Calculating LTE throughput is crucial for optimizing network performance and ensuring efficient resource utilization. As a telecommunications RF expert engineer, I’ll guide you through the process of calculating LTE throughput under optimal radio conditions, specifically using 16QAM modulation for both downlink and uplink.
LTE Throughput Calculation.
I shall also demonstrate how to determine the total number of bits in physical resource blocks (PRBs), accounting for overheads such as physical channels and synchronization signals.
OFDMA/SC-FDMA System Overview.
- LTE Radio Frame Duration: 10 ms
- Sub-frame Duration: 1 ms
- Time Slot Duration: 0.5 ms
- Symbol Duration: 0.5 ms / 7 (assuming normal CP)
- Symbols per Sub-frame: 7
- Subcarrier Bandwidth: 15 kHz
- Subcarrier Count per PRB: 12
- Transmission Time Interval: 1 ms (minimum scheduling time for a user, typically 2 PRBs at once).
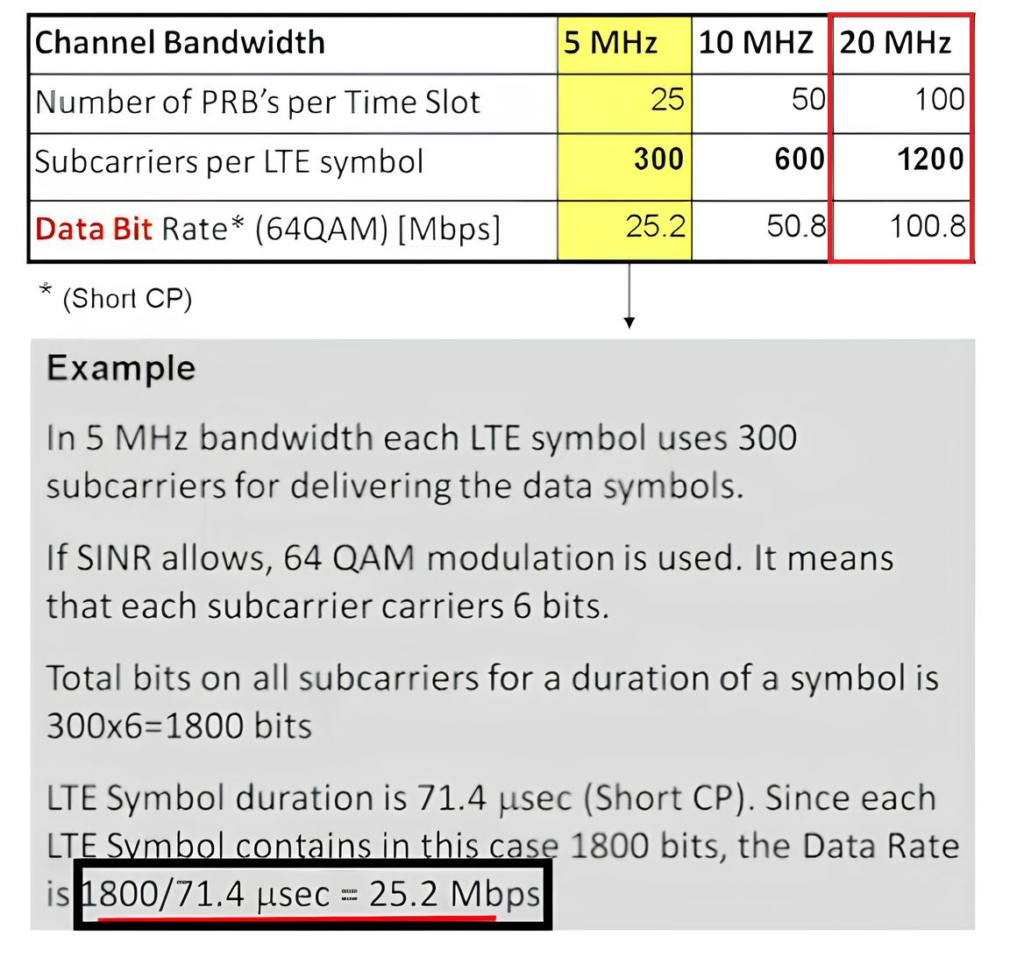
Steps to Calculate Downlink Throughput
Step 1: Bits per PRB Calculation:
- Number of subcarriers per PRB: 12
- Symbols per sub-frame: 7 (assuming normal CP)
- Bits per RE (Resource Element) for 16QAM modulation: 4
- Bits per PRB: 12 subcarriers × 7 symbols × 4 bits/RE = 336 bits (per 0.5 ms)
Step 2: Total Bits per ms for 100 PRBs:
- Total bits per ms: Bits per PRB × Number of PRBs
- Number of PRBs: 100 (for 20 MHz bandwidth)
- Total bits per ms: 336 bits/0.5 ms × 100 PRBs = 67,200 bits/ms
Step 3: Considering MIMO (2×2) Configuration:
- Total throughput considering MIMO: Total bits per ms × Number of antennas (transmit or receive, typically the same in LTE).
- Total throughput: 67,200 bits/ms × 2 (for 2T2R MIMO) = 134,400 bits/ms
Step 4: Net Throughput (Considering Resource Utilization):
- Assume 75% efficiency due to overheads (e.g., control signaling, channel coding).
- Net throughput: Total throughput × 0.75 = 134,400 bits/ms × 0.75 = 100,800 bits/ms
Step 5: Convert to Mbps:
- 1 Mbps = 1,000,000 bits per second
- Net throughput in Mbps: 100,800 bits/ms × 1,000 ms/s / 1,000,000 bits/Mbps = 100.8 Mbps
Uplink Throughput Calculation.
For the uplink, we follow a similar process but account for different configurations:
1️⃣ Modulation = 16QAM (4 bits per RE, most of the commercial UE support max 16QAM)
2️⃣ Antenna = 1T1R SISO
3️⃣ Bandwidth = 20MHz
Step 1: Bits per PRB Calculation:
- Modulation: 16QAM (4 bits per RE)
- Number of subcarriers per PRB: 12
- Symbols per sub-frame: 7 (assuming normal CP)
- Bits per PRB: 12 subcarriers × 7 symbols × 4 bits/RE = 336 bits (per 0.5 ms)
Step 2: Total Bits per ms for 100 PRBs:
- Minimum scheduling for user: 336 bits + 336 bits = 672 bits per ms
- Total bits per ms: PRBs × bits = 100 × 672 = 67,200 bits/ms
Step 3: Net Throughput (Considering Resource Utilization):
- Assume 75% efficiency due to overheads (e.g., control signaling, channel coding).
- Net throughput: 67,200 bits/ms × 0.75 = 50,400 bits/ms
Step 4: Convert to Mbps:
- Net throughput in Mbps: 50,400 bits/ms × 1,000 ms/s / 1,000,000 bits/Mbps = 50.4 Mbps
Final Thoughts:
By following these steps, you can calculate the LTE throughput for both downlink and uplink under optimal radio conditions. For 16QAM modulation:
- Downlink Net Throughput: 100.8 Mbps
- Uplink Net Throughput: 50.4 Mbps
Understanding these calculations helps in optimizing LTE network performance, ensuring efficient resource utilization, and meeting the high data rate demands of modern communication networks.