The RF module performs key functions in wireless communication systems, including the conversion between baseband signals and carrier signals. This process is carried out by components such as the digital-to-analog and analog-to-digital converters, frequency converters, amplifiers, and filters. These components work together to transmit and receive signals efficiently, ensuring that the baseband data is converted into the appropriate carrier signal for transmission through the antenna and vice versa.
How RF Module Works?
Baseband signals to carrier signals:
To convert baseband signals to carrier signals, the digital signals from the baseband processing unit are first up-converted by a digital frequency converter, then converted to analog intermediate frequency (IF) signals by a DAC. The IF signals are then modulated to the transmit frequency band by an analog frequency converter, amplified by a power amplifier (PA), and filtered by a filter to prevent interference with adjacent channels. This process ensures efficient transmission of RF signals through the antenna.
Carrier signals to baseband signals:
Carrier signals are received by the antenna and filtered by a filter to isolate specific frequency bands. The weak signals are amplified by the low noise amplifier (LNA) and then down-converted by the analog frequency converter to intermediate frequency (IF) signals. These analog signals are digitized by an ADC and then further down-converted by a digital frequency converter before being sent to the baseband processing unit for further processing. This process ensures that received signals are properly converted and prepared for network use.
Figure below shows an example block diagram of the RF hardware. The specific framework may vary with the module.
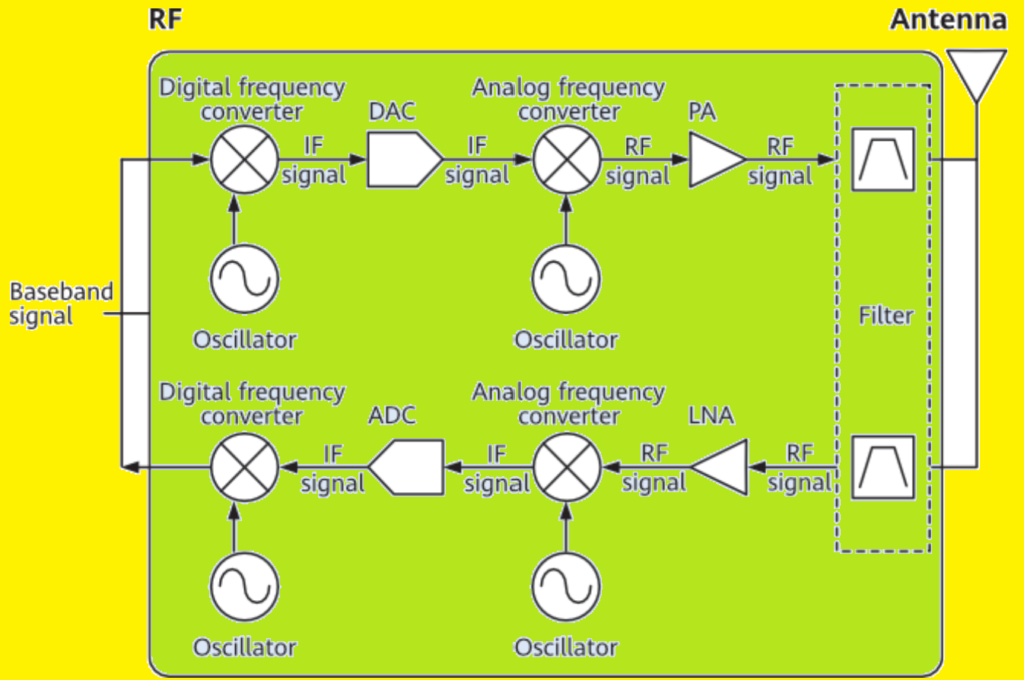
Functions of RF components
| Signal Direction | RF Component | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Downlink (transmitting signals) | Digital frequency converter (up-conversion). | Receives baseband signals and implements up-conversion through digital signal processing. |
| DAC | Converts digital signals into analog IF signals. | |
| Analog frequency converter (up-conversion). | Receives analog IF signals, modulates them to the transmit frequency band, and converts them to RF signals. | |
| PA | The power amplifier (PA) boosts these RF signals for antenna transmission. | |
| Filter | Filters RF signals to prevent high-power signals at the transmit end from interfering with adjacent channels. | |
| Uplink (receiving signals) | Filter | Filters signals of specific frequency bands. |
| LNA | Amplifies signals to the range that the frequency converter can identify. | |
| Analog frequency converter (down-conversion). | Down-converts the received RF signals at a specific frequency band to analog IF signals. | |
| ADC | Converts analog IF signals into digital IF signals. | |
| Digital frequency converter (down-conversion). | Implements down-conversion through digital signal processing and transmits digital signals to the baseband. |