This article is about INPUTS AND OUTPUTS OF COMPRESSOR CONTROL SYSTEM and focusing to the engineers, technicians and supervisors. You will find lot of documents related to this article. Just navigate our website www.paktechpoint.com and find more articles. Please! Do not forget to subscribe our You tube channel also. Thanks in Advance.
PLEASE SUBSCRIBE OUR PAKTECHPOINT YOUTUBE CHANNEL
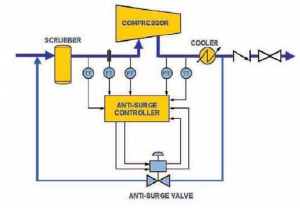
INPUTS AND OUTPUTS OF COMPRESSOR CONTROL SYSTEM
Speed Inputs
The CCS can accept one, two or three speed inputs. Each speed input is monitored by two module’s. With six possible speed signals from which to control with, the CCS can withstand multiple speed input failures with no loss of control functionality. Only one of the possible six inputs is required for speed control. The control can accept a ‘slow speed’ detect probe on channel 4 which can be unique or different from the other speed signals.
All speed inputs are connected to the control, via termination modules (FTMs). An inputs termination module is
used to terminate customer control wiring and distribute each input signal to the two module’s. After the control receives their input values, the Application Software Redundancy Manager then compares each module’s voted
result to select a value to be used within the application logic.
used to terminate customer control wiring and distribute each input signal to the two module’s. After the control receives their input values, the Application Software Redundancy Manager then compares each module’s voted
result to select a value to be used within the application logic.
A speed input signal is determined to be faulty and is taken out of the input voting logic when it is below its “Speed Failure Level” setting. This failure level setting is common to all inputs and can be adjusted via de CCT program’s Service mode.
An input deviation alarm is also used to annunciate if any of the three possible speed input channels is sensing a value that is different than the voted-good value used by the application. If an input channel’s sensed value deviates from the voted-good signal value, by a greater margin than the speed control’s “Max Deviation” setting, an input channel alarm will be issued.
This type of annunciation can be used to indicate when an input channel, or magnetic pickup unit is intermittently failing high or low. Max Deviation input settings are tunable via the CCT program’s Service mode, and are defaulted to 1% (deviation range = 0.01 to 20%) of the “Overspeed Limit” setting. If a deviation alarm condition occurs, the alarmed input is not removed from the control’s voting logic and still can be used to control with, in case all other channels fail.
This type of annunciation can be used to indicate when an input channel, or magnetic pickup unit is intermittently failing high or low. Max Deviation input settings are tunable via the CCT program’s Service mode, and are defaulted to 1% (deviation range = 0.01 to 20%) of the “Overspeed Limit” setting. If a deviation alarm condition occurs, the alarmed input is not removed from the control’s voting logic and still can be used to control with, in case all other channels fail.
Analog Inputs
The control can accept one or two transducer inputs for all critical parameters (ext/adm, aux, casc inputs). Only one input signal is accepted for non-critical functions (remote setpoint inputs). Each analgo input can withstand one failure with no loss of control functionality. If any of an analog input’s two “legs” are failed, the control uses the second healthy leg’s sensed input signal from which to control with.
All analog inputs are connected to the control, via field termination modules (FTMs). An input’s termination module is used to terminate customer control wiring and distribute each input signal to all two modules. After the control’s modules double exchange their input values, and vote out any erroneous values, the Application Software Redundancy Manager then compares each module’s voted result to select a value to be used within the application logic.
Optionally, each leg of an input channel can be tested and its calibration verified through the CCT program’s Service mode, by individually removing the other input leg.
An analog input signal is determined to be faulty when it is below its “Fail Low Value” setting, or above its “Fail High Value” setting. These failure level settings can be adjusted via the CCT program’s Service mode and are defaulted to values in engineering units which correspond to 2mA and 22mA respectively. If an input is determined to be failed, that input is removed from the control’s voting logic.