LoRa (Long Range) modulation is a key technology used in low-power wide-area networks (LPWANs), primarily for the Internet of Things (IoT) applications. It combines a unique form of modulation with robust performance characteristics to achieve long-range communication with low power consumption.
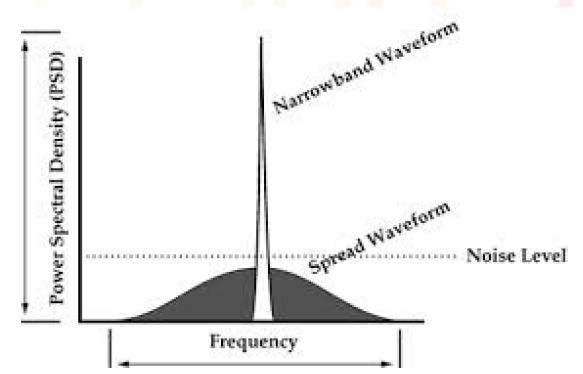
LoRa utilizes a spread spectrum based modulation which trades data rate for sensitivity
within a fixed channel bandwidth.
What is LoRa Modulation?
The LoRa modem is capable of co‐channel GMSK rejection of up to 19.5 dB below an interfering signal or the noise floor which has a better sensitivity than FSK modulation (better Eb/No). It can handle interference coexistence of LoRa modulated systems either in bands heavy spectral usage.
Communication between end-devices and gateways is spread out on different frequency
channels and data rates. The selection of the data rate is a trade-off between message
duration (time on air) and communication range.
ADR scheme maximize both battery life of the end-devices and overall network capacity.
LoRa network can manage the data rate and RF output for each end-device base on
average radio link that means
- If the average radio link is good the data rate can be increased
- If the demodulation is marginal, the data rate must be lowered
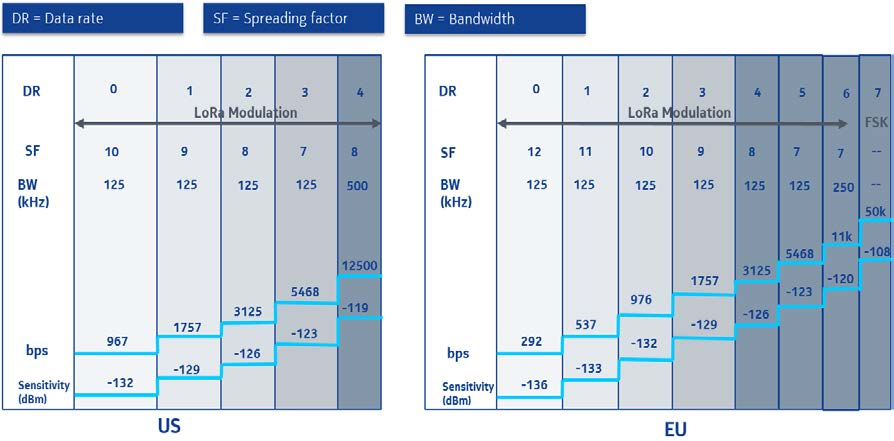
Figure 10 shows the modulation setting for both EU and US. When the spreading factor
changes, the effective data rate also changes. LoRa provides 6 spreading factor (SF)
parameters (7-12) settable per node via the LoRa Link Budget tool.