This article explains about all types of testing procedure required for medium voltage switchgear with pictures in Commercial buildings, plants and refineries.
Medium Voltage Switchgear Testing Procedure | Method Statement
5-1-1- Current transformer (CT) test procedure:
a- Test objective:
– This test is considered as one of the main test, it’s aimed to test:
- Current transformer ratio.
- Current transformer polarity.
- Burden of current transformer.
- Knee point of current transformer.
- Current transformer winding resistance.
- Magnetization curve of current transformer.
- Megger test (insulation test).
b- Required Equipment:
- Current transformer (CT) analyzer.
- Megger.
c- Mechanical check and visual inspection:
- Check tightness of all connection.
- Check ferrules
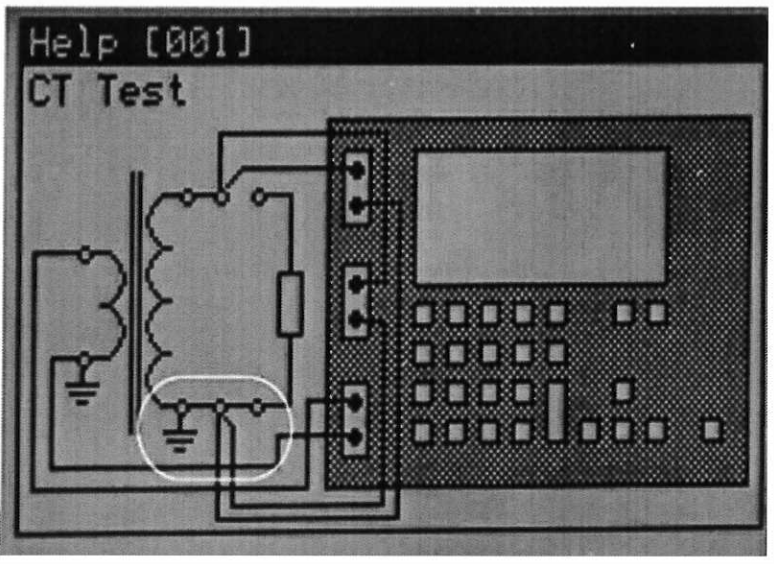
d- Current transformer analyzer connection:
- CT analyzer has 4 leads, two should be connected to primary side which contains primary side of CT and other two should be connected to secondary side of CT which you want to check its ratio.
- After connecting CT analyzer through laptop and using CT analyzer software, test can be started and result can be printed out for CT ratio, CT polarity, CT burden, CT knee point & CT winding resistance.
- This result should be compared with current transformer factory test and be sure that result within acceptable tolerance.
- To measure the burden: Inject 1 ampere on secondary side of CT, and using multi-meter you can measure voltage calculate burden by multiply voltage and current and compare it with CT burden.
- To test insulation: Using megger by 1 kilo volt injection for 1 minute, this test should be done between primary to secondary and secondary to secondary But for Primary to ground 5 kilo volt
injection for 1 minute. - See figure.1 which shows CT analyzer connection for CT TEST.
Figure.1 CT analyzer connection
5-1-2- Voltage transformer (VT) test procedure:
a- Test objective:
– This test also is considered as one of the main test and its purpose is to test:
- Voltage transformer ratio.
- Voltage transformer polarity.
- Voltage transformer winding resistance.
- Megger test (insulation).
b- Required equipment:
- CPC100.
- Multi-meter (Fluke).
c- Mechanical checked and visual inspection:
- Check tightness of connection.
- Check ferrules.
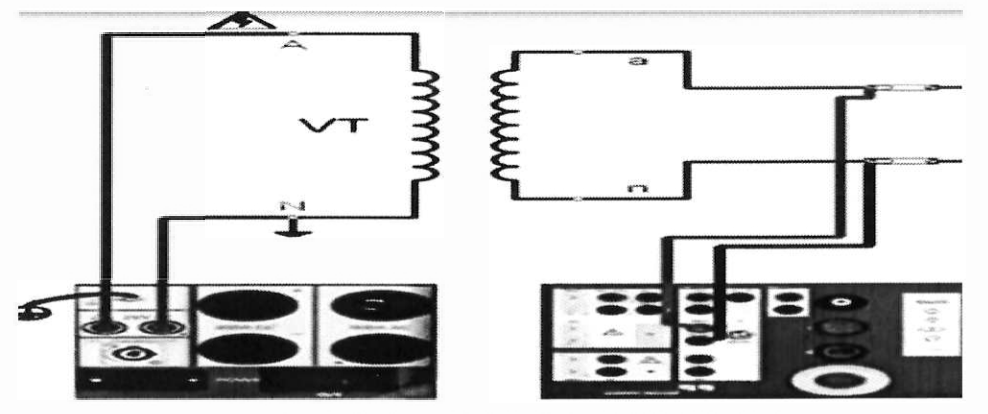
d- Voltage transformer test connection:
- Connect two leads from CPC device to primary side of voltage transformer and other two lead of CPC with secondary side of VT, then press start from VT page of CPC.
- Using CPC with same connection but from different page, you can measure winding resistance.
- To check the loop burden: inject the rated secondary voltage and measure the current. Burden will be the injected voltage* measured current and then compare it with VT burden.
- Insulation test: Using megger to test insulation by 1 kilo volt injection for 1 minute, this test should be done between primary to secondary and secondary to ground, But for primary to ground 5 kilo volt
injection for 1 minute. - See figure.2 which shows connection of VT Test.
Figure.2 show CPC100 connection to test
5-1-3- Timing test for Circuit breaker and megger test:
a- Test objective:
This test aimed to test the closing/opening time for circuit breaker and to make sure that there is no pole discrepancies between poles (red, yellow and blue) and CB closing/opening time within acceptable range according to factory test result.
b- Required equipment:
- EGIL breaker analyzer.
- B10E (used as DC supply and can resist high burden equipment).
- Megger.
- High potential test kit.
c- Timing and megger test connection:
- Connect B10 as external DC supply for closing (in case of measurement of closing time) circuit or opening (in case of measurement of opening time) circuit, for switching device that should be tested.
- Connect breaker analyzer in the circuit of opening or closing using dry contact from device to give command of open or close to the switching device and take contact from this device to work as feedback signal from the device while being closed or opened to measure CB closing/opening time.
- After opening or closing, the breaker analyzer will print the result which should be compared with factory test result to be sure that result within acceptable range.
- To start megger test: inject 1 KV for 1 minutes, when breaker open inject between the same pole (red-red, yellow-yellow and blue-blue) and when breaker close inject between pole and ground, between pole to pole.
d- High potential AC test:
- Applying high potential AC voltage when the breaker in service position line to line and line to ground (see number 5-1-4 point C).
5-1-4- High potential and contact resistance test for bus bar with circuit breaker:
a- Test objective:
- For contact Resistance, this test is aimed to measure the resistance of bus bar and for circuit breaker after being installed in the site to avoid high resistance which may be results from welding or installing in the site.
- For high potential this test is aimed to measure and test the withstand of the insulations and isolators against the high voltage without break down.
b- Required equipment:
- Micro-ohm meter Contact resistance device.
- High potential test kit.
c- High potential AC test:
- Insulation test by megger to test insulation by 5 kilo volt injection for 1 minute 3 phases line to line and line to ground.
- Applying high potential AC voltage on the bus bar line to line and line to ground and the CB in service position, protection relays are energized and the VTs are racked out.
- Applying high potential AC (higher voltage level than first applying time) voltage on the bus bar line to line and line to ground and the CB in test position, protection relays are energized and the VTs are
racked out. - Take the record of passing current in mille Amperes from the high potential test kit.
- Insulation test by megger to test insulation by 5 kilo volt injection for 1 minute 3 phases line to line and line to ground.
- Compare the insulation test results to gathers before and after high potential test.
d- Contact resistance test connection
- Contact resistance device has 4 leads, two for current and others for voltage, it depend on current injection on bus bar or circuit breaker then sense the voltage and calculate resistance by divide voltage on current (ohm’s law)
- Check the BB torqueing of all bolted and confirm the torque value as per factory inspection.
- Connect current leads between the device which you want to measure its resistance, connect voltage leads on the same terminals of current then adjust 100A injection then hold your hand on contact resistance pushbutton, after few second the result will be displayed.
- See figure.3 which shows connection of Contact Resistance Test.
Figure.3 shows contact resistance equipment connection
5-1-5- High potential test for circuit breaker:
a- Test objective:
- This test aimed to test if bus bar will withstand its withstand voltage after being installed in the site or it will breakdown and to check the vacuum bottle integrity, also to measure leakage current and insulation between CB and ground.
b- Testing equipment required:
- AC HI-voltage injection machine (100KV, 60HZ).
- Earthing Rod or Ground Discharge stick (coming with high pot tester)
- Megger 5KV DC Supply.
c- Mechanical and visual inspection:
- All safety rules should be taken into consideration.
- breaker cleaning and house keeping.
- Check all shipping devices removed.
- Inspect ground to switchgear ground bus.
- Ensure the adequate clearance (distance) between circuit test ends and to other Ground object and other phases (not under the test) and also with other electrical equipment’s to prevent flash over.
d- Test connection and test procedure
- Test VCB withstand voltage: VCB should be close , inject voltage as per FAT value.
- NOTE: When we conduct HIPOT Test for one phase, other remaining phases should be connected to Ground.
- Use Ground discharge stick with high tension Electrical for discharge the voltage from the system after each High potential Test.
- Test CB withstand voltage: VCB should be open , inject voltage as per FAT value.
- Measure insulation after high voltage test with CBs close and open status then inject 5 KV for 1 minute then record the value and compare it with the value before high voltage test.
NOTE:
Use Ground discharge stick with high tension Electrical for discharge the voltage from the system after each High potential Test.
5-1-6- Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB):
a- Test objective:
This test aimed to test the trip time characteristic of MCB if it’s within limits or no and check MCB auxiliary contact if it is available.
b- Required equipment:
- Sverker (used as current source).
- Multi-meter.
c- Mechanical checked and visual inspection:
- Check tightness for all wires.
- Check ferrules.
- Check for physical damage or defect.
d- Test connection and procedure:
- Connect sverker (which used as current source) direct to MCB, check MCB type and its rated current value.
- Inject from sverker twice of its rated current and measure the trip time in which MCB will be tripped, compare the measured trip time with its acceptable limit from MCB manual depending on its type.
- Auxiliary contact should be checked in both condition of MCB (open/close) and check that auxiliary contact change its status from being open to close or vise, depending on its nature Normally open or
Normally close.
5-1-7- Auxiliary relay test:
a- Test objective:
This test aimed to test relay’s output contact, pick-up and drop off voltage, operating and resetting time.
b- Required equipment:
- Sverker (used as Voltage source and used its voltmeter).
- Multi-meter [used as Ammeter].
- Miniature Circuit Breaker 2Pole (MCB).
c- Mechanical check and visual inspection:
- Check tightness for all wires.
- Check ferrules.
- Check for physical damage or defect.
d- Test connection:
I. Check output contact:
Our Auxiliary relay has several points, 2 used for Coil, before injecting any voltage on Auxiliary relay’s Coil, check contacts at its normal condition which mean Normally Open (NO) contact is being opened and Normally Closed (NC) contact is being closed, Inject the desired control voltage of Aux. coil (which is normally 125 volt DC), at which Aux. relay will pick up that’s mean its contact will change its position i.e NO contact will be closed and NC contact will be opened.
II. Pick-up and drop off current and voltage:
- Pick up voltage can be measured using voltmeter when the coil voltage is increased gradually from 0 volt, the Aux. relay will operate (i.e Contacts change its normal status No will be closed and vice
versa) at a certain voltage. This voltage is called pick-up voltage, Record the reading of voltmeter and Ammeter which is pick-up voltage and current. - Drop-off voltage can be measured using voltmeter when the coil voltage on an operate relay is decreased gradually, the relay will release (i.e its contact will return to its normal status) at a certain voltage. This voltage is called drop-off voltage, Record the reading of Ammeter which is drop-off current.
iii Operating and resetting time:
Adjust voltage source at the coil operation voltage of Aux. relay (in our case 125 v DC), To get operating time, adjust sverker at (on+time location) and switched MCB ON, To get resetting time, readjust voltage source at 125 volt DC and switch MCB OFF.
IV. Burden test:
- Adjust voltage source (sverker) at 125 volt DC, select on position and make MCB ON.
- Record reading of Ammeter.
- Calculate burden by multiplying coil operated voltage and reading of Ammeter.
5-1-8- Ammeter and voltmeter test:
a- Test objective:
This test is aimed to calibrate and adjust the reading of ammeter and voltmeter test.
b- Required equipment:
FREJA 300
c- Mechanical checked and visual inspection:
- Checked tightness of all connections.
- Checked ferrules.
- Inspection for physical damage or defects.
d- Test connection and procedure:
- Set the VT ratio (for voltmeter) and CT ratio (for ammeter).
- Inject different values (min. 3 values) of current (in case of ammeter) and voltage (in case of voltmeter) and compare the injected values with reading values, calculate error in each reading and check that its percentage error within the acceptable range.
5-1-9- Current transformer loop:
a- Test objective:
This test aimed to check all current transformer loop, starting from first panel and distributed in the whole switchgear depending on scheme, check shorting facility in terminal block [if exist].
b- Required equipment:
- FREJA (used as current injection).
- Multi-meter.
- Mini-clamp.
c- Mechanical check and visual inspection:
- Check tightness of all connection.
- Check ferrules for the whole looping.
- Check the single earth point.
d- Test connection
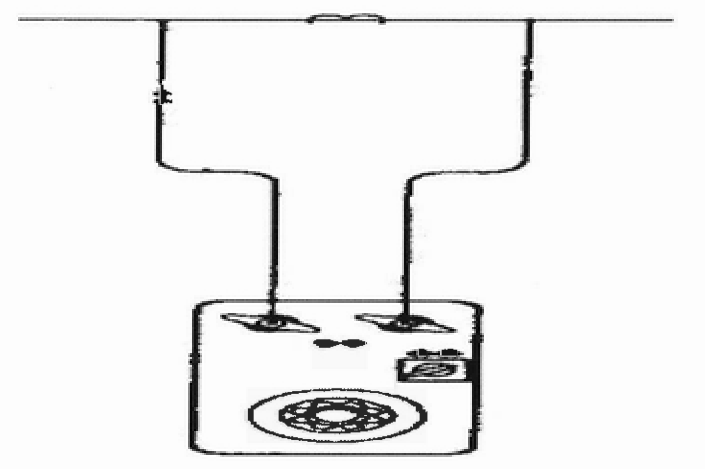
Connect three phase current from FREJA to secondary side of current transformer, inject three phase current by different values and use mini-clamp to measure current in each phase and follow the loop until the last point.
5-1-10-Voltage transformer loop:
a- Test objective:
This test is aimed to check the whole loop of VT starting from first panel and distributed in the whole substation depending on scheme (i.e. metering or protection purpose)
b- Required equipment:
- FREJA.
- Multi-meter.
c- Mechanical check and visual inspection:
Check all voltage transformer loops.
d- Test connection:
Connect FREJA which considered as voltage source to secondary side of VT, inject three phase voltage with different values on each phase and then use multi-meter to measure the voltage on the whole loop starting from first panel to different location depending on the function of each VT.
5-1-11- Lockout relay (86):
a- Test objective:
This test aimed to test lockout relay which is like muscles of the body and responsible to trip circuit breaker in case of trip order coming from protective relay
b- Testing Equipment Requirement:
- Sverker (used as Voltage source and used its voltmeter).
- Fluke [used as Ammeter].
- Miniature Circuit Breaker 2Pole (2MCB).
c- Mechanical check and visual inspection:
- Check for physical damage or defects.
- Check tightness of all connections.
- Check ferrules.
d- Test connection and test procedure:
i. All Contacts check:
- Before injecting any voltage on relay’s coil, check contacts at it normal condition which mean normally open (NO) contact is being opened and normally closed (NC) contact is being closed and check Red flag operation.
- Inject the desired control voltage of coil (which is in our case 125 volt DC), at which aux. relay will pick up that’s mean its contact will change its position i.e. NO contact will be closed and NC contact will be opened check red flag must be not shown.
ii. Pick up and drop off currents and voltages:
- Pick up voltage can be measured using voltmeter when the coil voltage is increased gradually from 0 volt, the relay will operate (i.e. contacts change its normal status should not be closed and red flag is shown and vice versa) at a certain voltage. This voltage is called pick-up voltage, Record the reading of voltmeter and Ammeter which is pick-up voltage and current.
- Drop-off voltage can be measured using voltmeter when the coil voltage on an operate relay is decreased gradually, the relay will release (i.e. its contact will return to its normal status) at a certain
voltage. This voltage is called drop-off voltage, Record the reading of ammeter which is drop-off current.
iii. Operating time and resetting time:
- Adjust voltage source at coil operated voltage of relay (in our case 125 v DC).
- To get operating time, adjust sverker at (on+time location) and switch MCB ON.
- To get resetting time, readjust voltage source at 125 volt DC and switch MCB OFF.
iv. Burden test:
- Adjust voltage source (sverker) at 125 volt DC, select on position and make MCB ON
- Record reading of Ammeter.
- Calculate burden by multiplying coil operated voltage and reading of Ammeter.
5-1-12- Lockout Supervision (74-86):
a- Test objective:
This test aimed to test lockout supervision relay which is responsible to supervise DC on lockout is it healthy or is there any lose or disconnect wires on it.
b- Testing Equipment Requirement:
- Sverker (used as Voltage source and used its voltmeter).
- Fluke [used as Ammeter].
- Miniature Circuit Breaker 2Pole (2MCB).
c- Mechanical check and visual inspection:
- Check for physical damage or defects.
- Check tightness of all connections.
- Check ferrules.
d- Test connection and test procedure:
i. All Contacts check:
- Before injecting any voltage on relay’s coil, check contacts at it normal condition which mean normally open (NO) contact is being opened and normally closed (NC) contact is being closed and check Red flag must be shown.
- Inject the desired control voltage of coil (which is in our case 125 volt DC), at which aux. relay will pick up that’s mean its contact will change its position i.e. NO contact will be closed and NC contact
will be opened check red flag must be not shown.
ii. Pick up and drop off currents and voltages:
- Pick up voltage can be measured using voltmeter when the coil voltage increased gradually from 0 volt, the relay will operate (i.e. contacts change its normal status should not be closed and red flag is shown and vice versa) at a certain voltage. This voltage is called pick-up voltage, Record the reading of voltmeter and Ammeter which is the pick-up voltage and current.
- Drop-off voltage can be measured using voltmeter when the coil voltage on an operate relay decreased gradually, the relay will release (i.e. its contact will return to its normal status) at a certain voltage. This voltage is called drop-off voltage, Record the reading of ammeter which is drop-off current.
iii. Operating time and resetting time:
- Adjust the voltage source at coil operated voltage of relay (in our case 125 v DC).
- To get operating time, adjust sverker at (on+time location) and switch MCB ON.
- To get resetting time, readjust voltage source at 125 volt DC and switch MCB OFF.
iv. Burden test:
- Adjust voltage source (sverker) at 125 volt DC, select on position and make MCB ON.
- Record reading of Ammeter.
- Calculate burden by multiplying coil operated voltage and reading of Ammeter.
5-1-13- DC Supervision Relay:
a- Test objective:
This test aimed to test DC supervision relay which supervises the most important DC loop in the panel (e.g. DC loop of relay binary input and relay output).
b- Required Equipment:
- Sverker (used as Voltage source and used its voltmeter).
- Multi-meter [used as Ammeter].
- Miniature Circuit Breaker 2Pole (2MCB).
c- Mechanical check and visual inspection:
- Check for physical damage or defects.
- Check tightness of all connections.
- Check ferrules.
d- Test connection and test procedure:
i. Check all contacts:
- Before injecting any voltage on relay’s Coil, check contacts at its normal condition which mean normally open (NO) contact is bein g opened and normally closed (NC) contacts is being closed and check red flag operation.
- Inject the desired control voltage of coil (which is in our case 125 volt DC), at which Aux. relay will pick up that’s mean its contact will change its position in no contact will be closed and NC contact will be opened and check Red flag operation.
ii. Pick up and drop off currents and voltages:
- Pick up voltage can be measured using voltmeter when the coil voltage is increased gradually from 0 volt, the relay will operate (i.e. contacts change its normal status (No) will be closed and red flag shown and vice versa) at a certain voltage. This voltage is called pick-up voltage; record the reading of voltmeter and Ammeter which is the pickup voltage and current.
- Drop-off voltage can be measured using voltmeter when the coil voltage on an operated relay is decreased gradually, the relay will release (i.e. its contact will return to its normal status) at a certain voltage. This voltage is called drop-off voltage, record the reading of ammeter which is drop-off current.
iii. Operating time and resetting time:
- Adjust voltage source at coil operated voltage of relay (in our case 125 v DC).
- To get operating time, adjust sverker at (on time location) and switched MCB ON.
- To get resetting time, re-adjust voltage source at 125 volt DC and switched MCB OFF.
iv. Burden test:
- Adjust voltage source (sverker) at 125 volt DC, select on position and make MCB ON.
- Record reading of Ammeter.
- Calculate burden by multiplying coil operated voltage and reading of Ammeter.
5-1-14- Trip Circuit Supervision Relays (TCS):
a- Test objective:
This test aimed to test trip circuit supervision which supervises the trip circuit and shows if it’s healthy or has any lose or disconnected wires in the trip circuit, in each panel there are two trip circuit supervision, first one to supervise trip circuit one and the other to supervise trip circuit two.
b- Testing Equipment Requirement:
- Sverker (used as Voltage source and used its voltmeter).
- Fluke [used as Ammeter].
- Miniature Circuit Breaker 2Pole (2MCB).
c- Mechanical checked and visual inspection:
- Check for physical damage or defects.
- Checked tightness of all connections.
- Checked ferrules.
d- Test connection and test procedure:
i. Check all Contacts:
- Before injecting any voltage on relay’s Coil, check contacts at its normal condition which mean Normally Open (NO) contact is being opened and normally closed (NC) contact is being closed.
- Inject the desired control voltage of coil (which is in our case 125 volt DC), at which Aux. relay will pick up that’s mean its contact will change its position i.e. NO contact will be closed and NC contact will be opened.
ii. Pick up and drop off currents and voltages:
- 03 Pick up voltage can be measured using voltmeter by increasing voltage gradually from 0 volt up to the relay will be operated (i.e. Contacts change its normal status, NO contact should be closed and vice versa) at a certain voltage. This voltage is called pick-up voltage, Record reading of V and A which is pick-up voltage and current. Drop-off voltage can be measured using voltmeter when the relay in an operate status and then decrease voltage gradually, the relay will release (i.e. its contact will return to its normal status) at a certain voltage. This voltage is considered drop-off voltage, Record the reading of voltmeter and Ammeter which is drop-off voltage and current.
iii. Resetting time:
- Adjust voltage source at relay rated voltage (in our case 125 v DC).
- To get resetting time, adjust the voltage source at 125 volt DC and switch MCB OFF.
iv. Burden test:
- Adjust voltage source (sverker) at 125 volt DC, select on position and make MCB ON Record reading of Ammeter.
- Calculate burden by multiplying coil operated voltage and reading of Ammeter.
- Same pervious procedure for each coil.
- Connection Diagram of Trip Circuit Supervision.
5-1-15- Primary injection test:
a- Test objective:
This test aimed to check that the selected ratio of current transformer is correct and current transformer relay setting is OK and considered as back-up test of CT loop.
b- Required equipment:
- Primary Injection Tester.
- Multi-meter.
- Mini-clamp.
- Power-clamp meter.
c- Mechanical check and visual inspection:
Check that all current transformer terminal block is tightened and normalized.
d- Test connection:
- Connect Primary Injection Tester to inject current on bus bar including current transformer.
- Start injection of current, using power clamp we can measure the injected current to make sure that injected current which appear on screen of primary injection tester is same as the actual injected current, then using of mini-clamp, we can measure the current at each point of the loop and read the primary current value on each relay.
5-1-16- Bus Bar Stability:
a- Test objective:
This test aimed to check that the selected ratio of BB current transformer is correct and CT relay setting is OK and considered as second back-up test of CT loop and polarity of BB CT is correct and to check at normal condition the summation of current is zero.
b- Required equipment:
- Primary Injection Tester.
- Multi-meter.
- Mini-clamp.
c- Mechanical check and visual inspection:
03 Check that all current transformer terminal block is normalize and wires is connected probably.
d- Test connection:
- Start sensitivity test: reverse the CT polarity from one side of CT only.
- Connect Primary Injection Tester to inject current on bus bar including current transformer.
- Start current injection and use mini-clamp to measure the current at the end of loop, measure the current after CT summation point it should be summation of the secondary side.
- Atart stability test at normal condition.
- Connect Primary Injection Tester to inject current on bus bar including current transformer.
- Start current injection and use mini-clamp to measure the current at the end point of each loop and read the primary current value on each relay measure the current after ct summation point it should be zero.
5-1-17- Medium voltage switchgear Function test:
a- Test objective:
This test is considered as a major test or combined test for the whole work in switchgear panels and finalizing phase for switchgear panels.
b- Required equipment:
No equipment used.
c- Mechanical checked and visual inspection:
Inspect for the whole panel if any missing or damage device which can be resulted from installation.
d- Test procedure:
- Segregation of DC loop inside panel, by switching on only one MCB and follow its loop and so on for other DC MCB.
- Check the circuit of closing command for circuit breaker.
- Check the circuit of opening command for circuit breaker.
- Check Automatic transfer switch (ATS) logic and functionality.
- Check anti parallel scheme.
- Check mechanical interlock.
- Check interlock of circuit breaker from close switch (CS) and bay control unit between CB and earth switch.
- Check alarm signal from source up to relay.
- Check inter trip between upper voltage level CB and switchgear CB, between lower voltage levels CB and switchgear CB.
- Confirm the relay logic.
- Check the CB functional like (travelling contact, manual charging, manual close & open, CB Rack in & out ,CB counter operation before and after test also check the CB TOC, MOC, Trip coil and close coil.
5-1-18- Protection relay (Main relay):
a- Test objective:
This test aimed to test function of main relay according to approved final setting for each one, but here we generally discussed main function which should be exist in most of approved final setting.
b- Required Equipment:
- FREJA 300.
- Multi-meter.
- Wires.
c- Mechanical check and visual inspection:
- Check for physical damage or defects.
- Check case earth.
- Check indication and LEDs.
- Check test switch for correct operation either shorting CT if exist or isolation of binary inputs/outputs.
d- Burden test
- Adjust voltage source at 125 volt DC.
- Record reading of Ammeter in case of all binary output deactivated and in case of binary output activation.
- Calculate burden in case of normal operation (all binary output deactivated) and abnormal operation (in case of binary output activated) by multiplying voltage and reading of ammeter.
- Compare the result with existing burden exist in relay manual.
e- Test connection and test procedure:
i. Binary input/output check:
- To test binary input: Apply rated binary input DC voltage on each input and verify the status of the input through relay’s software or from relay’s LCD [if exist].
- To test binary output: Using relay’s software you can force binary output to close for certain time and using multi-meter you can measure binary output contact resistance it should be around zero which indicates binary output being closed.
ii. Measurements
- Set CT ratio and VT ratio which used to the relay by studying the scheme.
- By using FREJA we inject secondary rated voltage and secondary rated current
- Record the primary value reading at relay’s screen.
iii. High Impedance Differential Protection for Bus Bar circuit (87B)
- As per final setting of relay set (Numerical relay-Resistor-Metrosil) the resistor must be adjusted to give the desired operating voltage at which the relay will operate.
- Numerical relay setting the value of secondary current and the value of resistor is inserted for relay then The relay calculate the actual voltage value by multiplying the value of secondary current and the resistor then compare it with the setting voltage value.
– To test Pick up and drop off test:- - Adjust the value of the series resistor as per final setting and measure its value.
- Inject current and gradually increase the value till relay operation.
- Measure the pickup current and voltage across the series resistor.
– To test Time: - Take one normally open contact of the relay, adjust the sverker to (on time) and apply a voltage more than the setting value.
iv. Transformer differential (87T):
- Transformer differential is a low impedance protection in which the current vector is measured as amplitude and angle and the measured current from transformer sides summed together to calculate the differential current, If the current value exceeds the setting value the relay generates a trip command.
- To test PICK UP & drop oft test, Inject current and increase it’s value gradually till relay operation, measure the value of the injected current and calculate the differential and restrain current, Repeat for each current transformer location, Decrease the current value gradually till relay drop off, Measure the current and repeat for each current transformer location.
- To test time test: Assign a normally open contact from the relay as a differential protection trip; inject a current more than the setting value, Measure the tripping time.
v. Instantaneous over-current (50)
- Pickup and drop off test: gradually increase secondary current to each phase separately in steps, until the LED which you used to indicate instantaneous over-current to operate this is considered pick-up value. The current must be reduced in the same manner until the LED reset and then this considered as drop-of value.
- Limits: then calculate the error and compare the error value with acceptable tolerance error that exist in manual of relay Timing test: set each phase separately to amount of current equal to 22ls, then inject this value of current and measure the time taken to close binary output of the relay which indicates that ins. Over-current trip.
- Limits: then calculate the error and compare the error value with acceptable tolerance error that exist in manual of relay.
vi. Instantaneous earth fault (50N):
- 03 Pickup and drop off test: gradually increase secondary current to each phase separately in steps, until the LED which you used to indicate inst. Earth fault to operate this is considered pick-up value. The current must be reduced in the same manner until the LED reset and then this considered as drop-of value.
- LED reset and then this considered as drop-off value.
- Limits: then calculate the error and compare the error value with acceptable tolerance error that exists in manual of relay.
- Timing test: set each phase separately to amount of current equal to 22ls, then inject this value of current and measure the time taken to close binary output of the relay which indicates that inst. E.F.
- Limits: then calculate the error and compare the error value with acceptable tolerance error that exist in manual of relay.
vii. Time delayed earth fault (51N):
- Pickup and drop off test: gradually increase secondary current to each phase separately in steps, until the LED which you used to indicate inst. Earth fault to operate this is considered pick-up value. The current must be reduced in the same manner until the LED reset and then this considered as drop-of value.
- Limits: then calculate the error and compare the error value with acceptable tolerance error that exists in manual of relay.
- Timing test: set each phase separately to amount of current equal to 22ls, then inject this value of current and measure the time taken to close binary output of the relay which indicates that inst. Earth fault.
- Limits: Limits: then calculate the error and compare the error value with acceptable tolerance error that exist in manual of relay.
viii. Thermal overload:
- Inject single phase current greater than setting current in the relay for certain time and take binary output from relay indicate thermal overload trip.
- After a time the binary output will be ON which indicate the thermal overload trip.
5-1-19- ATS and anti-parallel scheme Function Check:
a- Test Objective:
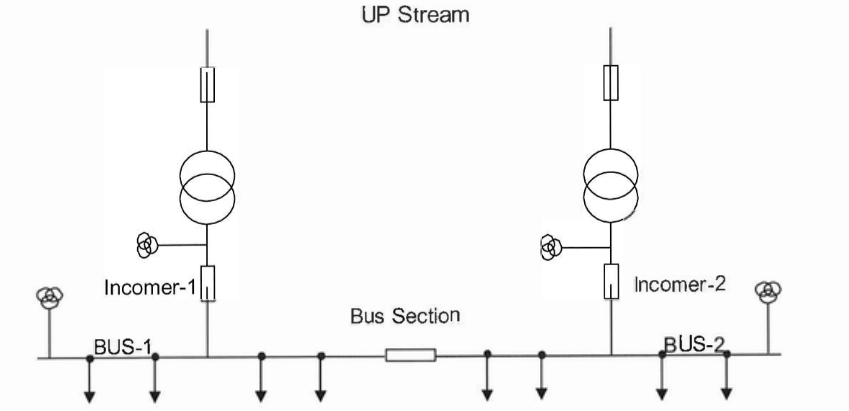
The principle of operation for the ATS (Automatic Transfer Switch) is that Two Incomers are feeding two busses divided through one Bus Section. In case of one incomer power supply lost (Incomer-1) hence the corresponding bus bar become dead (Bus Bar under voltage) and the bus section circuit breaker should close automatically to feed the load for the dead bus. When the incomer feeder be energized again the operator should block the ATS function by make it Manually and then choose through one selector switch which circuit breaker should open after he closes the incomer-1 circuit breaker hence he will give close command to the incomer-1 circuit breaker and after this incomer becomes closed the selected circuit breaker (Incomer-2 or the Bus Section) will trip automatically.
b- Test Equipment:
- Freja300
- Multi-meter (Fluke).
c- Test procedure:
- Connect 3phase voltage to the relay to simulate the line and bus VT source and then inject 3phase healthy voltage for both incomers (lncomer-1 & Incomer-2) through MCBs.
- Close both incomer-1 and incomer-2 and leave the bus section in the open position.
- Close the 4 MCBs that simulate Line-1, Bus-1, Line-2 and Bus-2 voltage to the relay.
- Make the selector switch of the ATS mode on Automatic.
- Open the MCBs that connect the Bus and Line voltage of the Bus-1 to the relay.
- 0 The relay will wait for some time and then it will give open command for incomer-1.
- Then the relay will wait for some time more and give close command to the bus section.
- Now close the MCB of the Line-1 voltage (simulation to energize the incomer-1).
- Now the relay will check the synchronization between line-1 and line-2 voltages.
- Then make the selector switch of the ATS mode on Manual.
- Select either Incomer-2 or Bus Section (through the selector switch) which you need to open after you close the incomer-1.
- Now give manual close command to the incomer-1 circuit breaker.
- If step no.9 achieved and the relay will enable the close command to incomer-1 circuit breaker.
- Then the relay will give an open command to the selected circuit breaker.
- Do the same steps for Incomer-2.