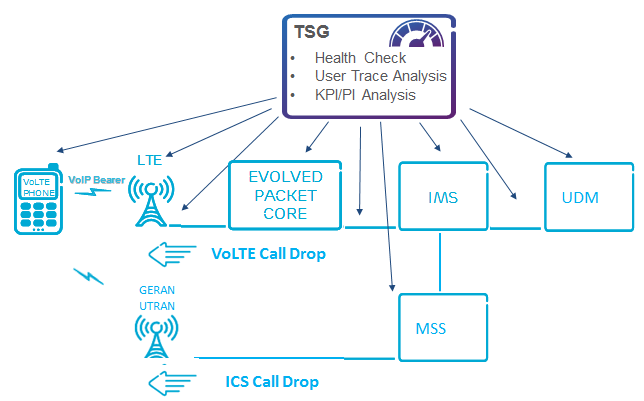
How to optimize VoLTE Call Drop?
Health Check
When a VoLTE-to-VoLTE call drop occurs, a thorough health check across LTE, EPC, IMS, and UDM is essential. For ICS call drops, the MSS domain must also be evaluated. The health check focuses on symptoms like user impact, LTE data status, or access dependencies. Below are specific scenarios:
- For multiple ICS call drops in specific BSS/RNCs, check related MSS.
- If area-wide VoLTE call drops occur, focus on RAN and EPC.
- User-specific VoLTE drops require checks in EPC, UDM (HSS), IMS (SBG/MTAS), and charging systems.
- For ICS call drops impacting individual users, evaluate MSS, HLR, and UDM (HSS), along with user credit status.
- In cases of VoLTE call drops across all areas, host EPC, IMS, and UDM should be reviewed.
- For both LTE data and VoLTE drops, prioritize health checks on originating RAN and EPC.
E2E Trace Analysis
Assume the E2E Trace on subscriber level has been collected, please compare call flow with acceptance test specification of this VoLTE deployment.
Performance Indicators in VoLTE
At the E2E VoLTE level, a key performance indicator (KPI) is defined for call completion. A successful call means the session is established, and a 200 OK (BYE) response is received by the user equipment (UE).
The Call Completion Success Ratio (CCSR) measures this and is used for troubleshooting VoLTE call drops, relying on both E2E and domain-specific KPIs.
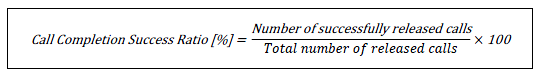
ICS calls aren’t covered since MSS lacks counters for call disconnection reasons.
A good KPI baseline is essential for identifying issues, which could occur in LTE, EPC, IMS, or a combination of domains. By analyzing KPIs in RAN, EPC, and IMS, faulty domains triggering failures can be identified. This helps isolate specific issues in nodes, interfaces, or features for resolution by following troubleshooting guides.
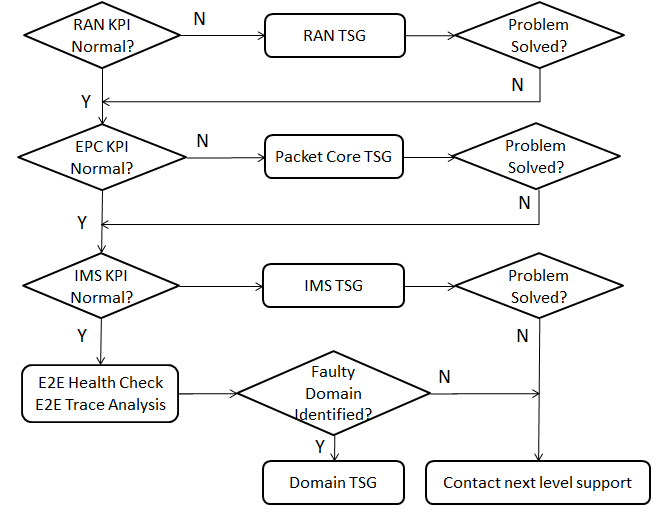
Step1: Check RAN KPIs
- E-RAB Retainability – Session Time normalized per QCI (QCI 1 only, QCI with ServiceType = VoIP ).
- E-RAB Retainability – Percentage per QCI (QCI 1 only, QCI with ServiceType = VoIP).
If the KPIs in LTE RAN show the successful ratio are lower than reference, it indicates the problem shall be at least in LTE, to futher troubleshoot in RAN. If the KPI in LTE RAN shows the successful ratio is normal, continue with Step 2.
Step2: Check EPC KPIs
- MME: Intra/inter MME TAU Failure Ratio (LTE).
- EPG: PGW S5 Update Dedicated Bearer Failure Ratio.
- EPG: PGW S5 Modify Bearer Failure Ratio.
- EPG: SGW S5 Update Dedicated Bearer Failure Ratio.
- EPG: SGW S5 Update Dedicated Bearer Failure Ratio.
If MME KPIs indicate higher failure ratio than reference, it indicates the problem shall be at least in MME. If EPG KPIs indicate higher failure ratio than reference, it indicates the
problem shall be at least in EPG or between EPG and MME. If MME and EPG KPIs indicate normal, then continue with step 3.
Step3: Check IMS KPIs
- IMS CSCF Session Completion Ratio.
- IMS CSCF Dropped Session Ratio.
- IMS SBG Incoming Session Completion Ratio.
- IMS SBG Outgoing Session Completion Ratio.
- IMS SBG Incoming Dropped Session Ratio.
- IMS SBG Outgoing Dropped Session Ratio.
- IMS MMTEL AS Originating Session Success Ratio.
- IMS MMTEL AS Terminating Session Success Ratio.
If IMS KPIs are abnormal by comparing with reference, it indicates the problem shall be in IMS. Depending on the failure KPIs the problem can be either in SBG, SCC-AS, CSCF etc. e.g If the SBG KPI indicates problems but the CSCF KPI is normal, that means SBG has some problem internally or on surrounding interfaces, so further check is needed on SBG.
Step4: If the problem domain is not identified by KPI analysis, please further
troubleshoot by E2E Health Check and E2E Trace Analysis. If faulty domain is
identified, please follow Domain Troubleshooting Guides.
Step 5: If problem is not solved, please contact next technical level support.