ACI 210R-93 ACI Standard Erosion of Concrete in Hydraulic Structures
ACI 210R-93 ACI Standard Erosion of Concrete in Hydraulic StructuresMechanism of cavitation
Cavitation is that the formation of bubbles or cavities in an exceedingly liquid. In hydraulic structures, the liquid is water, and the cavities square measure stuffed with vapor and air. The cavities form wherever the native pressure drops to a price which will cause the water to vaporize at the prevailing fluid temperature.
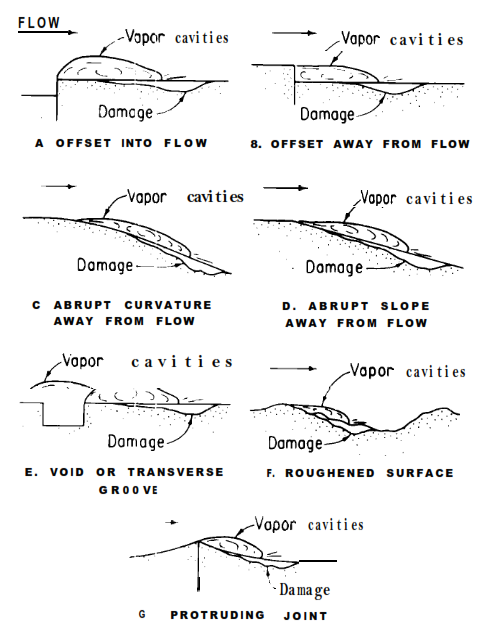
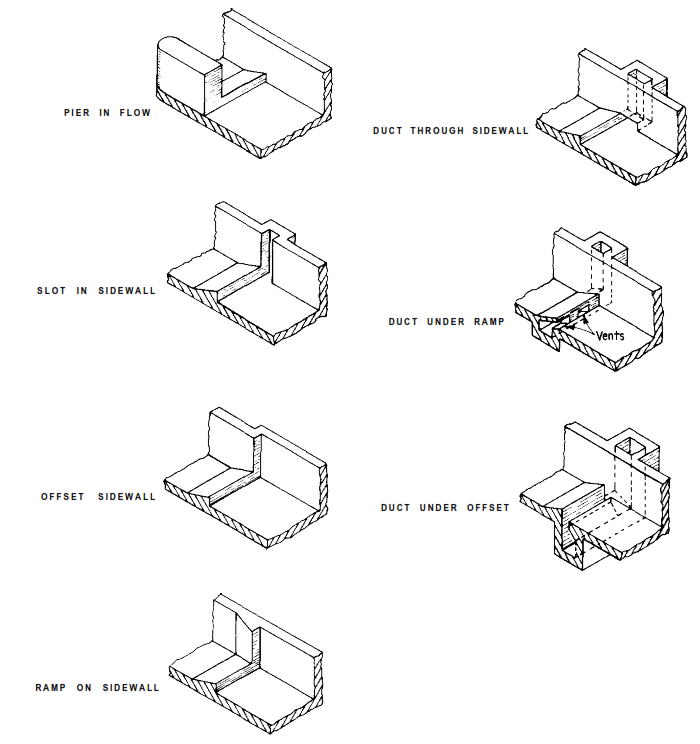
Fig. shows samples of concrete surface irregularities which can trigger formation of those cavities.
The pressure drop caused by these irregularities is usually abrupt and is caused by native high velocities and curved streamlines. Cavities usually begin to create close to curves or offsets in an exceedingly flow boundary or at the centers of vortices.
Cavitation situations at surface irregularities
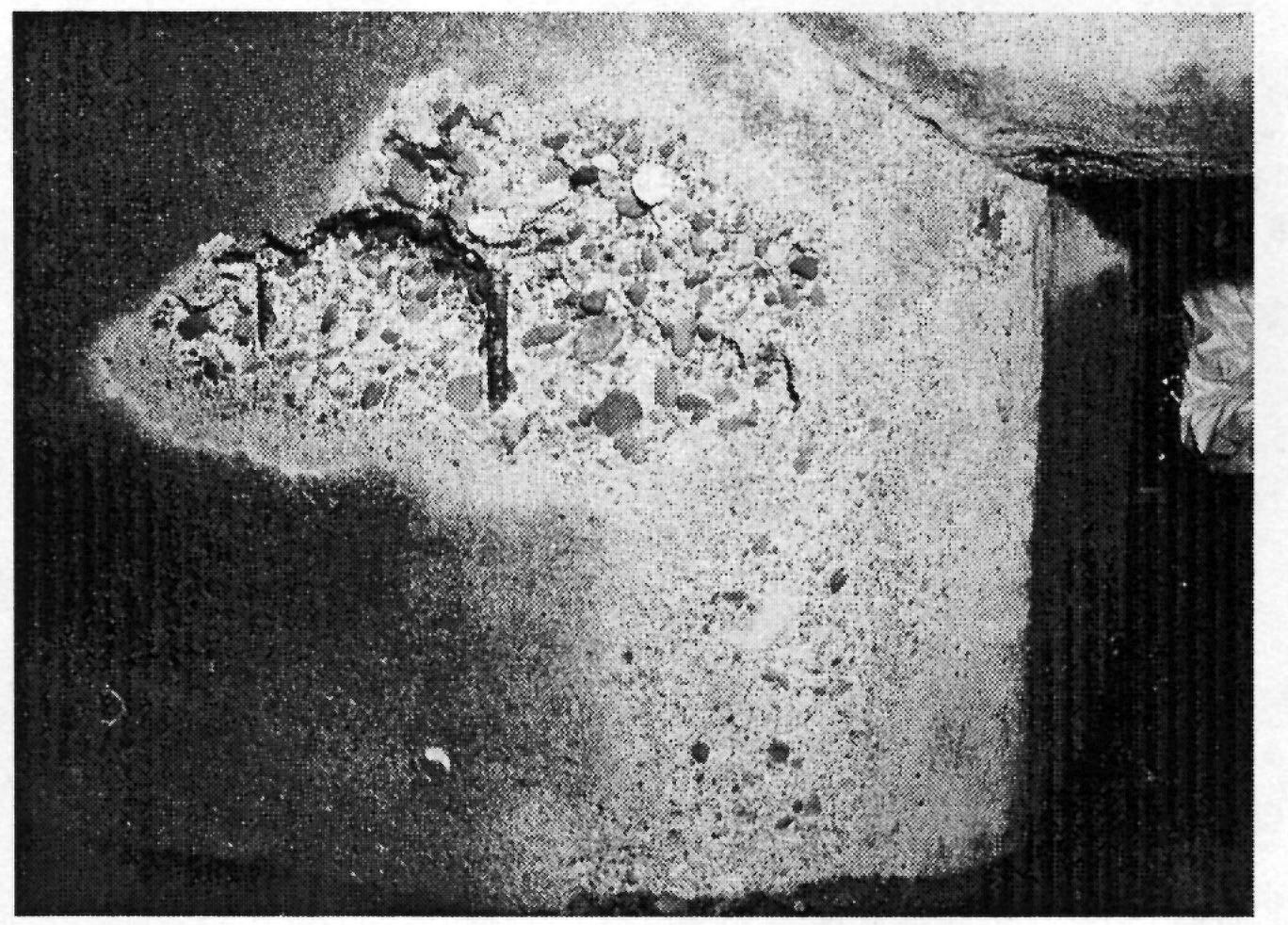
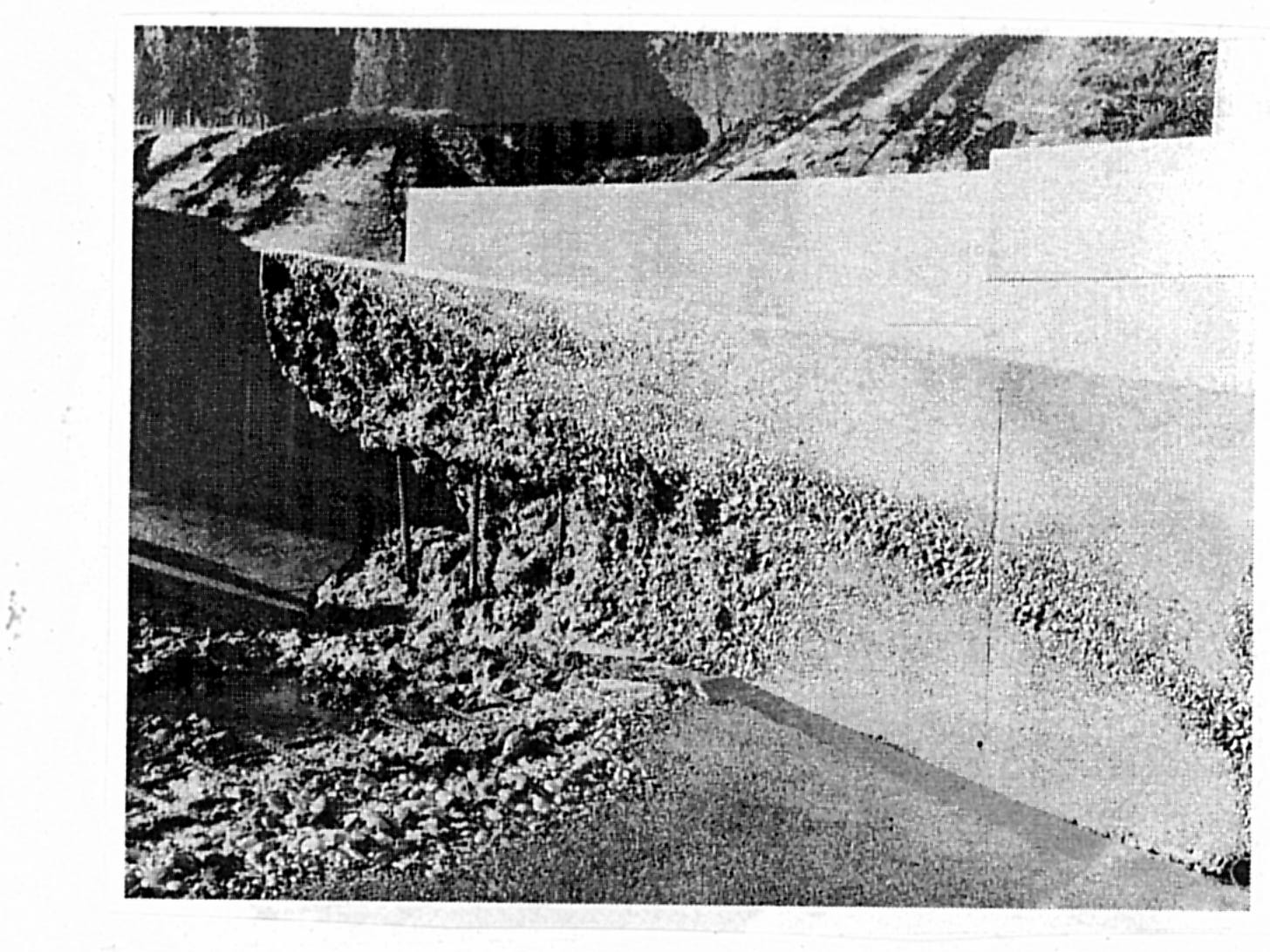
Tunnel contraction
Cavitation erosion of intake lock at point of tunnel contraction wall of a navigation
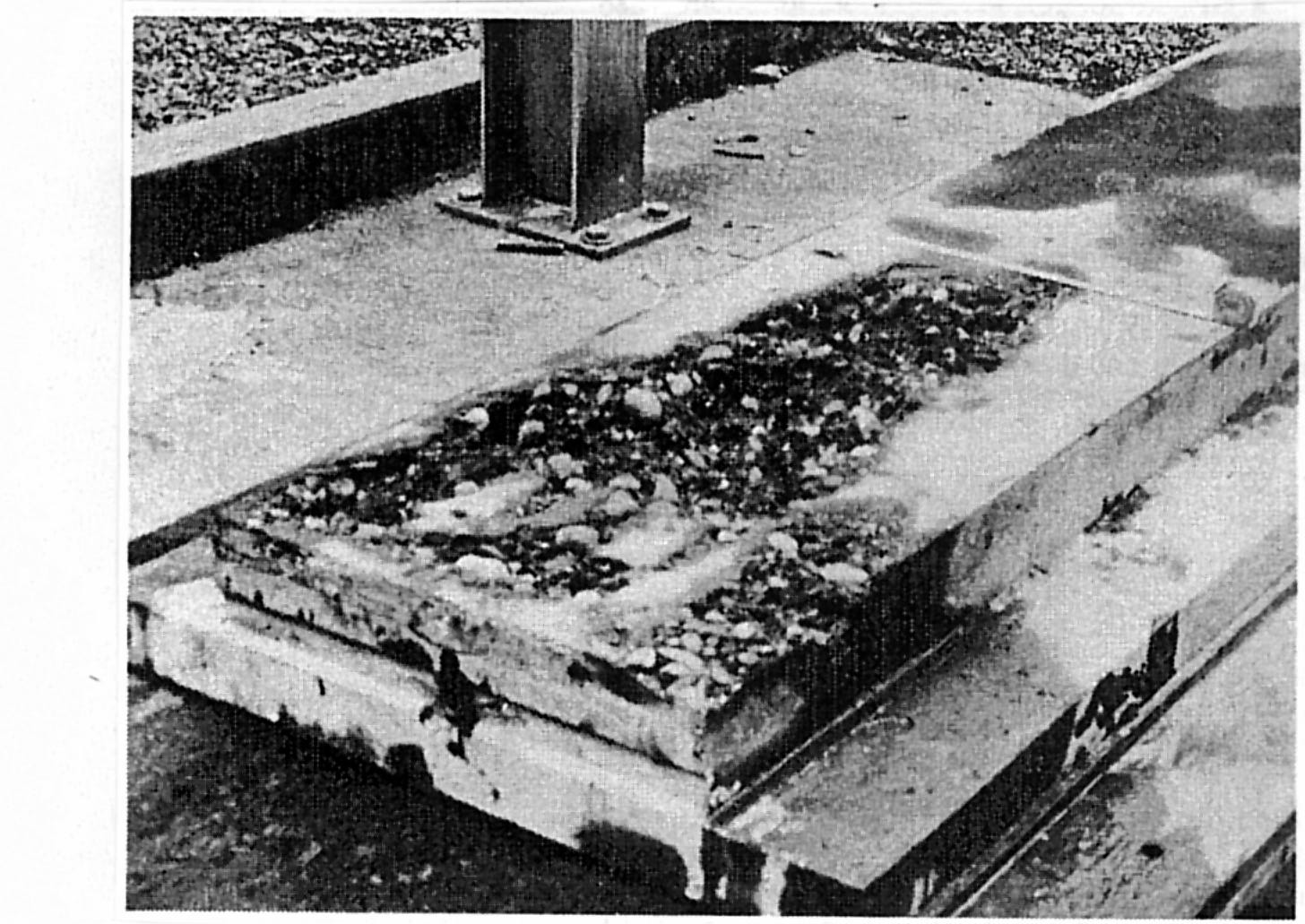
Concrete test slab fe aturing cavitation producing devices
Cavitation erosion pattern after 47 hours of testing at a 240 ft velocity head
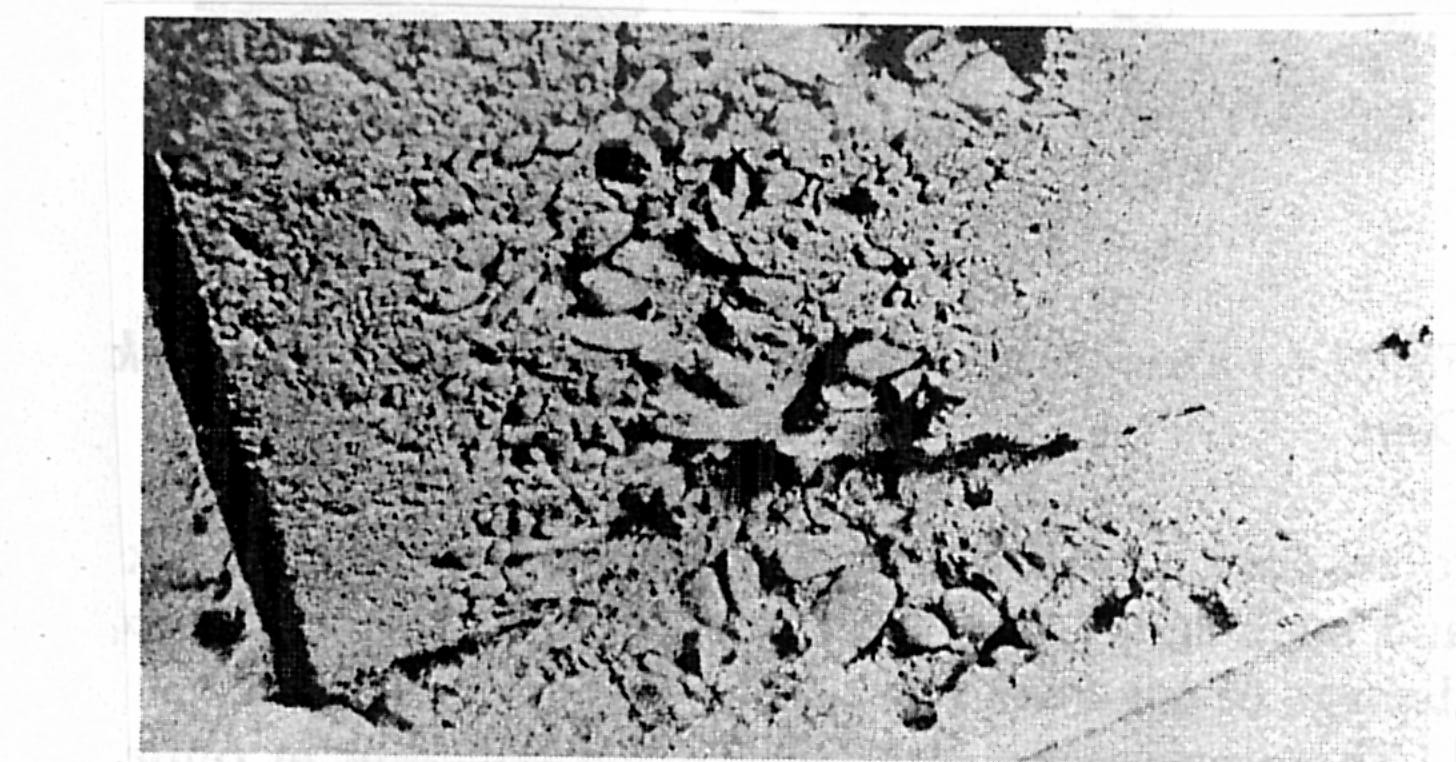
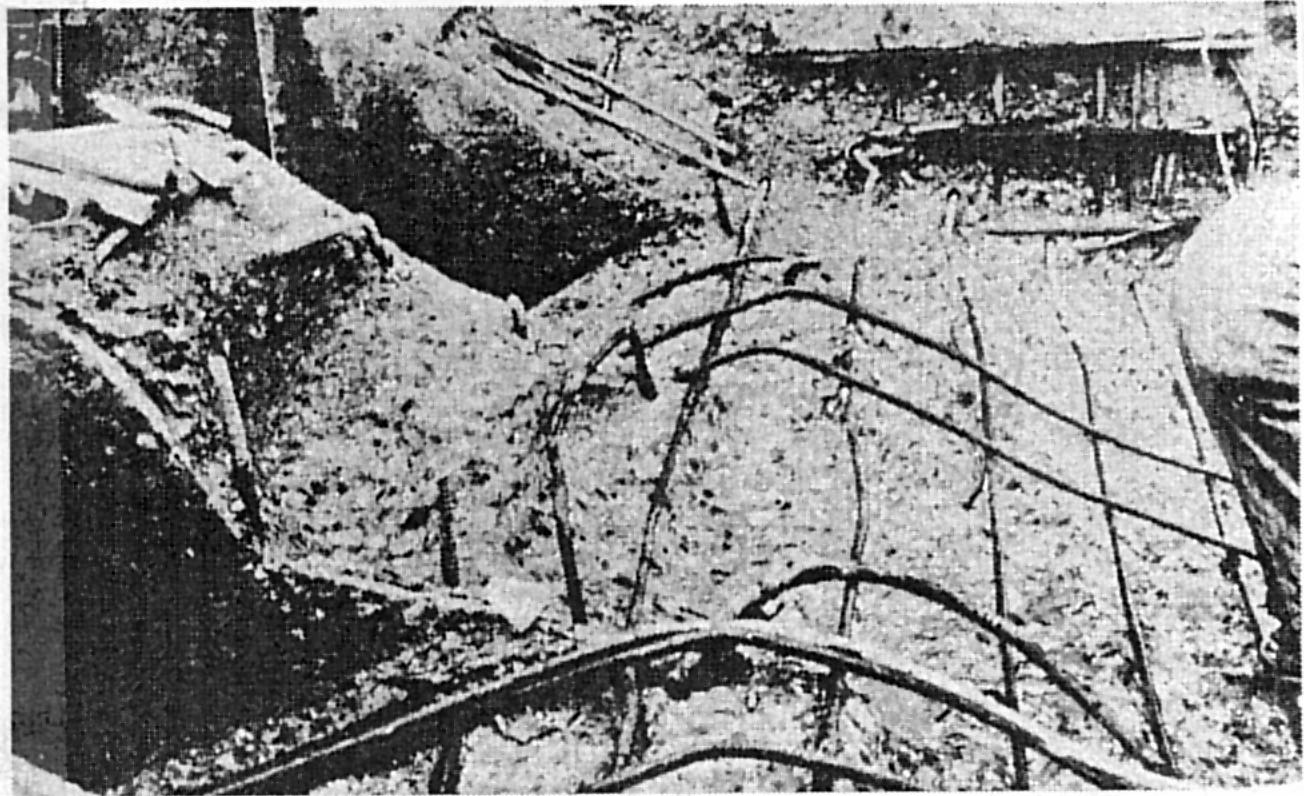
Cavitation erosion of discharge outlet training wall and flip bucket
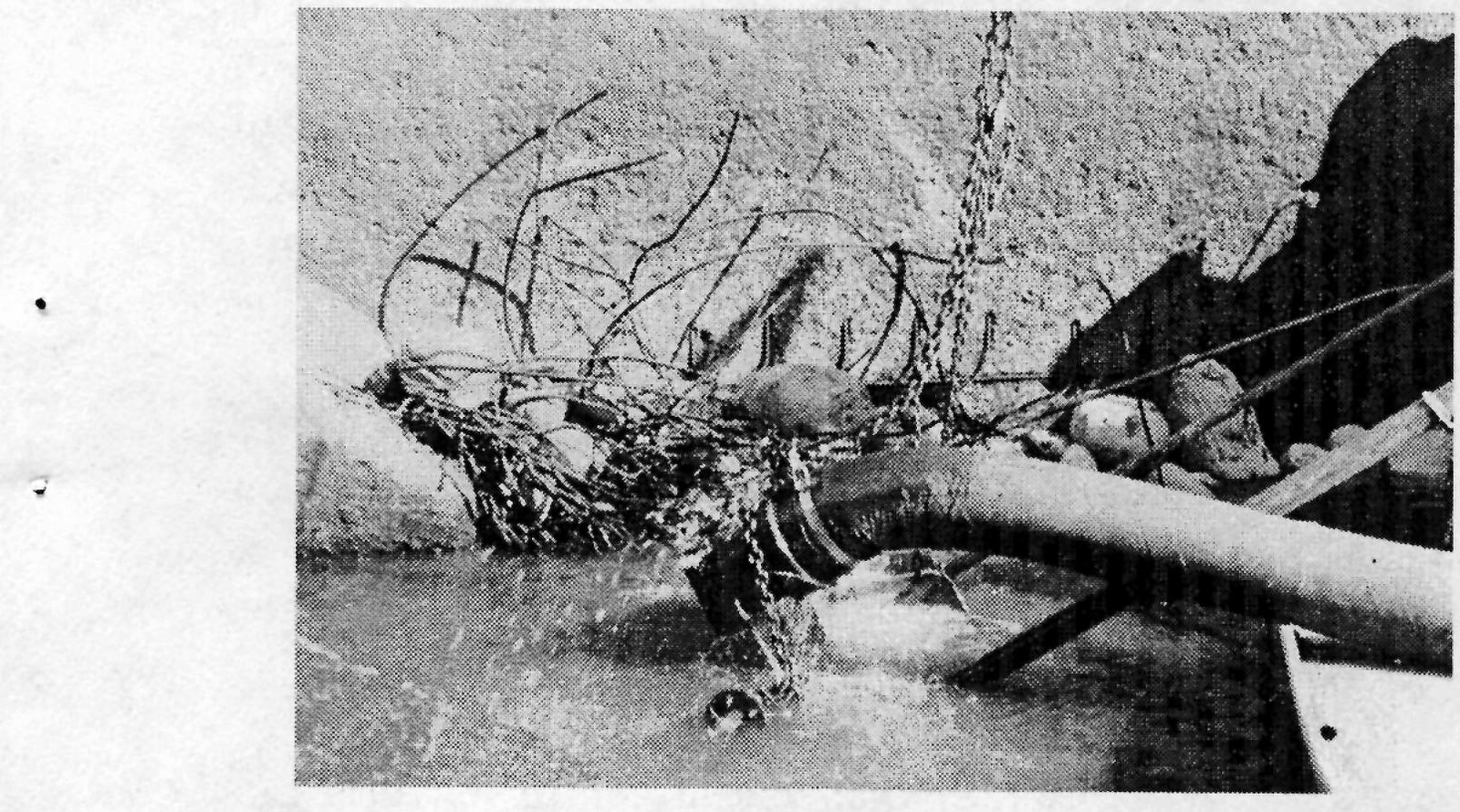
Cavitation erosion of baffle block and floor in stilling basin
Abrasion damage to concrete baffle blocks and floor area
Abrasion erosion damage to stilling basin, Nolin Dam
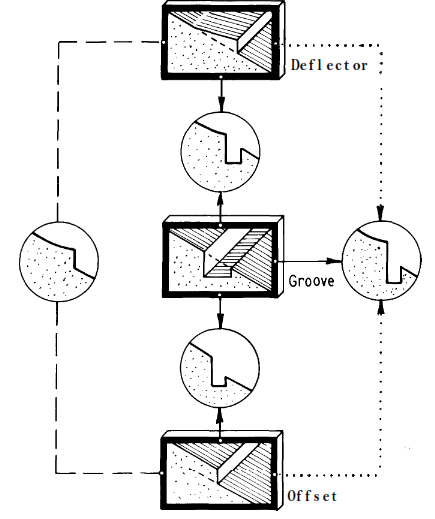
Types of aerators
Air supply to aerators
Recommended cement types to use in concrete when mixing water contains sulfates
Chapter 2-Erosion by cavitation
2.1-Mechanism of cavitation
2.2-Cavitation index
2.3-Cavitation damage
Chapter 3-Erosion by abrasion
3.1-General
3.2-Stilling basin injury
3.3-Navigation lock injury
3.4-Tunnel lining injury
Chapter 4-Eros particle by chemical attack,
4.1-Sources of chemical attack
4.2-Erosion by mineral-free water
4.3-Erosion by miscellaneous causes
PART 2-CONTROL of abrasion
Chapter 5-Control of cavitation erosion
5.1-Hydraulic style principles
5.2-Cavitation indexes for injury and construction tolerances
5.3 – Usi nanogram aeration to manage injury
5.4-Fatigue caused by vibration
5.5-Materials
5.6-Materials testing
5.7-Construction practices
Chapter 6-Control of abrasion erosion
6.1-Hydraulic concerns
6.2-Material analysis
6.3-Materials
Chapter 7-Control of abrasion by chemical attack
7.1-Control of abrasion by mineral-free water
7.2-Control of abrasion from microorganism action
7.3-Control of abrasion by miscellaneous chemical causes
PART3-MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR of abrasion
Chapter 8-Periodic inspections and corrective action
8.l-General
8.2-Inspection program
8.3-Inspection procedures
8.4-Reporting and analysis
Chapter 9-Repair ways and materials
9.1-Design concerns
9.2-Methods and materials
Chapter 1O-References
10.1-Specified and/or suggested references
10.2-Cited references