Massive MIMO leverages large antenna arrays to enhance spectral efficiency through SU-MIMO and MU-MI MO techniques, improving coverage and capacity.
1. SU-MIMO in Massive MIMO
1.1 Uplink Receive Diversity
Uplink Single-User MIMO (SU-MIMO) uses 32/64-antenna receive diversity to improve signal quality. The base station applies Maximum Ratio Combining (MRC) or Interference Rejection Combining (IRC) to boost SINR and demodulation performance.
SINR = Psignal / Pinterference + Pnoise
MRC maximizes signal power, while IRC optimizes SINR by suppressing interference
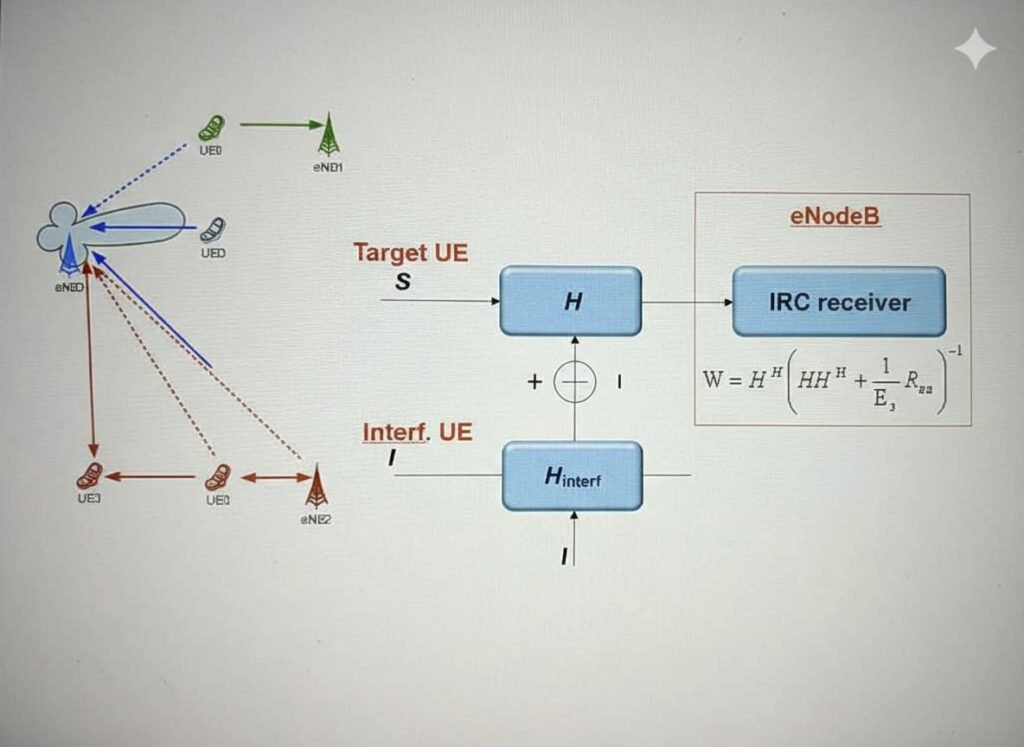
1.2 Activation Criteria
SU-MIMO is active when:
1 < Code0 UL Avg Layer Num < min(N_tx, N_rx)where N_tx and N_rx are gNodeB receive and UE transmit antenna counts.
2. MU-MIMO in Massive MIMO
2.1 Spatial Multiplexing
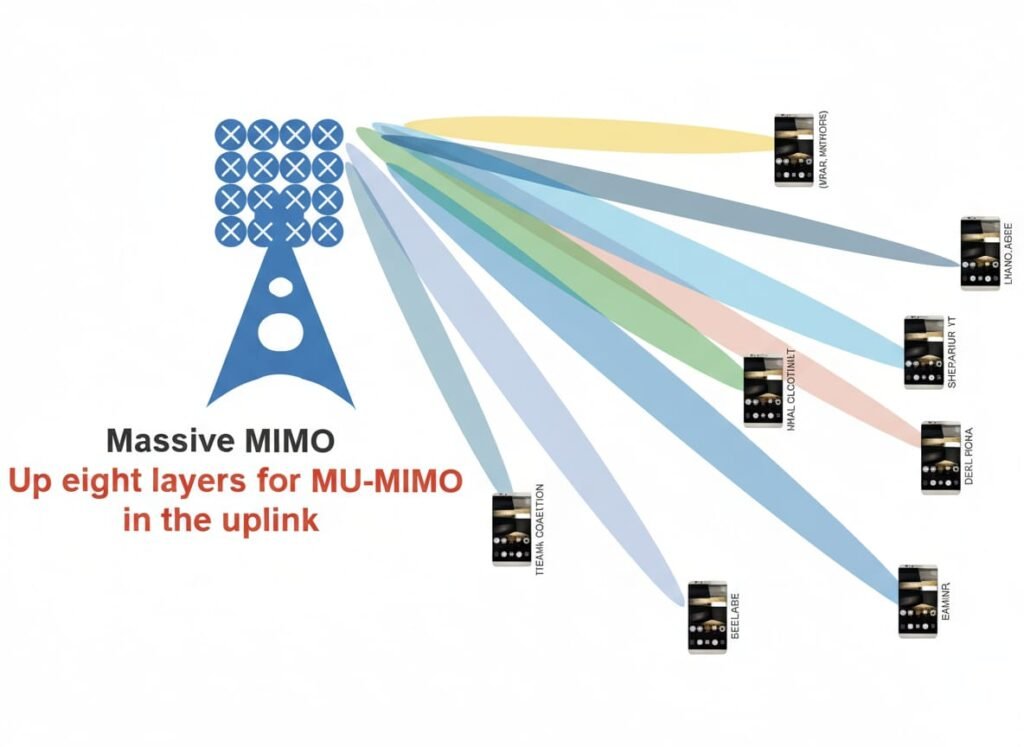
MU-MIMO enables multiple UEs to share the same time-frequency resources. Using spatial division multiple access (SDMA), up to eight UEs can be paired in uplink, significantly increasing spectral efficiency.
2.2 Downlink Scheduling Enhancements
Key switches under DLMuMimoSchSupplementSw optimize MU-MIMO:
DL_SE_SU_MU_MIMO_ADAPT_SW: Enables ad we switching between SU and MU based on spectral efficiency.
DL_MU_PRECISE_SCH_SW: Improves pairing rate and spectral efficiency.
Verification via counters like Number of Massive MIMO MUBF Success Pairing RB confirms activation.

3. Summary
| Feature | SU-MIMO | MU-MIMO |
| Purpose | Coverage & SINR Improvement | Capacity & Spectral efficiency |
| Key Techniques | MRC, IRC | SDMA, precoding |
| Max UEs Paired | 1 | upto 8 |
| Antenna Support | 32T/64T | 64T |
Massive MIMO combines both modes dynamically for optimal performance.