The table provides recommended DC test voltages for routine maintenance based on the AC rating of equipment:
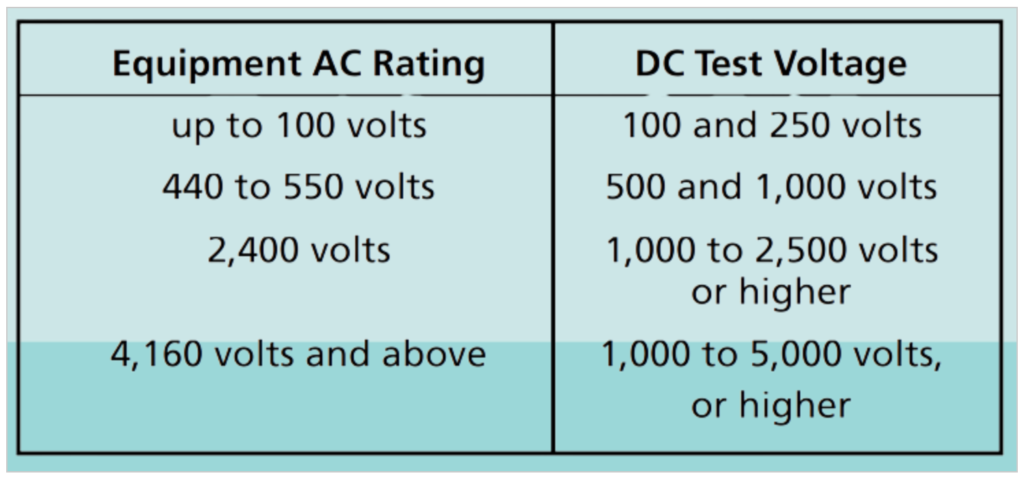
- For equipment with an AC rating up to 100 volts, DC test voltages of 100 and 250 volts are commonly used.
- For equipment rated between 440 and 550 volts, DC test voltages of 500 and 1,000 volts are recommended.
- Equipment with an AC rating of 2,400 volts should undergo DC testing with voltages ranging from 1,000 to 2,500 volts or higher.
- For equipment rated at 4,160 volts and above, DC test voltages of 1,000 to 5,000 volts or higher are advised.
Additionally, the proof test voltages for rotating equipment, which are typically higher than routine maintenance test voltages. These values are provided as follows:
- Factory AC Test: 2 times the nameplate rating (in VAC) plus 1,000 volts.
- DC Proof Test on Installation: 0.8 times the Factory AC Test value, multiplied by 1.6.
- DC Proof Test After Service: 0.6 times the Factory AC Test value, multiplied by 1.6.
As an example, for a motor with a nameplate rating of 2,400 VAC, the calculations would be as follows:
- Factory AC Test: 2 x 2,400 + 1,000 = 5,800 VAC
- Max. DC Test on Installation: 0.8 x 5,800 x 1.6 = 7,424 VDC
- Max. DC Test After Service: 0.6 x 5,800 x 1.6 = 5,568 VDC
These values are used to determine appropriate DC test voltages for proof testing of rotating equipment, ensuring that the equipment can safely handle the specified voltages during testing and operation.
Related Articles:
What is Good insulation?
What Makes Insulation Go Bad?
How Insulation Resistance is Measured.
How to Interpret Resistance Readings.
Factors Affecting Insulation Resistance Readings.
Types of Insulation Resistance Tests.
Test Voltage vs. Equipment Rating.
AC Testing vs. DC.
Use of DC Dielectric Test Set.
Tests During Drying out of Equipment.
Effect of Temperature on insulation Resistance.
Effects of humidity.
Preparation of Apparatus to test.
Safety Precautions.
Connections for testing insulation resistance of electrical equipment.
Additional Notes About using A Megger Insulation Tester.
Interpretation-Minimum Values.
Minimum Values for Insulation Resistance.
Tests Using Multi-Voltage Megger Insulation Testers.
Step-Voltage Method.
Use of a Guard Terminal.
Outdoor Oil Circuit Breaker.