SRVCC (Single Radio Voice Call Continuity) enables seamless handover of IMS voice services from LTE to legacy UTRAN or GERAN networks when leaving LTE coverage. Scenarios such as SRVCC to WCDMA, GSM, and PS HO are addressed in specific MSS and Packet Core troubleshooting guides. However, cases like Mid-call SRVCC, Priority SRVCC, and SRVCC Cancellation are excluded. The primary domains involved are LTE, EPC, IMS, and MSS. Troubleshooting does not include GERAN or UTRAN aspects.
The overall SRVCC call follow is as below.
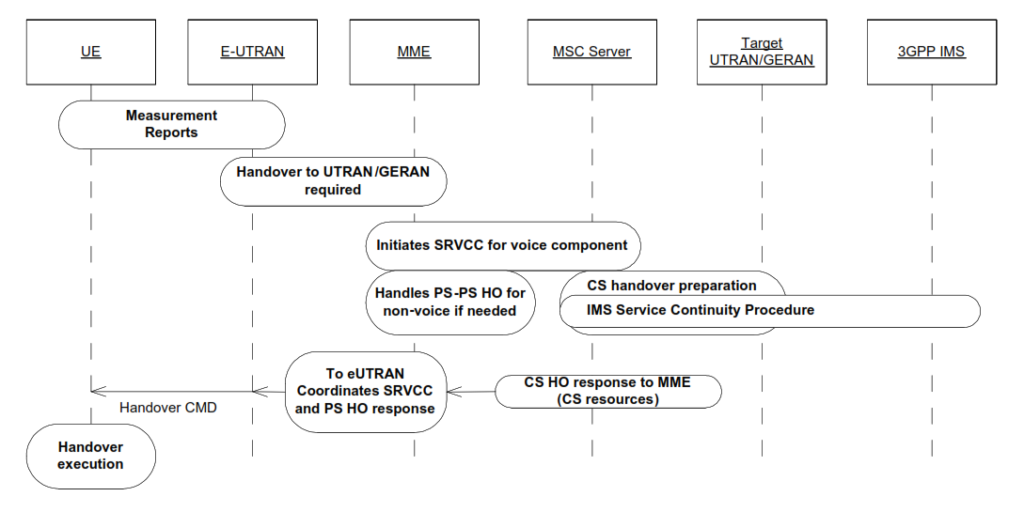
In accordance to overall SRVCC call flow, the general troubleshooting flow of SRVCC is as below.
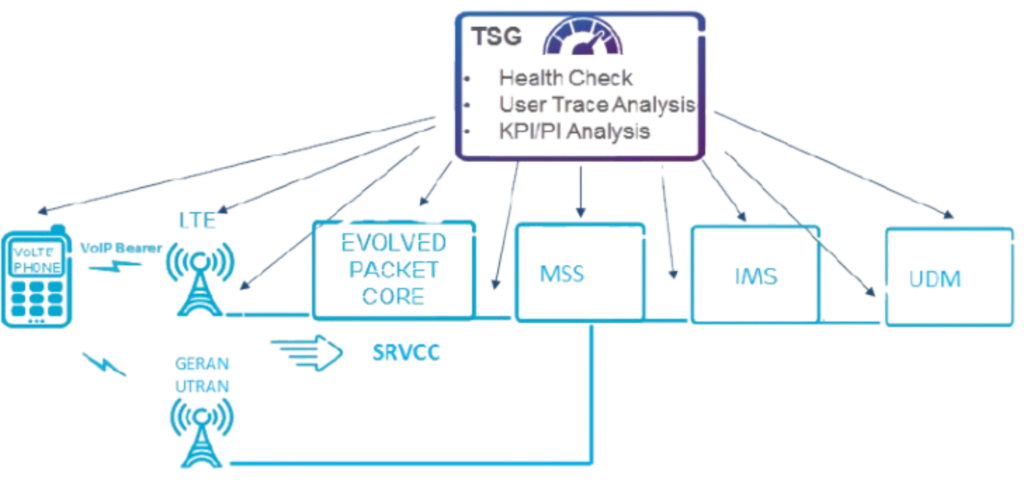
Health Check.
When SRVCC failures occur, a comprehensive Health Check must focus on LTE, EPC, MSS, IMS, and UDM. Depending on symptoms like user count or LTE data status, checks can target specific domains:
- If LTE data also fails, inspect the originating RAN and EPC.
- For individual failures, verify user data in HLR, EPC, and IMS.
- If failures occur in certain cells, examine RAN and target MSC.
- In location areas, check RAN, MSCs, and anchored MSC.
- In tracking areas, focus on RAN, MSS, and EPC.
- For widespread failures, check MSS, EPC, IMS, and UDM.
E2E Trace Analysis
For E2E Trace Analysis, once the trace for a subscriber is collected, compare the call flow against the acceptance test specification of the VoLTE deployment. Reference other E2E traces as needed.
Due to variations in site design and setup, the collected trace may differ from reference traces in terms of call flow, message content, or header values.
Performance Indicators
At the E2E VoLTE level, SRVCC handover success is defined as both IRAT handover and session transfer being successful. Total handover attempts are counted via “HO Command” messages received by the UE. A successful handover requires the UE to send “HO Complete” and the ATCF to receive “SIP ACK.”
The abstract formula for SRVCC handover success ratio is:
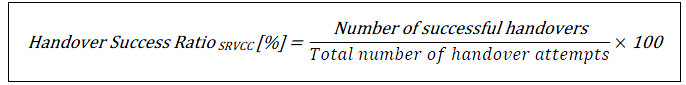
The SRVCC success ratio KPI identifies potential issues across RAN, MSS, EPC, IMS, or UDM domains. Accurate KPI baselines are crucial. Troubleshooting typically begins with RAN and proceeds to EPC, MSS, and IMS, aligning with SRVCC signaling. IMS session transfers are initiated during IRAT handovers but remain independent of IRAT success. Thus, SRVCC failures might show correct KPIs for RAN and EPC but incorrect ones for IMS.
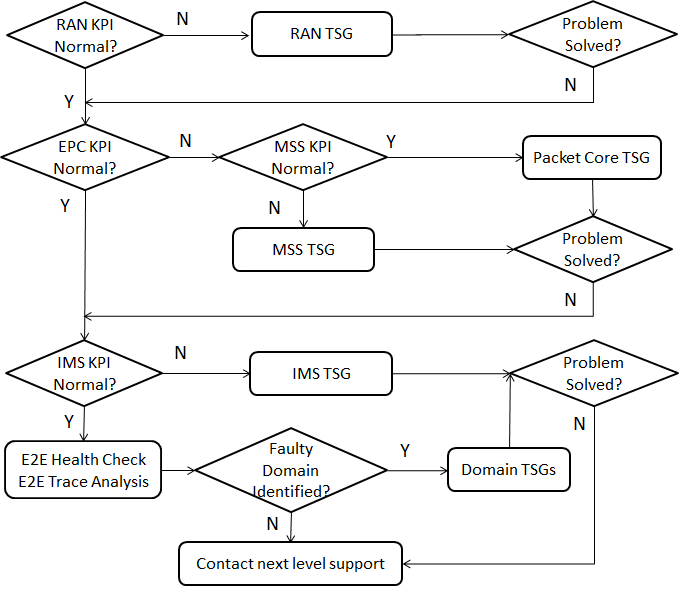
Step1: Check LTE RAN KPI
Start with the following KPI in LTE RAN.
- Mobility Success Rate.
If LTE RAN KPI indicate normal success rate, please continue with Step 2 to check EPC KPI. It’s also possible that handset issue leads to SRVCC failure. Please consult handset vendor support.
If LTE RAN KPI indicates less than reference value, it indicates problem shall
be at least on LTE RAN or UTRAN/GSM. To further troubleshoot in LTE RAN,
please refer to LTE RAN Troubleshooting Guide. At the meantime
continue with Step 2 to check EPC KPI to see if it is EPC issue which leads to
SRVCC failure.
Step2: Check EPC KPIs
- MME: SRVCC to GERAN Failure Ratio.
- MME: SRVCC to WCDMA Failure Ratio.
- MME: Inter SGSN-MME IRAT Handover Failure Ratio as Source (LTE).
The first two KPIs are for SRVCC to GERAN or UTRAN. The third KPI is additionally for SRVCC with PS handover. If EPC KPIs on MME indicate normal value, then continue with Step 4 to check IMS KPI.
If EPC KPIs on MME indicate higher failure ratio value than reference, it indicates problem shall be at least on MME. To further troubleshoot in EPC, please refer to Packet Core Troubleshooting Guide. At the meantime continue with Step 3 to check MSS KPI.
Step3: Check MSS KPIs and PIs
- SRVCC from LTE success rate per MME.
- SRVCC from LTE success rate per MSC.
- LTE to WCMDA handover success rate per MME.
- LTE to WCMDA handover success rate per MSC.
- LTE to GSM handover success rate per MME.
- LTE to GSM handover success rate per MSC.
- SIP, Initial INVITE Request Performance per Route.
- If MSC KPIs on MSC indicate lower value than reference, it indicates the problem shall be at least on MSC.
Step 4: Check IMS KPIs
- IMS SBG Incoming Session Set-up Success Ratio for CS network
- IMS SCC AS Single Radio Voice Call Continuity (SRVCC) Access.
Transfer Success Ratio.
If IMS KPIs indicated normal success ratio value, it indicates IMS and UDM is not the faulty domain. Futher check is needed on LTE RAN, EPC, MSS which is in progress at the meantime.
If IMS KPIs indicated lower value than reference value, it indicates the problem shall be at least in IMS. The root cause can be either in SBG, SCCAS, CSCF.
For example, if SBG KPI indicates problems but SCC AS KPI is normal, this indicates that the transferred request from MSC is rejected by SBG (ATCF).
Step 5: Check UDM KPIs
There are no specific counters for SRVCC in HSS. However a sharp drop of Location Info Success Rate could be useful to locate problems in HSS during SRVCC access transfer. The corresponding counters are described in ISM Measurements.
Cx: Location Info Success Ratio.
Step 6: If the problem domain is not identified by KPI analysis, please further troubleshoot by E2E Health Check and E2E Trace Analysis. If faulty domain is identified, please follow Domain Troubleshooting.
Step 7: If problem is not solved, please contact next level technical support.