5G New Radio (NR) networks introduce advanced capabilities such as ultra-high data rates, low latency, and network slicing. However, ensuring optimal network performance requires continuous monitoring, troubleshooting, and optimization to address 5G abnormal events that can degrade service quality. This article explores common NR abnormal events, their causes, and optimization techniques to improve network performance.
Below are outline of this topic which i will discuss in details one by one.
- NR Access Optimization.
- NR Abnormal Handover Event Optimization.
- NR Abnormal Call Drop Event Optimization.
1. NR Access Optimization
NR access optimization involves identifying and resolving issues that affect 5G network accessibility through a structured troubleshooting approach. The process begins with site alarm and status checks to isolate any RAN-related faults. Drive test (DT) log analysis is then conducted to examine coverage gaps, abnormal events, and signaling failures.
Additionally, KPIs such as accessibility success rates, failure causes, coverage, interference, and resource allocation are reviewed to optimize connectivity and minimize access failures.
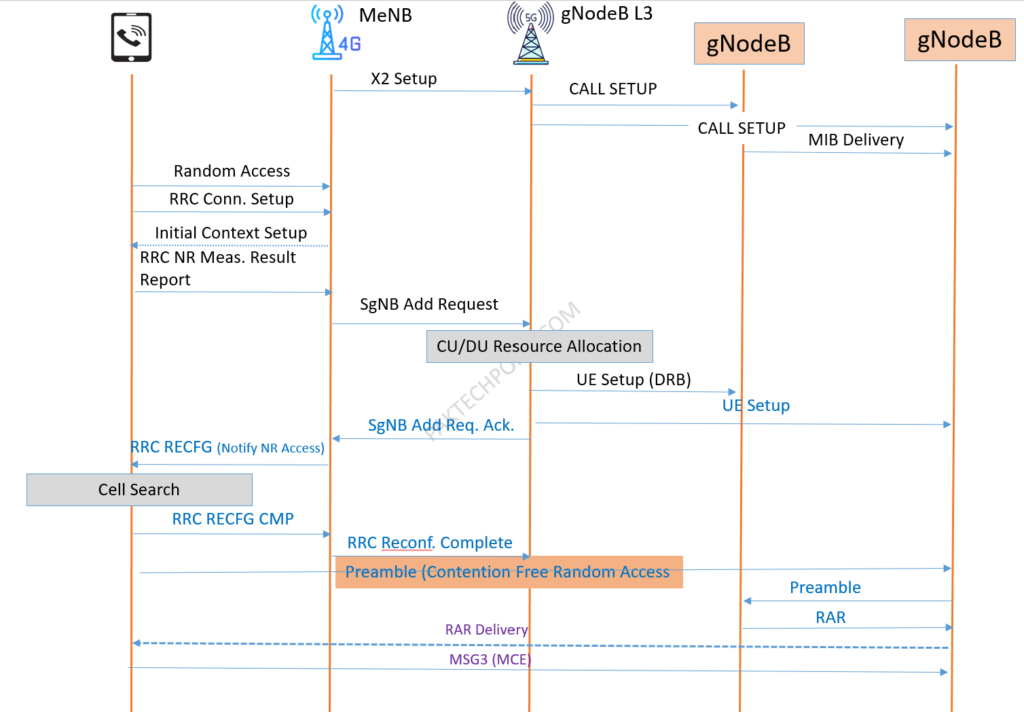
Below we summarize Reverse signaling procedure check.
NSA Access Problems
- Procedures on the LTE Side.
- LTE Access Failures.
- LTE does not deliver 5G measurement configuration after UE access the LTE network.
- UE does not send 5G B1 NR.
- Access Preparation Phase.
- LTE does not send SgNB Add Request after receiving B1 measurement report.
- 5G responds with SgNB add reject.
- LTE does not send SgNB Reconfiguration Complete to 5G.
- 5G Air interface phase.
- UE does not initiate random access over the air interface.
- RAR times out.
- MSG3 fails after UE receives RAR.
2. NR Abnormal Handover Event Optimization.
In NSA, handovers involve switching both the LTE anchor cell and the 5G cell. Since the gNB and eNB do not have direct knowledge of the UE’s location or signal quality, the UE must send measurement reports containing radio quality data. This helps the network decide when and where to hand over the connection, ensuring a smooth transition between cells and reducing service interruptions.
Below picture shows NSA Mobility Overview:
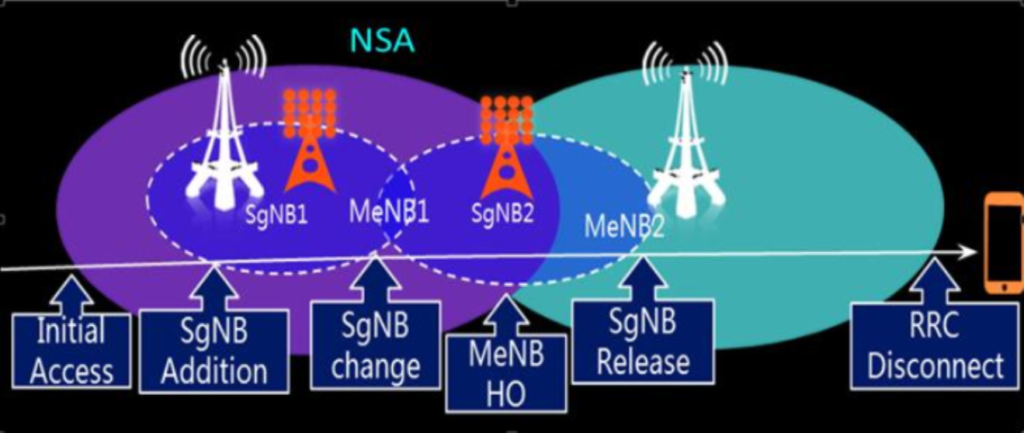
The handover process in NSA begins when the eNodeB detects a measurement or handover event and sends a handover command to the UE. Upon receiving this command, the UE stops communication with the current cell and prepares to switch. The source cell then hands over the connection to the target cell as per the handover command. Finally, signaling interaction between the UE and the target cell ensures the handover is successfully completed, allowing seamless service continuity.
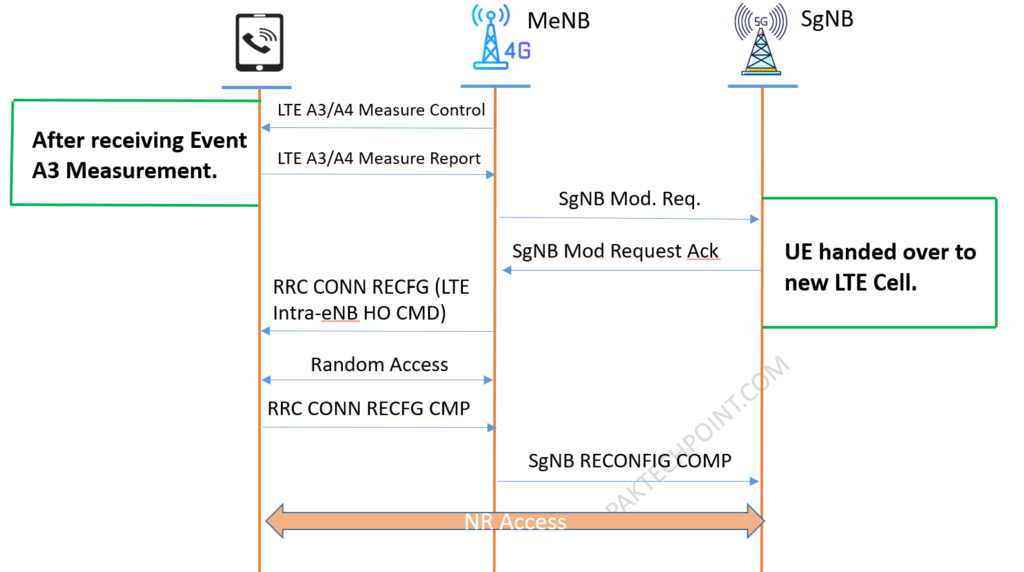
NR Abnormal Handover Event Optimization for 4G MeNB Handover
To change Pcell within same MeNB with SgNB. Intra-MeNB handover (Intra or Inter-frequency).
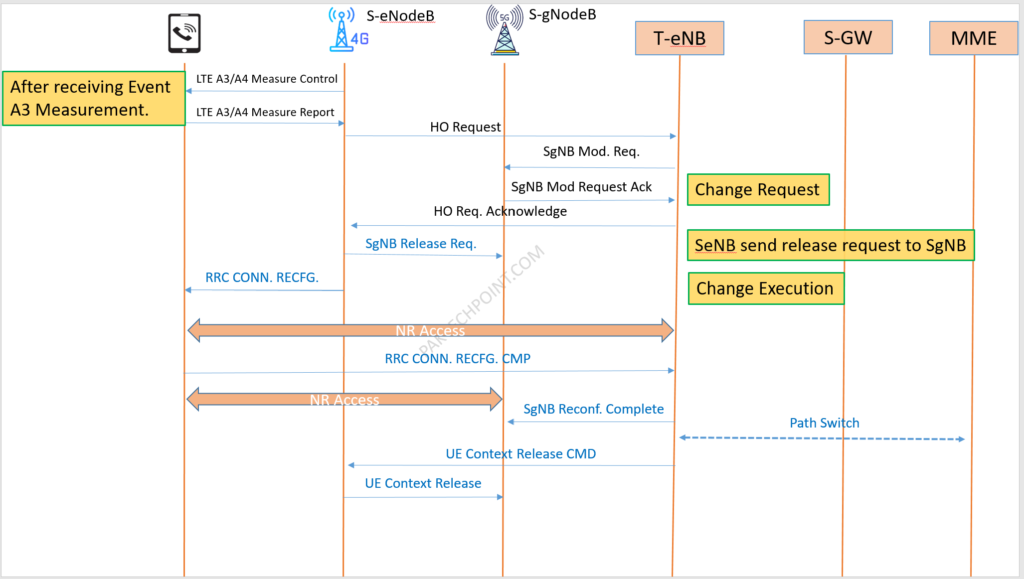
To change Pcell with different MeNB with SgNB. Inter-MeNB handover (Intra or Inter-frequency).
NR Abnormal Handover Event Optimization for 5G SgNB Handover:
To change PSCell within same SgNB. (SgNB Modification Triggered by the SgNB)
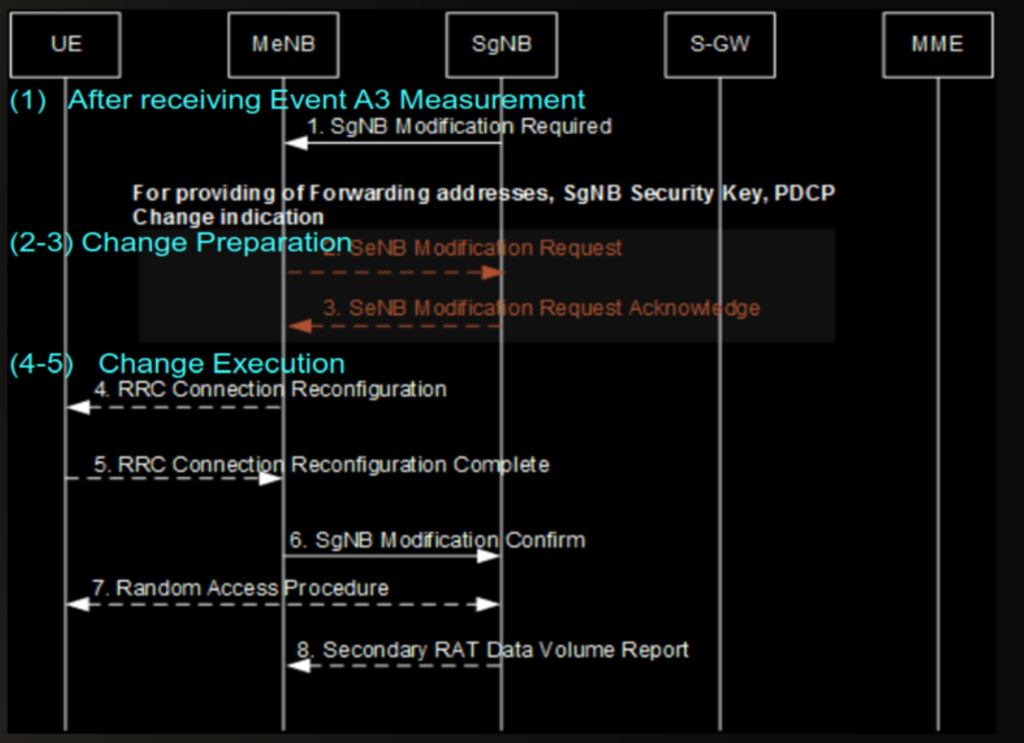
To change PSCell within different SgNB. (SgNB Change Triggered by the SgNB)
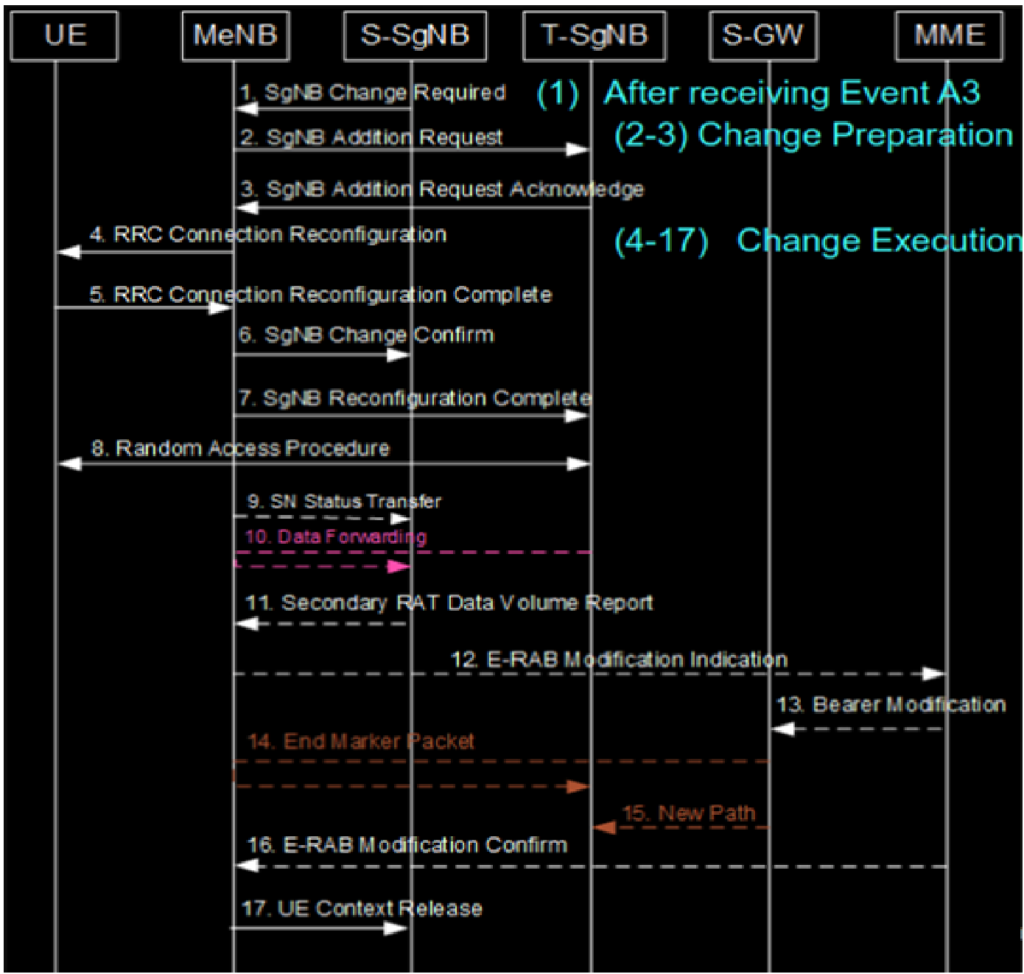
NR Abnormal Handover Event Optimization:
General Principles for locating NR Handover Failure through signaling procedure from the Uu Interface.
- Measurement Configuration Loss.
- Coverage Reasons.
- Restricted Channels, Including the PDCCH/PDSCH.
- No 5G neighboring Cell Configured.
- Measurement Report Loss.
- UE Exceptions.
- Coverage Reasons.
- Restricted Channels, including the PDCCH/PUSCH.
- Handover Command (RRC Connection Reconfiguration) Message Loss.
- Coverage Reasons.
- Restricted Channels, including the PDCCH/PUSCH.
- eNodeB or gNodeB handover decision failures or Internal Exceptions.
- Handover Completion (RRC Connection Reconfiguration Complete) Message Loss.
- Coverage Reasons.
- UE Exceptions.
- Restricted Channels, including the PDCCH/PUSCH.
- Random Access Failure at the gNodeB.
- Coverage Reasons.
- eNodeB or gNodeB Internal Exceptions.
- Restricted Channels, including the PRACH/PDCCH/PDSCH/PUSCH.
- The RLC SN Size Configuration of the source cell is inconsistent with that of the target cell.
3. NR Abnormal Call Drop Event Optimization
There are two types of call drops on the terminal side in NSA networks. The first occurs when the network sends a direct command to release the 5G connection, indicated by the nrConfig-r15 field in the RRCConnectionReconfiguration message, leading to an NR eRAB abnormal release.
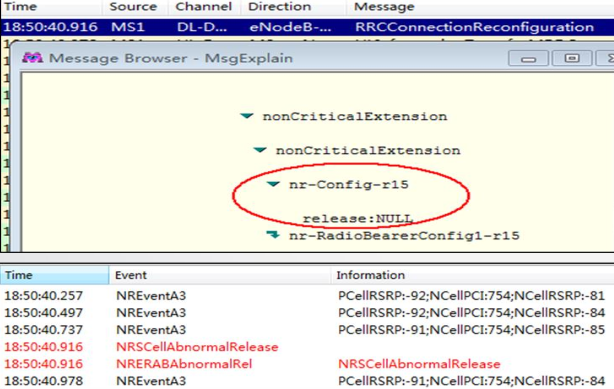
The second happens when the UE detects an issue, reports SCGFailureInformationNR, and then requests a release. In this case, the base station delivers the release indication after receiving the failure report from the UE.
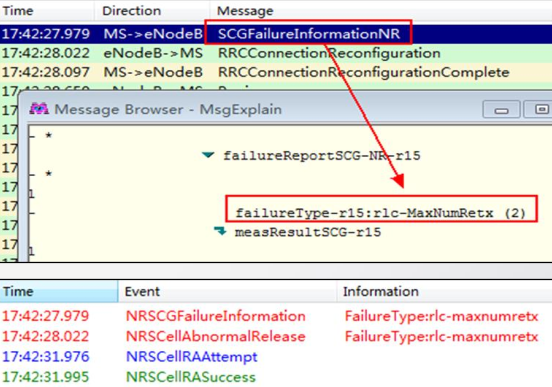
NR Call Drop in following scenarios:
Signaling Process of analysis mostly involves:
1.Who initiate call drop?
2.What is the release cause in the signaling?
3.What signaling procedures occurs before call drops occur?
NSA Service Drop Fault Tree
| 5G initiates an abnormal release. | 1. Service drops occur because the downlink RLC retransmissions of the DRE reaches the maximum. 2. Service drops are caused by random access failures during handovers. 3. Service drops are caused by the expiry of the timer for waiting for the LTE response over the X2 interface. 4. Service drops are caused by 5G transmission faults. 5. Service drops are caused by unavailable SG cells. 6. Service drops are caused by top UE problems. 7. UEs are released due to other exceptions. |
| 5G initiates a normal release. | 1. The RSRP of the NR cell is lower than the A2 threshold, causing normal releases. 2. The Inactive Timer expires, causing normal releases. |
| LTE initiates an abnormal release. | 1. The core network releases UEs. 2. Bearer modification fails on the core network. 3. LTE releases are caused by service drops or RRC connection reestablishments on the LTE side. 4. During an inter-eNodeB handover, NR is not correctly configured on the target side. 5. Service drops are caused by LTE transmission faults. 6. Service drops are caused by X2 automatic removal on the LTE side. 7. Service drops are caused by rlc-MaxNumRetx reported by the UE. 8. Service drops are caused by random Access Problem reported by the UE. 9. Service drops are caused by scg-reconfigFailure reported by the UE. 10. Service drops are caused by t310-Expiry reported by the UE. 11. Service drops are caused by synchReconfigFailure-SCG reported by the UE. 12. Service drops are caused by srb3-IntegrityFailure reported by the UE. 13. Service drops are caused by top UE problems. 14. LTE releases are caused by other exceptions. |
| LTE initiates a normal release. | 1. NR releases are caused by inter-RAT redirections on the L TE side. 2. NR releases are caused by CSFBs on the LTE side. 3. The VOLTE and NR mutually exclusive switch is turned on, causing NR releases. |
Possible Cause and troubleshooting direction:
1. UE.
| Release Cause | Possible Cause & Check Direction |
| randomAccessProblem | The TA times out or the number of SRS reaches the maximum number (Probe KeyEventList can be specified). Check the signal quality and bit errors on the air interface. |
| rlc-MaxNumRetx | The number of uplink RLC retransmissions reaches the maximum. Check the bit errors on the air interface and set the RLC parameters. |
| scg-reconfigFailure | If an internal procedure conflict occurs on the UE side or a cell fails to be verified, contact UE engineers for analysis and confirmation. |
| scg-ChangeFailure | During a UE handover (5G handover or 5G random access during an LTE handover), cell search fails. Check the neighboring cell, X2 configuration, and target cell status. |
2. 4G Base Station.
| Release Cause | Possible Cause & Check Direction |
| failure-in-the-radio-procedure | The UE sends an SCG Failure message over the air interface. For details, see. RRC connection reestablishment occurs on the LTE side. |
| transport-resource-unavailable | If the problem is caused by S1-U or X2-U, rectify the fault according to the transmission problem. |
| rrm-purpose | Other signaling procedures on the LTE side are abnormal. For example, after NR is added, the LTE core network sends a bearer modification request, but no response from the core network is received within the timeout period. Check the signaling procedure before the release on the LTE side. |
| Mcg-mobility | During an inter-eNodeB handover, the source eNodeB is released normally, which is not a call drop. |
| Unspecified | The CN initiates a release procedure. |
3. 5G Base Station.
| Release Cause | Possible Cause & Check Direction |
| Radio-connection-with-UE-lost | The number of downlink RLC retransmissions reaches the maximum. Check the signal quality, air interface bit errors, and RLC parameters. |
| No-radio-resources-available | Check the internal release cause values and debug logs of the CHR to determine the resource allocation failure. |
| transport-resource-unavailable | If the transmission of the S1-U or X2 is faulty, rectify the fault according to the transmission problem. |
| Mcg-mobility | During an inter-eNodeB handover, the source eNodeB is released normally, which is not a call drop. |
| Scg-mobility | Normal release. The UE reports A2 normal release. Check whether the 5G A2 threshold is too high. |
Reverse Check
Reverse checking to Identify the scenarios where the problem occurs based on the root cause.
| Service Drop Category | Common Cause |
| Service Drop Due to 5G Coverage Problems. | 1. The coverage is weak. 2. At a specific location, a timing offset exists due to multipathing and missing DCI detection occurs, causing service drops. 3. There is no primary coverage cell in the handover area and the signal strength is equivalent in a large number of cells, resulting in handover failures. |
| Service Drop Due to 5G Interference. | 1. External interference causes service drops. 2. Neighboring cell interference causes service drops. |
| Service Drop Due to 5G Configuration Problems. | 1. RLC parameters are incorrectly configured. As a result, the status report cannot be sent in a timely manner and the number of RLC retransmissions reaches the maximum, causing service drops. 2. The SRS adaptive threshold is incorrectly configured. As a result, the SRS bandwidth at the cell edge cannot be changed to narrowband. The SRS detected on the base station is weak. TA values cannot be accurately measured, causing service drops. 3. The configured A2 threshold is too high. As a result, the UE is normally released. 4. Missing neiahboring cells cause handover failures, resulting in service drops. |
| Service Drop Due to LTE Configuration Problems. | Missing configuration of 5G neighboring cells or X2 interface on the LTE network causes 5G handover failures, resulting in service drops. |
| Service Drop Due to Handover Failures. | 1. Random access fails on the target base station during a 5G handover. 2. 5G random access triggered by an LTE handover fails, resulting in service drops. |
| Service Drop Due to Transmission Faults. | 1. Transmission congestion causes a long signaling delay, resulting in service drops. 2. Transmission faults cause the base station to initiate a release. |
| Service Drop Due to Cell Faults. | 1. Insufficient power supply for the AAU causes cell faults. 2. Transmission faults cause cell faults. |
| Service Drop Due to SCG Reconfiguration Failures. | Check whether the downlink and uplink IBLERs converge to the target values and whether the residual BLER and retransmission rate are high. |
| Service Drop Due to Core Network Problems. | 1. Bearer modification fails on the core network, resulting in service drops. 2. Abnormal releases from the core network cause service drops. |
| 5G Service Drop Due to LTE Service Drop and Reestablishment. | In NSA networking, the LTE service drop and reestablishment cause the release on the 5G side. |