The Permit to Work system (PTW) is a comprehensive safety management process implemented in workplaces, particularly in high-risk environments such as industrial plants, construction sites, and offshore facilities. It is designed to control hazardous work activities by ensuring that proper risk assessments are conducted, appropriate safety measures are implemented, and work is authorized before it commences.
What is Permit To Work System (PTW)?
1. Purpose of Permit To Work System.
A Permit To Work System (PTW) is a formal written authorisation used to control certain types of work that are identified as non-routine, high risk and critical activities.
A Permit To Work System allows means of co-ordination, control and supervision of work activities performed by Company or Contractor personnel. It provides a written method of ensuring that work carried out is strictly controlled by defined work practices and safety precautions.
This procedure covers all activities of Company, including contractor’s personnel working for Company. Contractors with their own HSE arrangements must also comply with this procedure as a minimum. It has been developed to achieve compliance with Element B1 and CS of the HSE Integrated Management System (IMS) of Eni Exploration & Production Division (Ref 1) and its Application Requirements (Ref 2, Ref 8)), and PETRO BEL HSE IMS (Ref 3). It is aligned with the general principles of international HSE management standards (Refs 4, 5 and 6).
2. Objectives of Permit To Work System.
The objectives and function of the Permit To Work System are to:
- Ensure that personnel who carry out the work clearly understand the nature of the work, the hazards of the job, and the time periods when the work can be done.
- Ensure that the HSE hazards and risks are identified, and adequate and appropriate controls selected to minimise the risks.
- Specify the precautions to be taken before starting, during the work and after completion.
- Provide a record showing that the type of work and the proper procedures have been checked by an approved person.
- Ensure that proper authorisation is given to carry out work.
- Provide for the suitable display of open or suspended permits.
- Provide a control mechanism for times when work must be suspended.
- Provide control or arrangements for other activities that may interact or affect one another.
- Provide a formal hand-over procedure for use when work to be carried out extends for a period longer than a shift or when the signatories are changed.
- Provide a formal hand-back procedure to ensure that work is completed and the worksite left in a safe condition.
- Provide a mechanism to ensure all isolations and controls are carried out appropriate to the task.
3. Risk Assessment and Control.
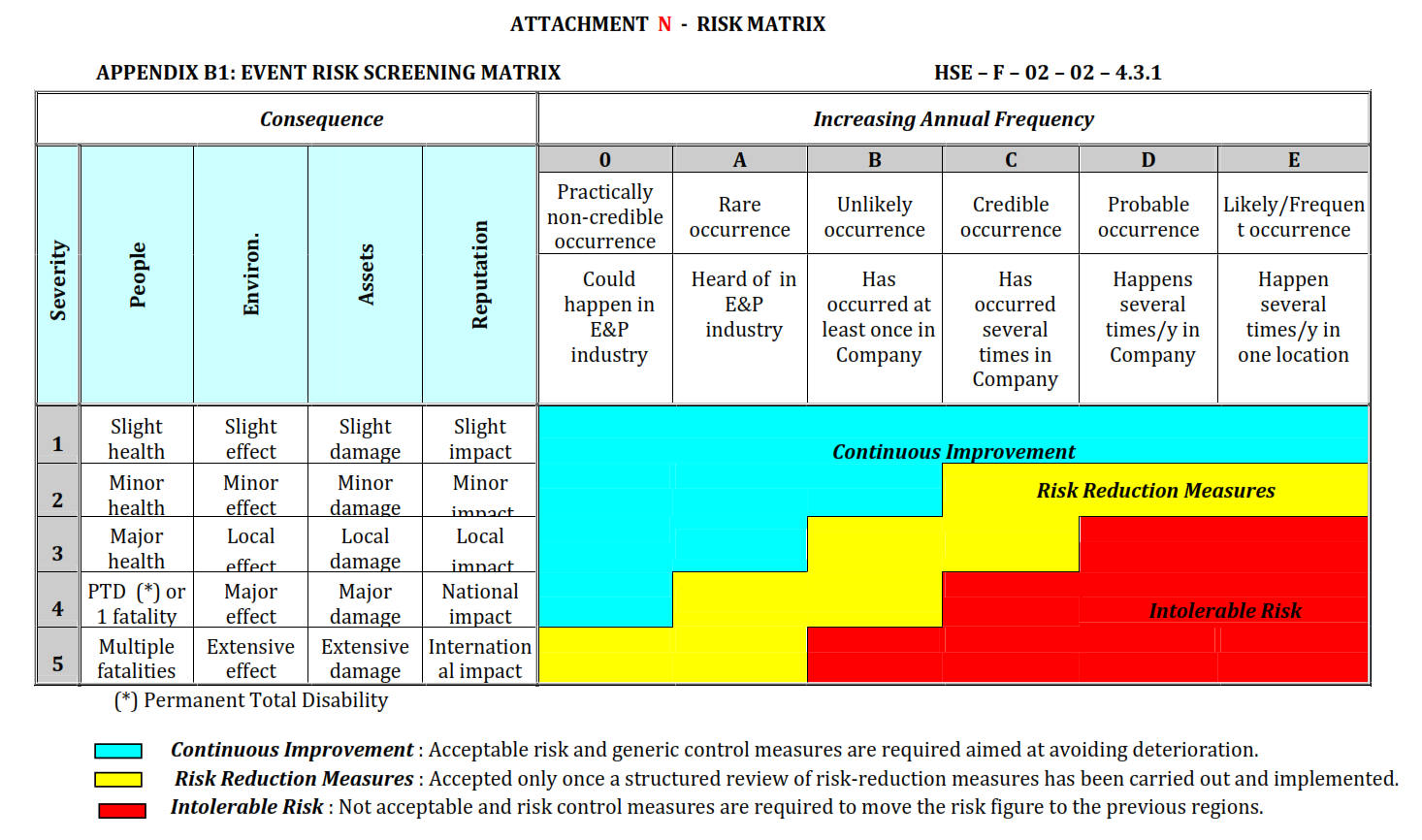
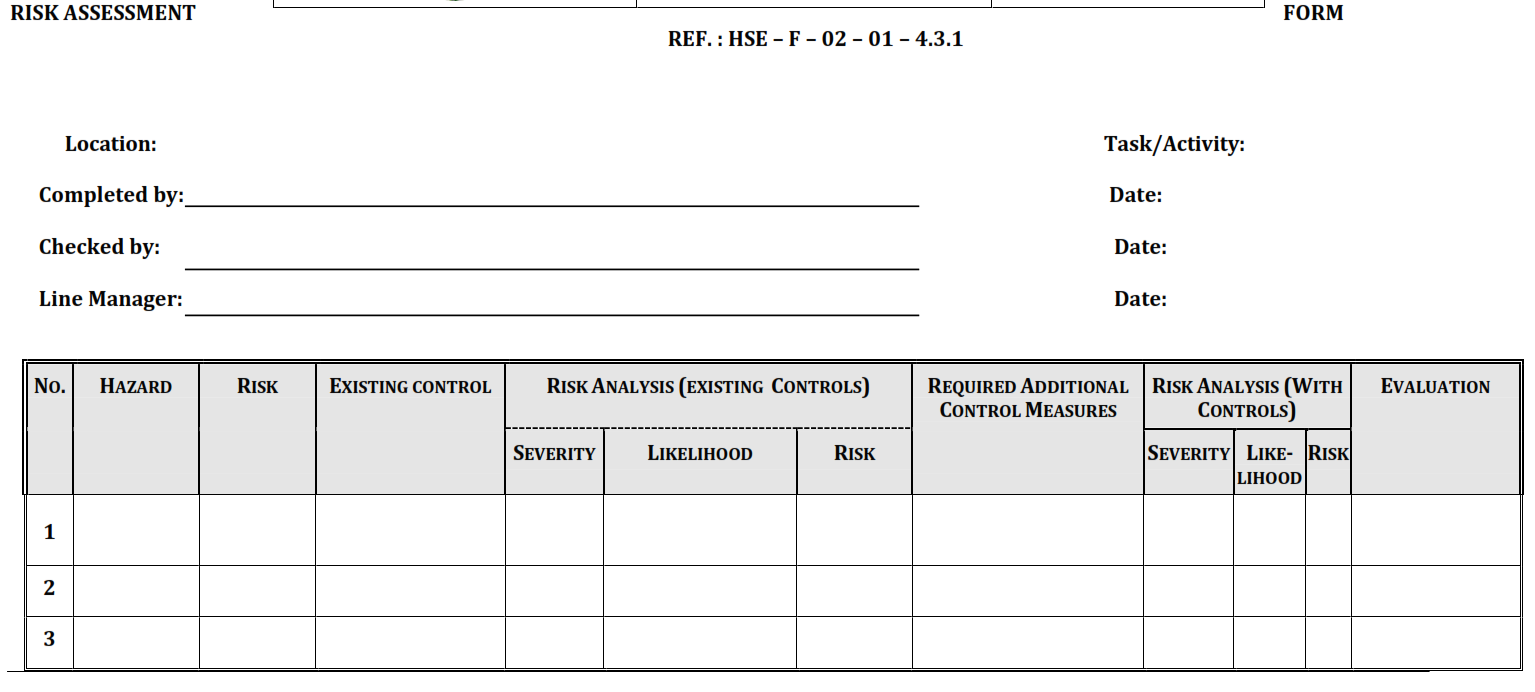
The initial steps of the Permit to Work system are hazard identification, risk assessment and selection and recording of controls. This should be conducted in accordance with the HSE IMS Risk Screening and Assessment Procedure (Ref 7).
The risk assessment should record the risk ranking as indicated in the Risk Matrix, included here as Attachment M. The Risk Assessment Form, included here as Attachment N, should be used to record existing controls and additional required controls.
Guidance for hazard identification, in the form of key words and tables of hazard checklists, is provided in Appendices 1 and 2 of the Risk Screening and Assessment Procedure, and guidance on Control Measures in Appendix 3.
4. Permit Forms, Types of Work Permit System and Isolation Certificates.
PTW system aims to ensure that proper planning and consideration are given to the risks of a particular job. The permit form is a written document that authorises certain people to carry out specific work, at a certain time and place, and that sets out the main precautions needed to complete the job safely. Company generally has six types of Work Permit forms. The type of work dictates the type of Work Permit form that is to be used. The six types of company Work Permits are uniquely coloured to allow easy identification of the type of work to be done.
4.1. Types of Work Permits Used.
| Permit Types | Colour |
| Hot Work Permit. | Red |
| Cold and Gas Hazardous Work Permit. | Yellow |
| Confined Space/Vessel Entry Work Permit. | Green |
| Excavation Permit. | White |
| Radiography Permit. | Orange |
| Rig Move Work Permit. | Blue |
4.2. Types of Certificates used:
| Certificate Types |
| Electrical Isolation Certificate. |
| Mechanical Isolation Certificate. |
| Protective Systems Isolation Certificate. |
| Gas Clearance Certificate. |
A certificate is only valid when there is a supporting permit. The certificate forms part of the permit and the conditions specified on the certificate are to be taken as permit conditions.
The purpose of an isolation certificate is to certify that the plant or equipment has been thoroughly isolated (locked out) from sources of power or process fluid/gas and the necessary tags placed at the points of isolation. All work stated on a Certificate is to be performed only by Authorised Personnel. A Work Permit is normally initiated before raising isolation certificate(s) of any kind.
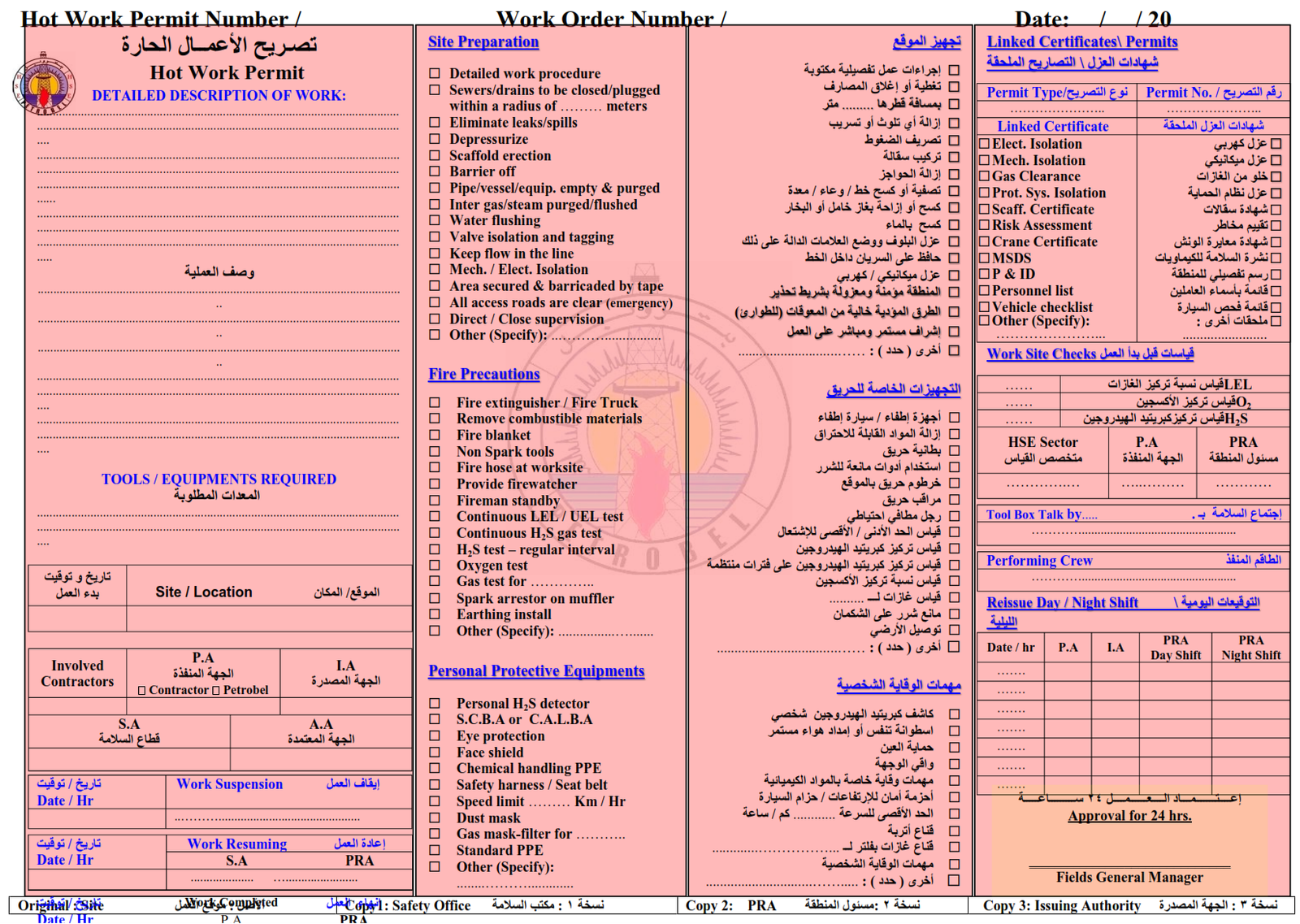
5. Hot Work Permit.
A Hot Work Permit is required for any work involving burning, welding or grinding, radioactive sources, explosives, vehicle entry or electrical work that can generate heat or a spark when working in a classified hazardous area. At least three meters from a live hydrocarbon line shall be ensured.
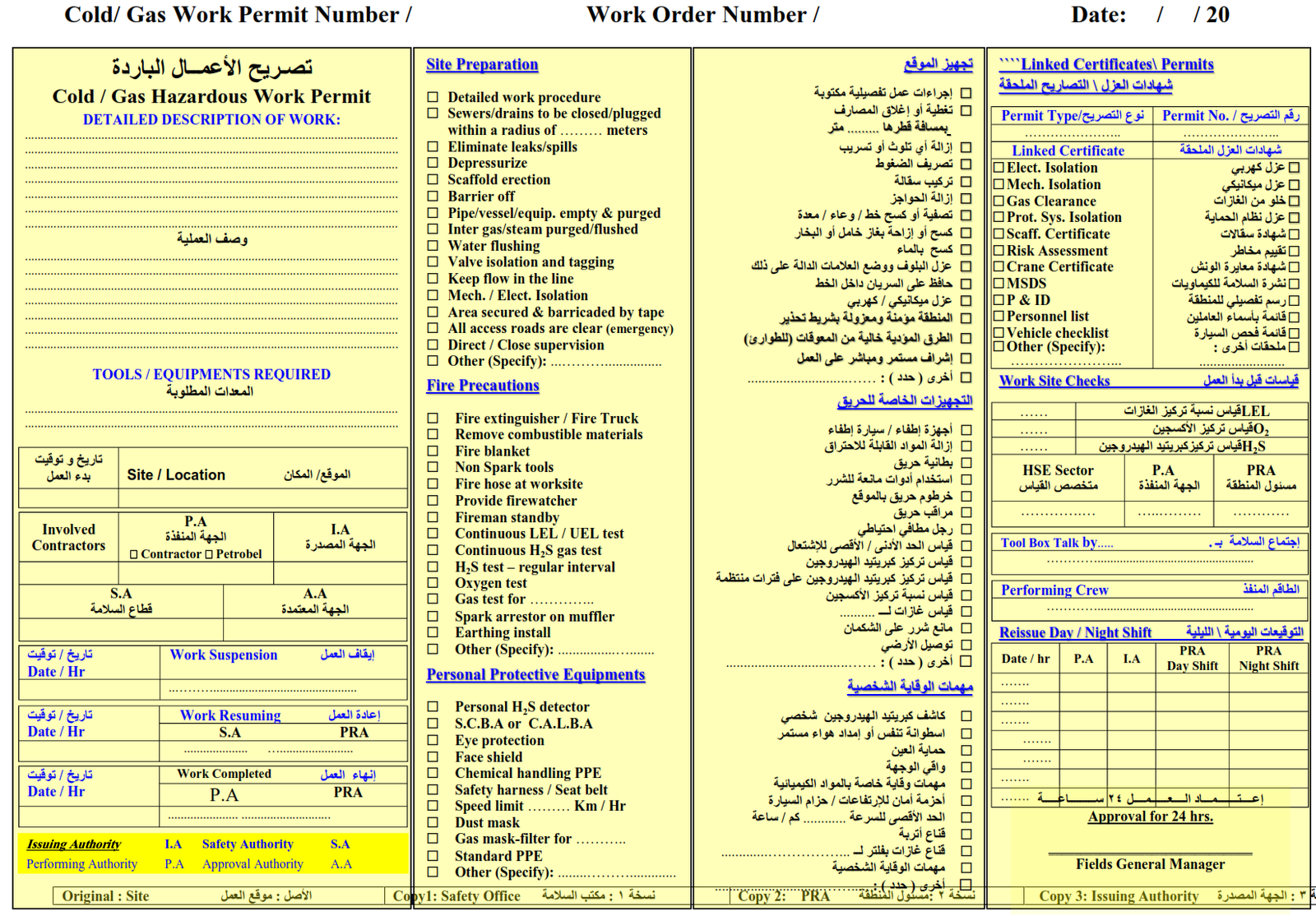
6. Cold and Gas Hazardous Work Permit.
Cold and gas hazardous work is any work that does not generate heat or sparks. A Cold and Gas Hazardous Work Permit is required for work involving pressure testing, handling hazardous chemicals, gas hazardous work, painting, scaffolding, working at height, and mechanical maintenance (involving use of mechanical hand tools). Any cold work that is to be carried out inside classified hazardous areas requires a Cold and Gas Hazardous Work Permit.
7. Confined Space / Vessel Entry Permit.
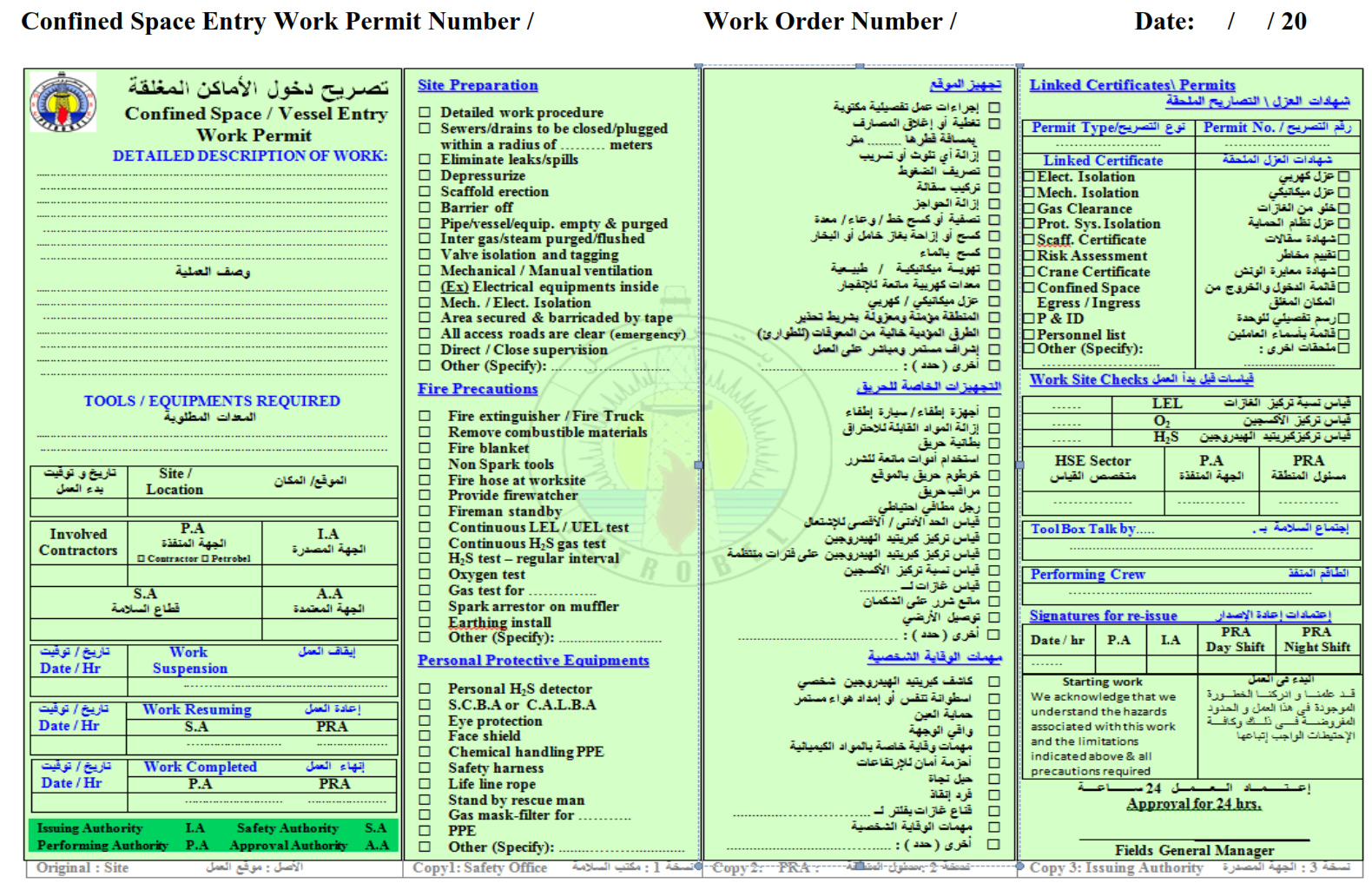
A Confined Space/Vessel Entry Permit is required prior to the entry of personnel into any confined space, vessel, valve pit or enclosure. Issue of this permit does not replace Hot and Cold and Hazardous Work Permits for the individual work specified. They will be required for the work to be carried out in the confined space. The Confined Space/Vessel Entry Permit is valid for one day. However it could be extended if the safe work conditions still available. A Vessel Entry Permit requires a Gas Clearance Certificate and relevant Mechanical /Electrical Isolation Certificate(s) issued in conjunction with the Permit.
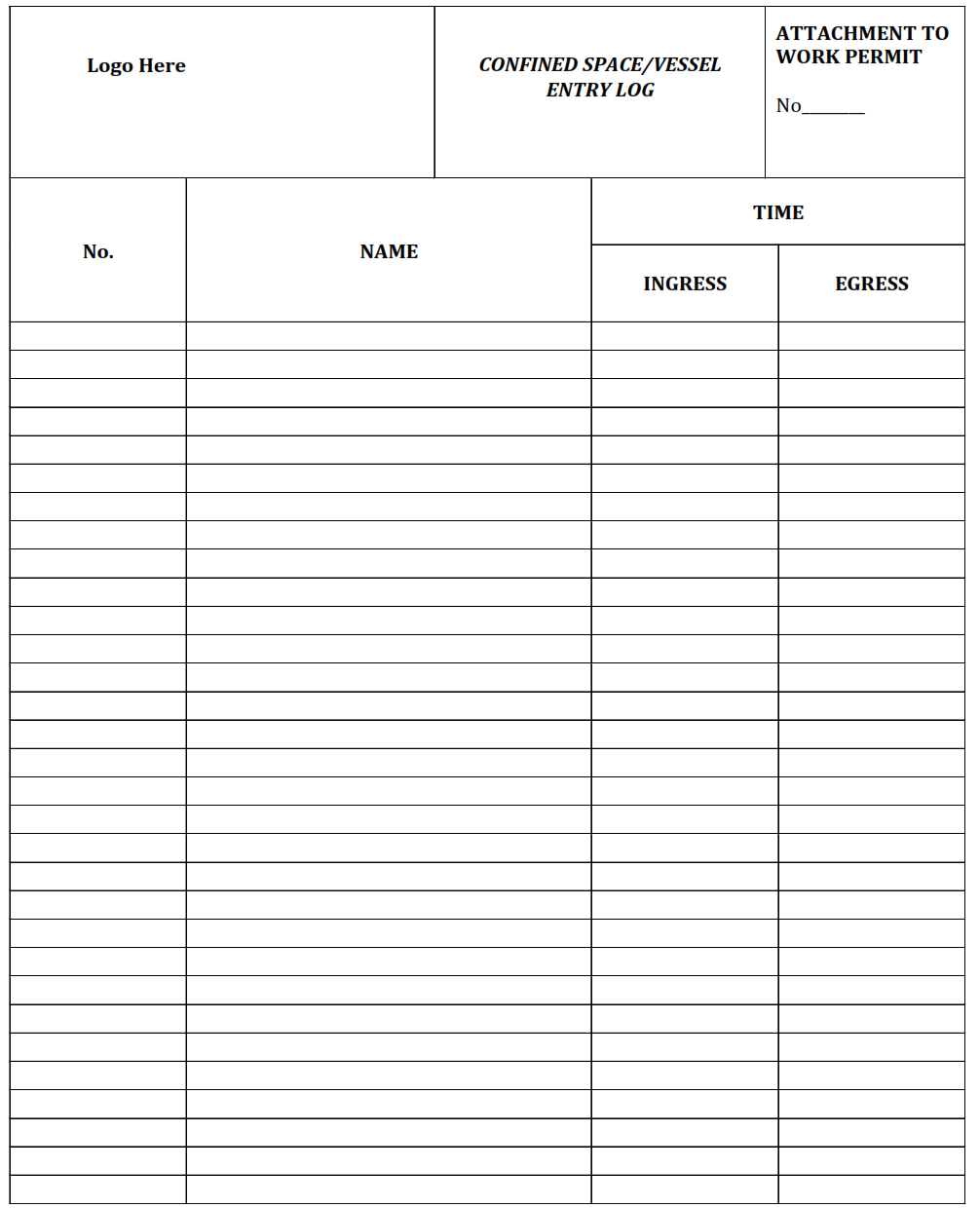
Confined Space/Vessel Entry Log.
8. Excavation Permit.
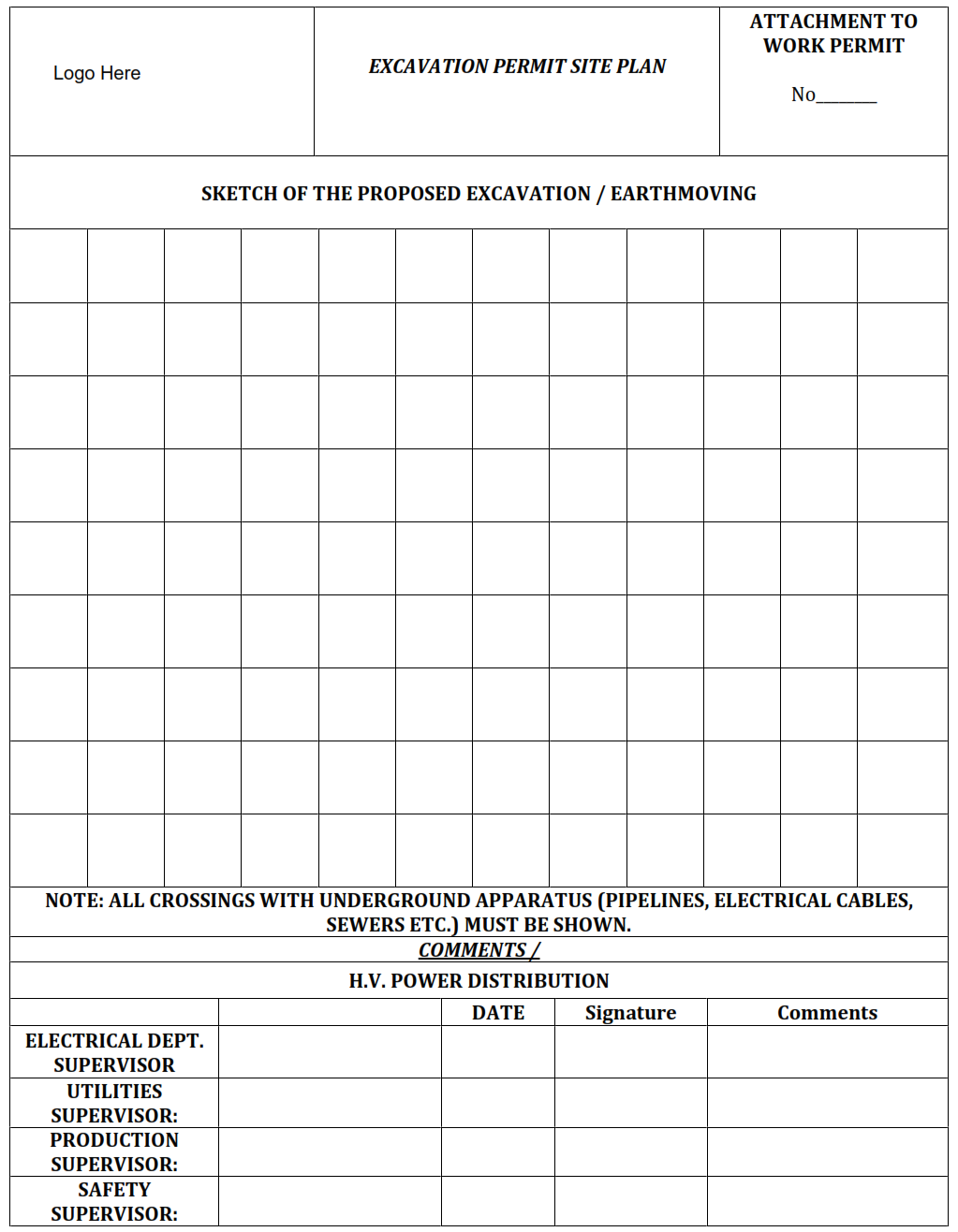
An Excavation Permit is required prior to beginning any excavation and generally any ground disturbing activity in a classified area. It is required when any digging, excavating or boring has to be done to ensure that no underground apparatuses are damaged. Movement and placing of heavy equipment may also require an excavation permit. A sketch of the proposed excavation track together with a layout drawing highlighting the presence of existing underground apparatuses (such as facilities/flow lines or buried cables) must be attached with the permit request.
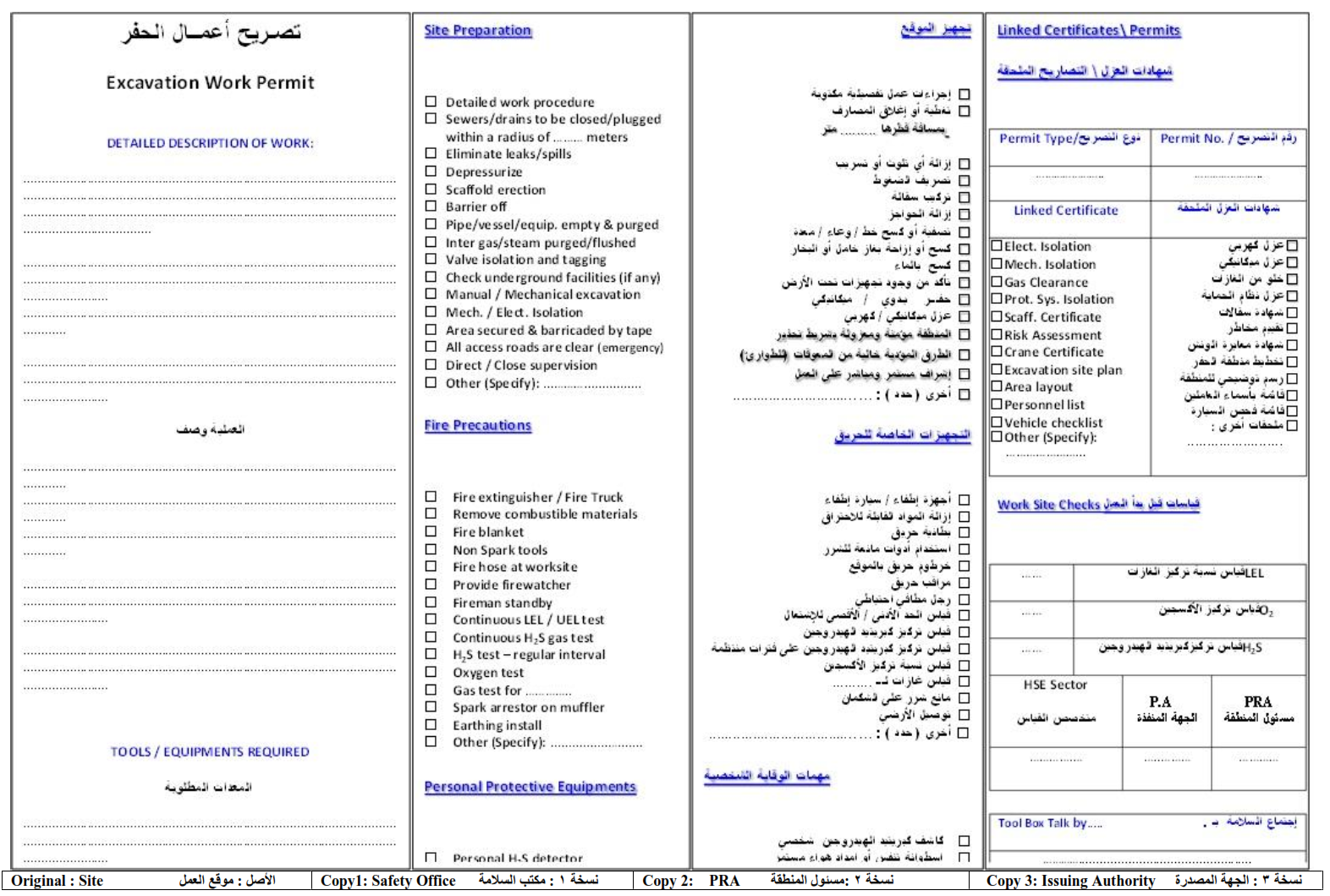
Note: An Excavation Permit does not replace the Hot or Cold Work Permit for the individual work specified but must contain additional precautions as required under the normal Hot/Cold and Gas Hazardous Work Permit. Hot/Cold and Gas Hazardous Work Permits will be required for any work performed in the excavation.
Excavation Permit Site Plan.
9. Radiography Work Permit.
A Radiography Work Permit is required for any work involving radioactive sources for radiography work. The precautions for the correct and safe use of the radioactive materials must be specified in the Radiography Work Permit & comply with the national legal requirements. To use, monitor and control the radiation sources specified on the permit requires the presence of a competent Company or Contractor Radiation Representative.
10. Rig move Work Permit.
A Rig move Work Permit is required for any work involving move of any land rigs (drilling/work over) & offshore rigs (MODUs – Mobile Offshore Drilling Units). The precautions for the correct and safe way & practices for rig move operations must be specified in the Rig move Work Permit & comply with the international standard requirements.

To control the rig move operations & security of production facilities, all the precautions shall be specified in the permit & it requires the presence of a competent Company or Contractor Rig mover Representative.
11. Electrical Isolation Certificate.
The purpose of an Electrical Isolation Certificate is to confirm that the plant or equipment has been isolated from an electrical power supply by an Authorised Electrician with necessary lock out and tag out, and is in a safe condition to work upon.
The certificate must be issued if work involves:
- Normally live electrical cables or equipment
- Electrically driven plant or equipment.
Work under a Permit cannot proceed until all cables, equipment and plant have been electrically secured, the power supply isolated, locked out and a warning tag attached to the supply panel by an Authorised Electrician.
12. Mechanical Isolation Certificate.
The purpose of Mechanical Isolation Certificate is to confirm that all equipment, machinery and plant (to be worked upon) have been mechanically isolated from power supply (pneumatic, hydraulic or engine driven) and process fluid/gas with necessary lock out and tag out by an Authorised Mechanic/Specialist. The drawing with highlighted isolations must be attached to the Mechanical Certificate.

The following isolation activities require a Mechanical Isolation Certificate:
- Valves locking open or locking close and tagging
- Inserting spades or line blinds
- Physical disconnection and blanking
13. Protective Systems Isolation Certificate.
A Protective Systems Isolation Certificate is required when the work involves over• ride (disconnection) of safety and emergency systems or its component parts have to be isolated, such as:
- Relief /Safety (PSV) Valves.
- Emergency Shut Down System (ESD).
- Fire and Gas Alarm system.
- Fire and Gas Detection System.
- Firewater System.
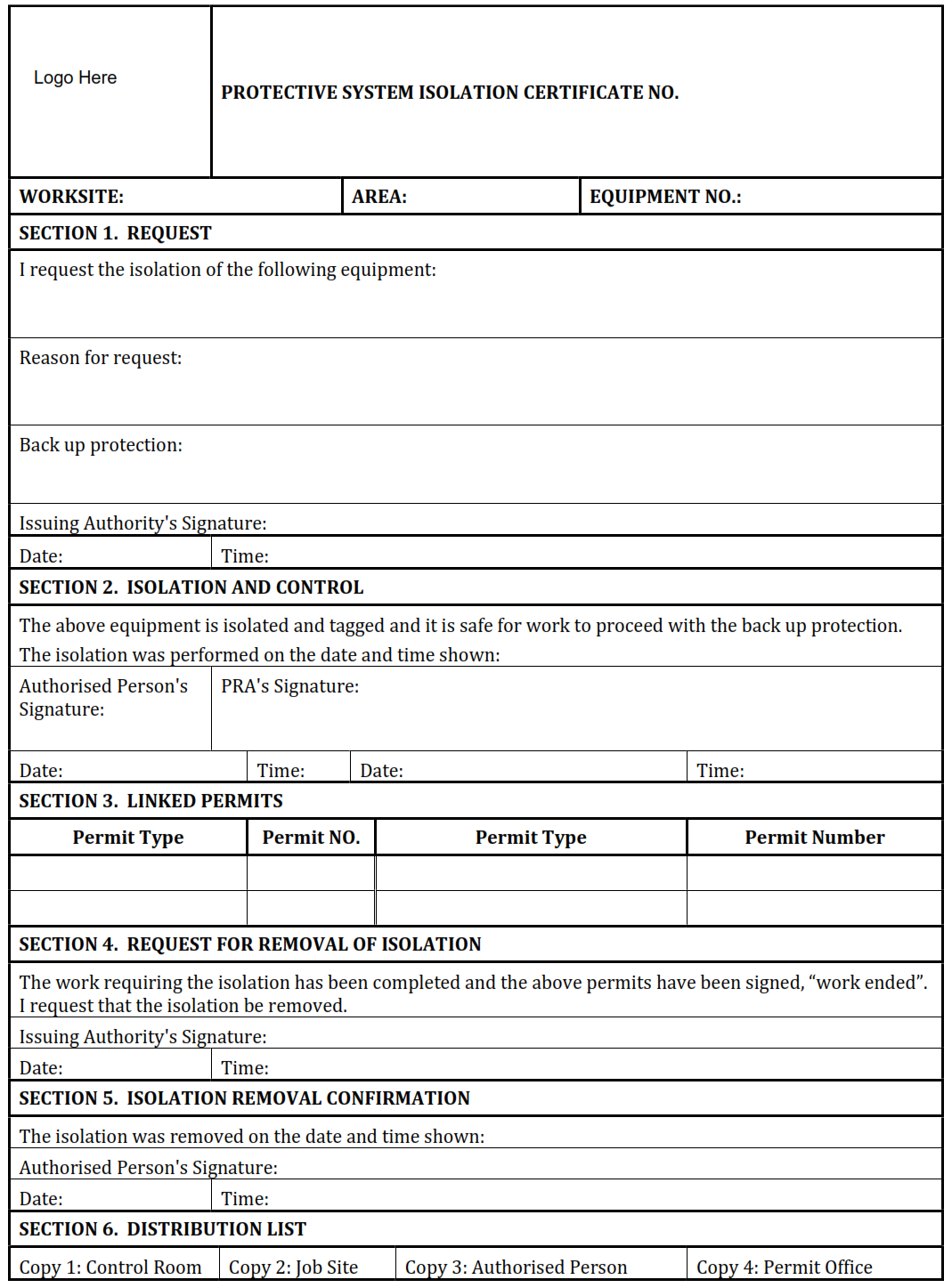
An Authorised Person performs work stated in the certificate after obtaining necessary approval signatures. The duration and extent of each over-ride shall be kept to a minimum. Alternative means of protection must be provided and recorded on the Protective Systems Isolation Certificate. For example, if a fire detector is over-ridden, then a fire watch must be provided for the area until the fire detector is returned back into service.
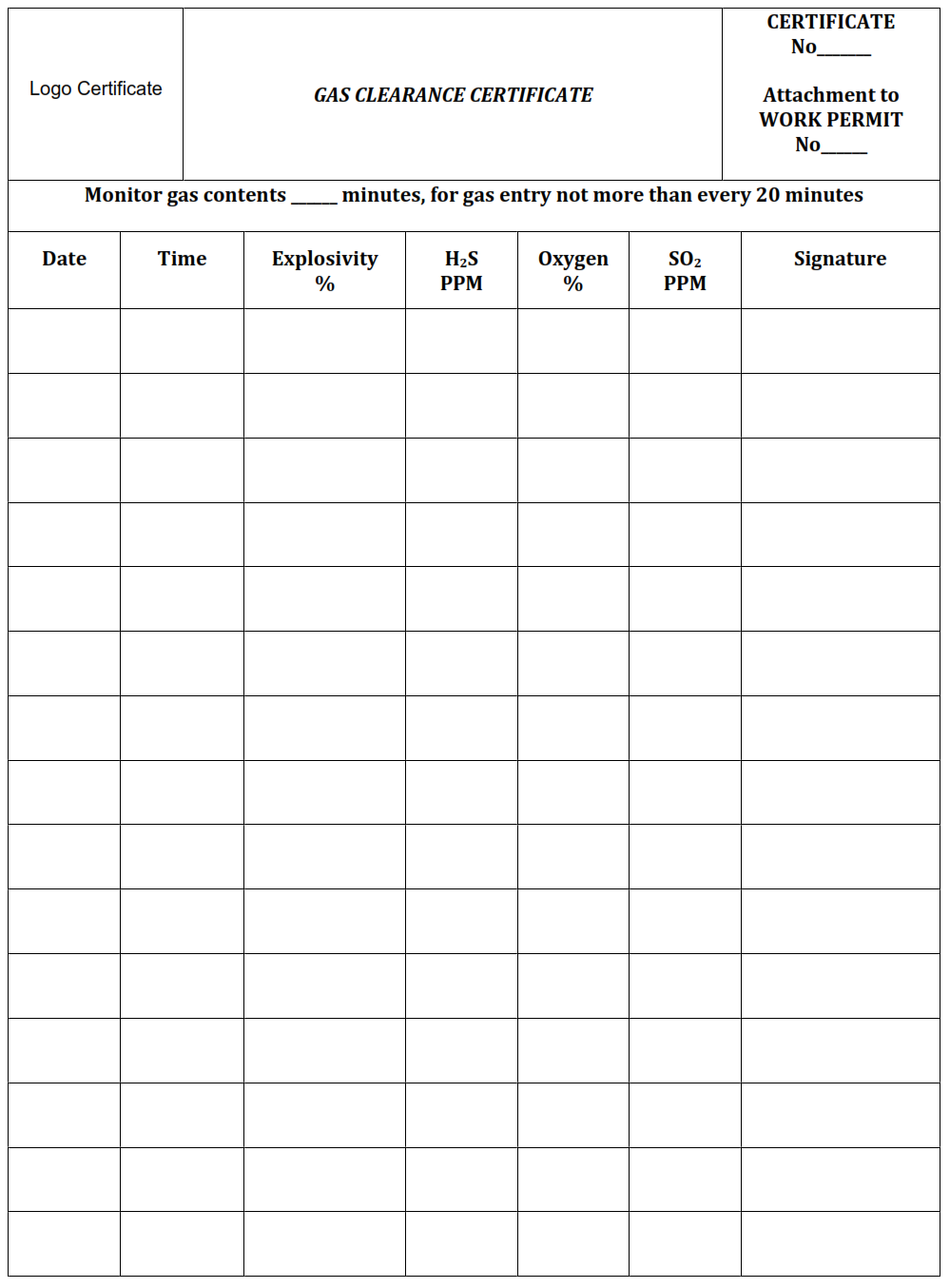
14. Gas Clearance Certificate.
A Gas Clearance Certificate is required to confirm that the atmospheric condition is safe for work (such as combustible or toxic gasses, or oxygen in air checks). The Hot, Cold and Gas Hazardous and Confined Space/Vessel Entry Permit Forms contain a section for the initial testing of atmospheric conditions. A Gas Clearance Certificate is required to accompany those permits where further testing is stipulated on the Permit. An Authorised Gas Tester performs work stated on the Certificate. Lock out / isolation shall be in place.
15. List of Personnel.
Space is provided on the main Work Permit for recording the names of personnel working on the job. These personnel must be instructed in and fully understand the scope of work, the hazards involved and the precautions required to be taken to ensure their safety. If the number of personnel exceeds the space provided, then an additional List of Personnel must be used.

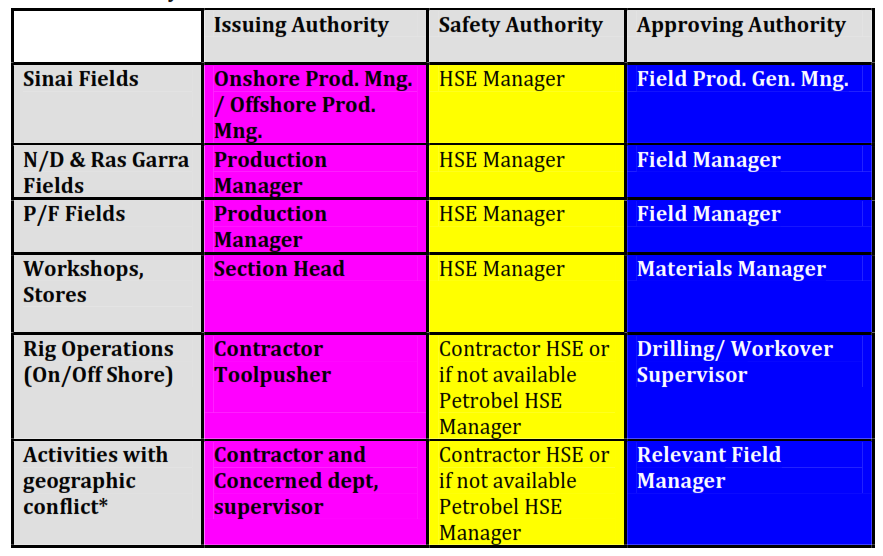
16. Parties Involved in Work Permit System.
| Performing Authority. | A person responsible for performing the work to be carried out under a Work Permit. |
| Issuing Authority. | A person responsible for issuing Work Permits at the facility or site. |
| Safety Authority. | A person responsible for checking necessary safety precautions stated on the Work Permit. |
| Approving Authority. | A person responsible for approving a Work Permit at the facility or site. |
| Person Responsible for Area. | A person responsible for authorising the start of work at the work site A person appropriately trained and appointed. |
| Authorised Person | in writing by Site Approving Authority to carry out certain duties. |
| Authorised Electrical Person. | A competent electrically trained person with sufficient technical knowledge and experience. |
| Authorised Gas Tester. | A person appointed by Site Approving Authority for carrying out gas tests. |
Company normally assign the following positions as authorised signatories for the Permit-To-Work System:
Authorized signatories shall ensure:
- That they are informed of and understand the broad principles of the Company PTW system and the work areas or facilities/operations for which they have specific responsibilities for under the PTW system.
- That they have received the appropriate training and understand the operation of the PTW system and their specific responsibilities within it.
17. Responsibilities
Responsibilities of the Issuing Authority.
a) To ensure that any work requiring a Work Permit (non-routine, high risk and hazardous activities) does not start until the relevant Permit is authorised and issued
b) To issue Work Permits with all necessary conditions and safety precautions clearly Specified on the Permit.
c) Ensure that all hazards associated with the work have been identified d) Ensure that Work site has been inspected;
e) ensure that person in charge of work (performing authority) is aware of precautions taken, additional ones required, equipment used, and procedures to follow;
f) Ensure that the permit specifies the action to be taken if the work has to be suspended; The work site is examined when work is suspended or completed;
g) To liaise with the Person Responsible for an Area (PRA).
h) If issuing of mechanical or electrical certificate is required, the authorised electrician, mechanic or production technician will be consider as issuing authority for the isolating performing side and in this case he shall liaise with person responsible for the work area (PRA).
Example: In case of repairing a mechanical issue & that repair requires an electrical isolation, mechanical Div. will be the issuing authority & electrical Div. will be the performing authority & Production Rep. will be the PRA in the issued isolation certificate”
i) To ensure that the conditions and precautions specified on a Work Permit are understood and are strictly adhered to by those carrying out the job covered by a Work Permit
j) To suspend any other work, which, if taken concurrently with a job task under the Work Permit, could affect safety
k) To sign off the Work Permit and associated Certificates when the work specified has been completed and the work site is in a safe condition
Responsibilities of the Performing Authority
a) To fully understand Work Permit procedures applicable to their area of responsibility
b) To conduct a risk assessment and record existing controls and additional required controls
c) To complete or prepare a Work Permit form after preliminary discussion of the work with the Issuing Authority and HSE representative. Permit applications should be made 24 hours in advance by the Performing Authority to allow proper co-ordination and planning of work activities
d) To ensure that any work requiring a Work Permit does not start until the relevant Work Permit is authorised and issued to the Performing Authority
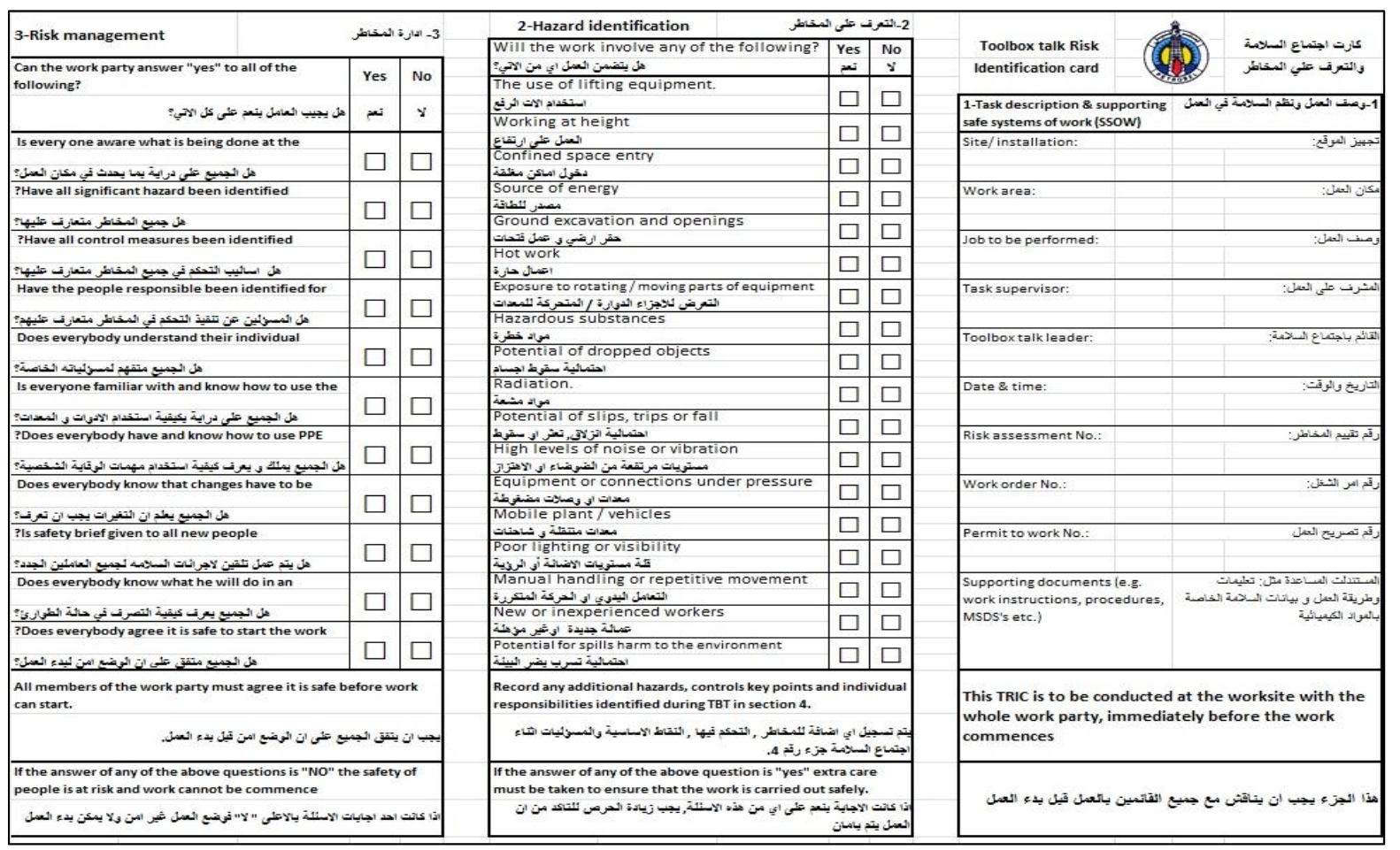
e) To ensure that the conditions and precautions specified on a Work Permit are understood and are strictly adhered to by those carrying out the job covered by a Work Permit (TBT – Tool Box Talk, Attachment P), including completion of the Personnel List (Attachment M).

f) To provide any additional instructions, equipment, training, or other assistance necessary for the Worker(s) to carry out work specified on the Permit
g) Ensure that the Issuing Supervisor is informed when work is suspended or completed;
h) Ensure that after the completion and suspension of the permit shall be formally handed back and signed off by the proper Issuing Supervisor;
i) Ensure to personally inspect the job site along with the Issuing Authority and a PTW copy is posted on the Job site;
j) Ensure that the work environment is monitored on continues basis and ensure no deviation from the approved work scope covered by the permit;
k) Ensure that all people involved in the WORK performed under the issued PTW are competent and properly trained, the training should insure that the personnel understand the PTW system and procedures in general, and the specific precautions required for their work.
l) To ensure plant and equipment is handed back to operations in a safe condition.
Responsibilities of the Safety Authority
a) To ensure that all the potential hazards identified and necessary safety precautions are specified on the Work Permit.
b) To ensure that the conditions and precautions specified on a Work Permit are understood and are strictly adhered to by those carrying out the job covered by a Work Permit.
c) To inspect and audit worksite for compliance with Work Permit conditions
d) Provide and conduct training to familiarize Company employees with the PTW System & Procedure.
Responsibilities of Fire Watcher
To help the performers in prevention of the occurrence of any uncontrolled fire when performing hot work based on the instruction of the issuing Authority and under the supervision of the Performing Authority.
Responsibilities of PTW Controller
- To inform immediately the Issuing Authority and/or Approving Authority of any situation presenting and impact on the safe completion of an activity or on the associated precautions;
- To check and review all PTW associated documents supplied for completeness by Performing Authority applies for a PTW i.e.: Work Procedure and Task Risk Assessment, As built drawings / other documents , Implement the Certificate requirements (Gas testing, Isolation Certificates … etc.) in order to complete the requirements of a PTW before issue;
- To maintain up to date written or computer-based registers of permits and supplementary certificates;
- To ensure a display board of all Permits and Certificates is maintained and used;
- To collect all copies of each PTW at the end of the shift / day for revalidation or cancellation as is required;
- To ensure and securely store all the completed and cancelled PTW’s following cancellation for the agreed period of 2 years at site and 5 years at Head Office.
Responsibilities of the Approving Authority
a) To approve Work Permits.
b) To ensure that satisfactory facilities, including training exist for implementing the procedures on a daily basis.
c) To monitor the implementation of the procedures on a regular basis to ensure they are being properly applied. This is achieved via a Permit Audit System.
d) To ensure that the procedures are regularly revised, when necessary.
e) In case of operational emergencies, when following the process of issuing and approving a PTW is not practicable, the field manager(s) are accountable and responsible for taking the required actions and setting proper controls to be in place to mitigate the operational problems and its relevant hazards (1st priority) without compromising the need for PTW issuance (2nd priority).
f) To ensure that PTW process is applied all the times covering all shifts (day and night shifts). In fields where field management are not present during night shift, they may delegate other field’s managers. This delegation shall be limited, written and communicated to all field personnel.
g) To clearly identify all persons responsible for administering the Work Permit (such as signatories).
h) The Approving Authority is also responsible for addressing the following specific issues:
♦ Simultaneous Operations.
Construction, Commissioning, Production and Well Operations activities undertaken and performed by two or more independently managed organisations where the physical proximity or activities on one work location have the potential to impact another work location.
SIMOPS are also:
- Those activities for which either organization must advise the other whenever they are to be carried out; and
- Those for which dual authorization is required
The Field Responsible Person defined by a procedure or the locally designated area authority has responsibility for coordinating the activities and for ensuring that permits to work are issued only after hazard identification and risk assessment has been carried out and any risk mitigation measured agreed.
The Approving Authority should set up displays to enable the following types of work conflict to be identified:
♦ Areas of Geographical Conflict
Where the close proximity of worksites or work activities causes interaction, or has the potential to impact upon the other. Those activities for which either party must advise the other whenever they are to be carried out and those for which dual authorization is required, good communications shall be established.
For those activities managed by departments, which does not belong to the field ( e.g. construction , rig-less activities, exploration … etc.) that might impact the production facilities and /or taking place within the boundaries of the field facilities, the contract holder/concerned department will be the issuing authority and the relevant field manager will be the approving authority.
Example:
Rig or ship activity operation in close proximity to a fixed facility or in a production platform (operational or under construction) and where activities such as well clean up, well testing or flaring will be carried out.
♦ Interconnecting Systems
Special arrangement must be made where independent facilitates or work sites, although physically separated, may be connected by existing interconnecting systems.
In these situations, the PTW system shall contain specific arrangements that will
- Ensure control of isolation and de-isolation of interconnecting pipelines.
- Provide notice of any work that may interface with other interconnected facilitates or work sites.
- Ensure verification is obtained from the interconnecting facility or work sites so that the work may proceed.
♦ Inhibited Safety Systems
Where work on one task may be hazardous, if carried out at the same time as another task, for which safety systems have been inhibited.
♦ Provision of Visual Displays
Visual displays will include a structured display of permits, separating them by area and by status (such as approved, issued, or suspended), and a simple graphic display of the location of works currently being carried out under work permits, by marked up plot plans or general arrangement drawings.
Responsibilities of the Person Responsible for the Area (PRA)
a) To check each relevant work site to ensure that the work can be safely carried out and authorise start of work by signing off Work Permits & isolation certificates (if any) before the start-up of work activity
b) To stop any unsafe working practices encountered in his area once the work specified on the Work Permit has begun
c) Inspecting and auditing worksite for compliance with Work Permit conditions
d) To sign off the Work Permit & isolation certificates (if any) when the work specified has been completed and the work site is in safe condition
Responsibilities of Authorised Personnel (Authorised Electrician, Authorised Mechanic, Authorised Gas Tester)
- a) To carry out necessary checks, tests or isolations; demonstrate verification of their checks, tests or isolations to the Issuing Authority and Performing Authority
- b) To issue the relevant certificate
- c) To countersign the associated Work Permit (if required)
Responsibilities of an Individual Worker
a) To have a general understanding of Work Permit System
b) To have a detailed working knowledge of Work Permit procedure as it applies to his/her own work
c) To ensure that NO work is begun that requires a Work Permit until one has been approved and issued
d) To ensure they fully understand and adhere to the conditions and safety precautions stated in the Work Permit
e) To avoid working alone without control & to take all the necessary precautions required for working in a far work place
18. Permit To Work System Process.
The PTW process and approval routing and signature steps required from Permit initiator to work completion are shown below.
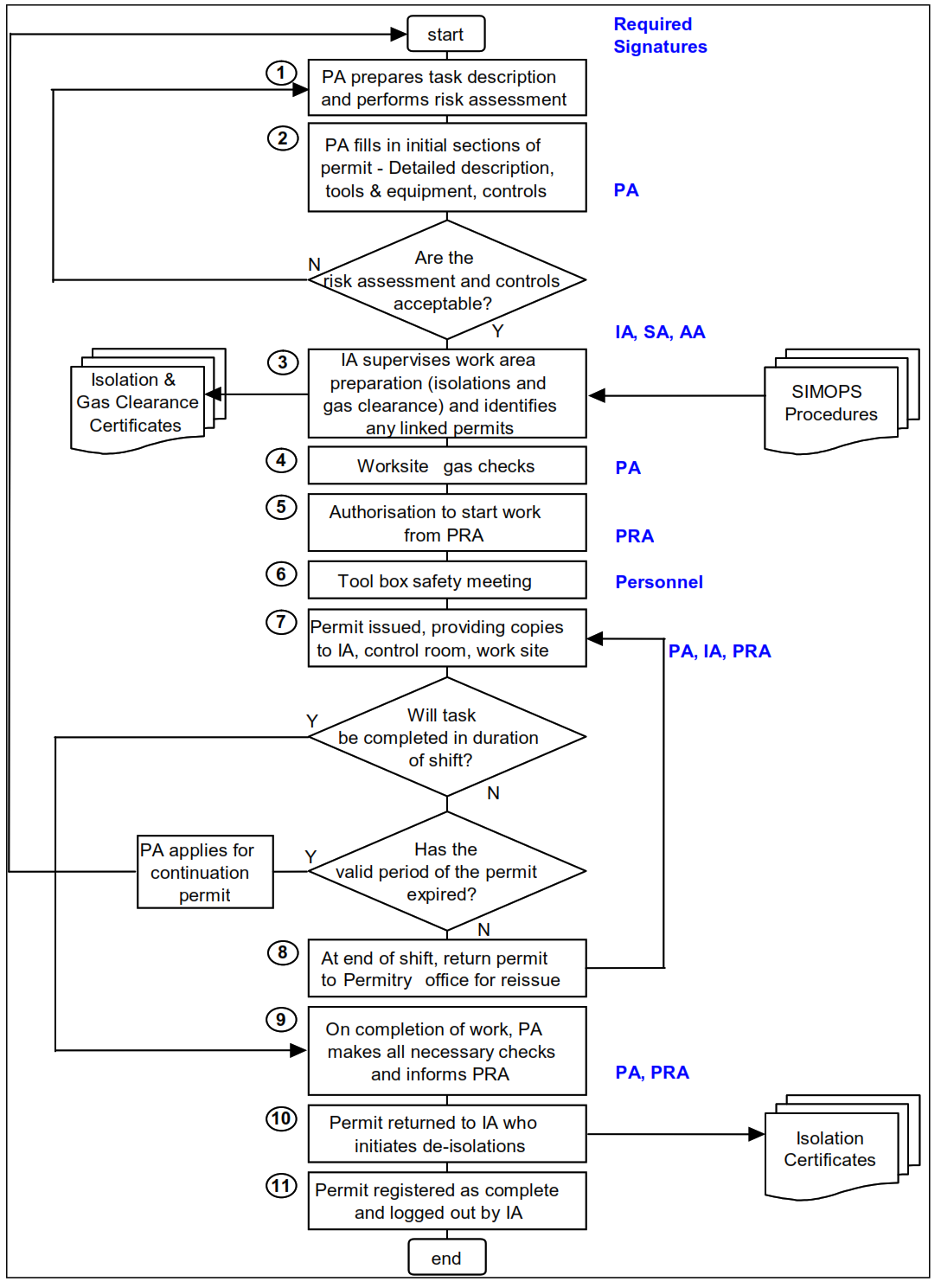
Permit To Work System Process.
The following paragraphs give a detailed explanation of the PTW process:
► Step 1: Work Preparation
- PA shall prepare a description & task risk assessment for the task requiring a PTW.
- PA shall decide the type of PTW form(s) to be used.
► Step2: Initial Filling of PTW form by PA
- PA shall initially fill the following sections of the PTW and then submit it to the IA:
o Site preparations;
o Fire precautions;
o Personal Protective Equipment;
o Any required mechanical / electrical isolation;
o Any required gas site checks;
► Gate 1: Are the Risk Assessments & Controls acceptable?
- IA (in consultation with SA) shall the review the initial risk assessment & proposed controls are initially accepted or not.
- In case if the risk assessment is initially accepted, then proceed to step 3, otherwise, return back to step 1.
► Step3: Issuing Authority Supervision of Work Site.
- Upon review & acceptance of the task risk assessment by the IA (in consultation with the SA), IA shall supervise the work area and verify if that the following items are accepted as initially listed by the PA in the PTW & risk assessment or if any additional modification shall be needed:
- Site preparations;
- Fire precautions;
- Personal Protective Equipment;
- Any required mechanical / electrical isolation;
- Any required gas site checks;
- If there are any SIMOPS operations taking place at the work site;
- If there are any linked work permits or isolation certification.
- At this step, the IA (in consultation with SA) can perform additional precautions, and shall record it accordingly in the PTW form and/or task risk assessment;
- If mechanical and/ electrical isolation is required, the PA shall issue the relevant isolation certificate and the isolation shall be performed by the competent authorized person (Isolation Authority);
- The Isolation Certificate shall be signed by the PA, IA for requesting the isolation;
- The competent authorized person (Isolation Authority) shall describe the means of isolations, sign in and specify the linked permit(s) number(s) according to them he performed the isolation.
- The approved isolation certificate(s) number(s) shall be recorded on the PTW form in its relevant section.
► Step4: Work Site Gas Checks (when Required).
- If gas check is required, the PA shall perform the required gas checks, either directly should the PA has an Authorized Gas Tester (AGT) or through the SA depending on the site conditions to make sure that the LEL percentage is not greater than 20%, the Oxygen concentration is not less than 20 % and more than 23.5 % and HS concentration is not more than 10 ppm (in case of H»S availability at site).
- The measured values shall be recorded in its section in the PTW form, the AGT / SA, PA & IA shall sign below these values thus granting their acceptance of such measured values of gases are acceptable for work commencement.
- In case of working in confined spaces where it is possible that the gas concentration varies with time, a clearance gas certificate (Attachment I) shall be issued, where the values of explosive limits, Oxygen, HS and SO» shall be measured every 20 minutes to verify that these limits are always with the acceptable limits for safe work (explosive limits not greater than 20%, Oxygen Concentration between 20% and 23.5%, H»S concentration is not more than 10 ppm, SO2 concentration is not more than 5 ppm).
► Step 5: PTW Authorization
- Upon performing all of the steps above, the PA, SA, IA shall sign in their relevant sections in the permit, and the permit shall be submitted to the Approving Authority (AA) or his designate for work permit approval and authorization.
► Step 6: Toolbox talk
- The PA shall hold a toolbox talk where he shall ensure that the PTW and its associated documents, e.g. Isolation Certification, Risk Assessment are reviewed, prior to the start of the job, and are fully understood by all persons involved in the task
- If anyone at this stage identifies some additional hazards that have not been properly assessed or thinks the control measures are inadequate, the job should not proceed until the PTW & its associated documents have been re-evaluated and appropriate controls identified to ensure that the task risks are ALARP.
- Toolbox talks must be recorded; using the form in Attachment K; original Toolbox Talk records should be retained at site for a period not less than one year for sake of auditing.
► Step 7: PTW Distribution & Logging-in
- Upon authorization of the PTW by the involved parties, the permit shall be distribute;
- The original copy of the Permit shall be displayed at the work place; first copy shall be kept at the Approving Authority, second copy at the Issuing Authority and 3rd copy at the Safety Authority (Permit Office/ Control Room);
- The original copy of isolation certificate shall be kept by the Authorized Person, 1s copy at the SA (Permit Office / Control Room), 2nd copy at the IA & 3 copy at Approving Authority;
- All PTWs shall be logged-in using the log form attached in Attachment L by Permit Controller / SA / IA.
► Gate 2: Will task be completed in the duration of the shift?
- If the task will be completed in the duration of the shift, proceed to Step 9;
- If the task will not be completed in the duration of the shift, proceed to Gate 3.
► Gate 3: Has the valid period of the permit expired?
- If the valid period of the permit has expired, the PA shall apply for a continuation period, thus returning back to Step 1;
- If the permit is still valid, proceed to step 8.
► Step 8: New Shift Reissue
- At the end of the shift, the permit shall be returned by the PA to the SA at the Permit Office/Control Room for reissue by the new shift.
► Step 9: Work Completion
- On completion of work, PA makes all necessary checks and informs the IA;
- PA sign-off the PTW at the “Work Completed” section.
► Step 10: De-Isolation
- PA submit the PTW after signing it off by his side to the IA;
- The IA initiates the de-isolation process by signing off the isolation certificate requesting from the competent authorized person to perform the de-isolation;
- Upon performing the de-isolation by the competent authorized person, he shall sign off the isolation certificate and give it back to the IA.
► Step 11: PTW Signing-off & Log-out
- IA submit the PTW to AA (or his designate) for signing-off the PTW under the “Work Completed Section”;
- PTW shall be recorded as logged-off in the PTW log by Permit Controller / SA / IA.
19. Completion of the Work Task / End of Shift.
Once the work has been completed, the Performing Authority (supervisor in charge of the work) shall make all necessary checks and if satisfied, inform the PRA. Both parties can then sign off the “work completed” section of the Permit displayed at the work site. The Performing Authority shall bring copies of Work Permit from work site and control room/rig site to the issuing Authority (Permit Office). De-isolations (if required) can then be initiated by Issuing Authority and performed by Authorised Personnel.
The Permit shall then be registered as completed and logged out by the Issuing Authority. This closes the Work Permit. Copies will be filed for a period of two years.
20. Validity of Work Permits and Isolation Certificates
Work Permits shall not be carried over from one shift crew to another. A Work Permit is valid for a twelve-hour (12) period (one shift) but can be re-issued for the next shift. This will require the signatures of the Performing Authority, Issuing Authority and the Person Responsible for the Area (PRA). The Hot Work, Cold & Gas Hazardous, Excavation, Radiography & Rig Move Permits are valid for seven (7) days maximum in case of their daily reissue.
Note: Confined Space/Vessel Entry Permit is only valid for one day.
The Isolation Certificate is valid for the duration of the relevant Permits and until the de-isolations have been performed.
A Work Permit is no longer valid.
- When the working conditions change, conditions appear that were not anticipated when issuing the Work Permit
- If the Work permit is suspended
- Under NO circumstances shall a task that is subject to a Work Permit be continued if the permit in force is no longer valid.
21. Alterations To Work Permits.
Work Permits cannot be altered unless authorised by the Approving Authority or his Designate.
22. Suspension of Work Permits
In the event that the work is suspended before completion of the work, the area shall be secured and zoned off if necessary. If isolation is in force, it shall be maintained and ALL OPEN ENDS BLINDED.
23. Display of Valid or Suspended Work Permits.
In order to monitor the Work Permits, a system of display shall be implemented. This will allow personnel on the work site to know the current status of the ongoing work.
The display shall be as follows:
- The original at the work site
- One copy at the Permit Office (HSE Div.)
- One copy at the Issuing Authority
- One copy at the Control Room/ Rig Site / PRA
24. Emergencies.
A site specific safety induction provides details of the site emergency alarm. In the event of an emergency, STOP WORK and ensure equipment and machinery used for carrying out the work is switched off and left in a safe condition. Work cannot be restarted until the Issuing & Safety authorities give permission.
25. Permit-To-Work System Review.
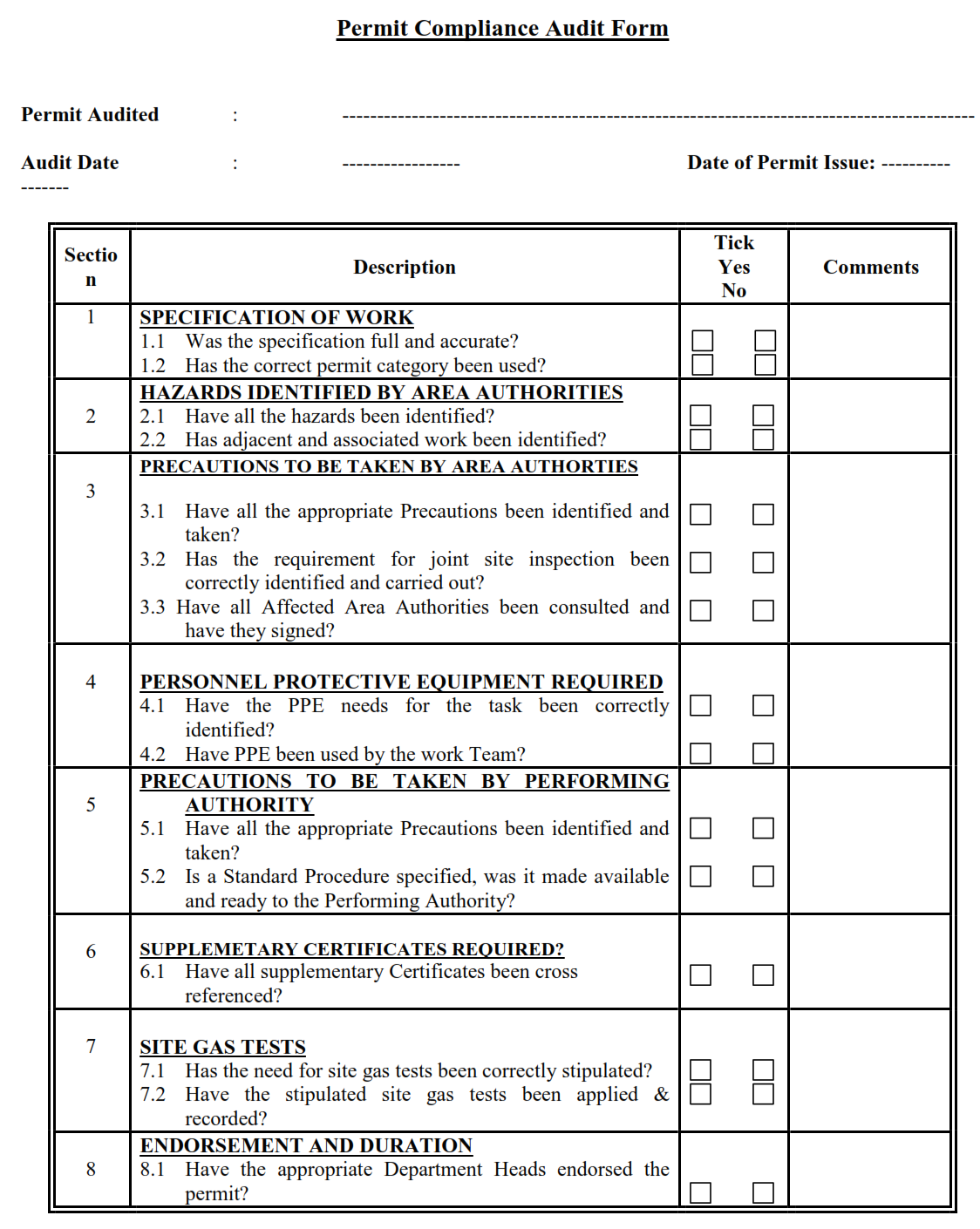
To ensure the ongoing effectiveness of the Permit system, the Approving Authority shall periodically check the implementation of the system. These checks shall take the form of unannounced spot checks on particular permits and work sites to check that the work is being performed safely and all permit conditions are being complied with. Administration of the permit system shall also be included in these checks (Permit To Work System Compliance Inspection).
In addition to the checks made by the Approving Authority, the HSE Department will include the Permit-To-Work system in the program of annual safety audits. This will involve periodical audit to verify that the permit system continues to meet all requirements and that the system is effectively implemented. The form reported in annex Q to be used for auditing the PTW.
26. References for Article.
1. ISO 14001.
2. OHSAS.
3. ISO 9000.
Permit Compliance Audit Form.