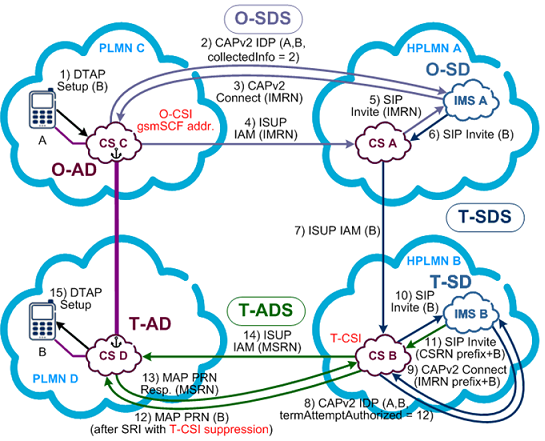
ICS (IMS Centralized Services) supports VoLTE UEs in CS coverage (2G/3G) when LTE coverage is unavailable, using IMS for call setup. This version covers only CAMEL-based ICS.
ICS call flow involves the Mg interface and routes through IMS. The scenario assumes VoLTE call setup in LTE works without issues. Failures in ICS call setup typically involve MSS, IMS, and UDM domains.
Unexpected call releases or media issues like one-way speech are not included here. The call flow describes scenarios where both caller and callee are in 2G/3G and belong to different home networks.
In accordance to overall ICS call flow, the general troubleshooting flow of ICS call failure is as below.
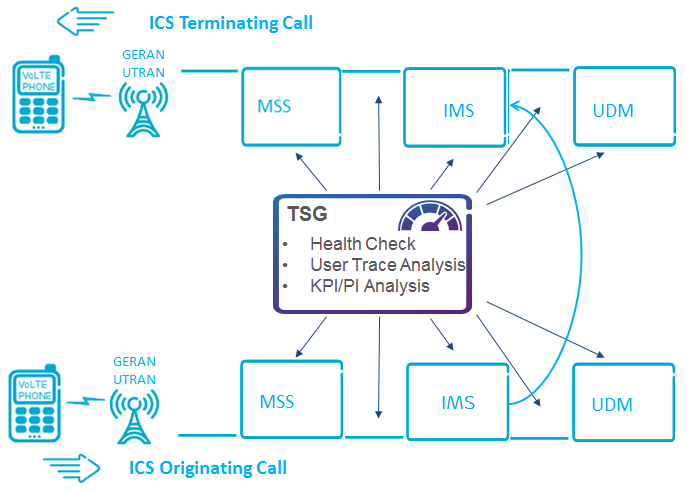
Health Check for ICS Call Failures
When ICS call establishment failures occur, a comprehensive health check is required, focusing on MSS and IMS, especially when both caller and callee are in 2G/3G coverage. Depending on the symptoms, further checks can be done in the suspected domain:
- For failures with a few users, check HLR and IMS (HSS) for user data provisioning.
- For many users failing in specific BSS/RNC areas, inspect the related MSS.
- For widespread failures, perform checks on IMS, MSS, and UDM.
E2E Trace Analysis
When analyzing E2E traces collected at the subscriber level, compare the call flow to the acceptance test specifications for the specific VoLTE deployment. Keep in mind that the collected trace might differ from reference traces due to site-specific configurations, including call flow variations, message content, and header values. Additional E2E reference traces from internal documentation or tools can be helpful for comparison and analysis.
Performance indicators.
At the E2E VoLTE level, KPIs measure call completion success, assuming LTE-originating or terminating calls work fine. A successful call setup is defined by “CC Alerting” (GSM/UMTS) or “Service Connect Complete” (1xRTT CDMA). Attempts are logged via “CM Service Request” (GSM/UMTS) or “Origination” (ORM) message (1xRTT CDMA).
ICS failure troubleshooting relies on E2E and domain KPIs to identify issues. Analysis in MSC and IMS helps find faulty nodes or features. Issues may stem from Handset, MSS, IMS, UDM, or combinations. Troubleshooting starts at MSC, progressing to IMS and UDM based on signaling flow.
The abstract formula for call completion success ratio is:

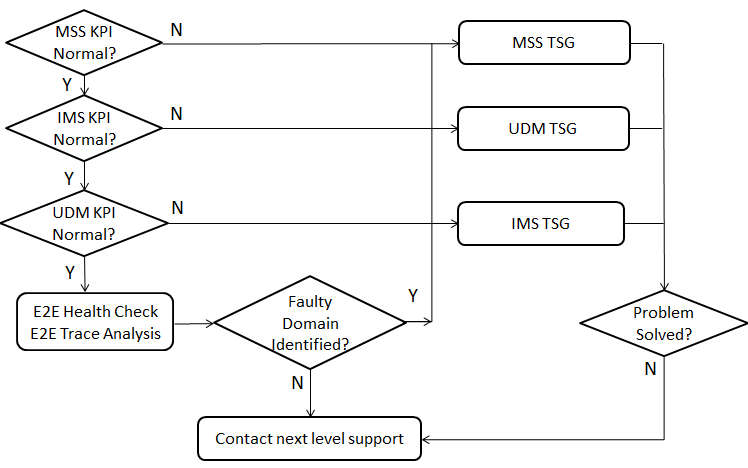
Step1: Check MSS KPI and PI.
- Objet type SHIST for CAMEL PI.
- SIP, Initial INVITE Request Performance per Route.
- If MSC KPIs indicates lower value than reference, it indicates the problem
shall be at least in MSC. To further troubleshoot in MSS. - If MSC KPIs indicates normal value, continue step2 to check IMS KPI.
Step2: Check IMS KPIs.
- IMS SCC AS CAP Request Success Ratio.
- IMS SCC AS Originating Unregistered Service from CS Success Ratio.
- IMS SCC AS Originating Service from PS Success Ratio.
- IMS SCC AS Originating Unregistered Service from PS Success Ratio.
- IMS SCC AS Terminating Service Success Ratio.
- IMS SCC AS Terminating Unregistered Service Success Ratio.
- IMS SCC AS Terminating Unregistered Service to VoLTE CS UE Success
Ratio. - IMS SCC AS Terminating Service to VoLTE PS UE Success Ratio
- IMS SCC AS Terminating Unregistered Service to VoLTE PS UE Success Ratio.
If IMS KPIs indicates lower value than reference value, it indicates the
problem shall be at least in IMS. Depending on the steps the problem can be
either in SBG, SCC-AS, CSCF etc. To futher troubleshoot in IMS.
Step3: Check UDM KPI.
There are no specific counters for ICS in HSS. However a sharp drop of SDA Data Read Success Ratio could be useful to locate problems in HSS during ICS call setup. The corresponding counters are described in ISM Measurements.
Sh: SDA Data Read Success Ratio.
Step4: If the problem domain is not identified by KPI analysis, please further
troubleshoot by E2E Health Check and E2E Trace Analysis. If faulty domain is
identified, please follow Domain Troubleshooting.