Thisarticle is for Types of Conduits and Tubing, Rigid Metal Conduit, Intermediate Metal Conduit(IMC, Electrical Metallic Tubing EMT, PVC Conduit, used as raceways for electrical wiring in plants and process industry facilities.
Following definitions are to be used here
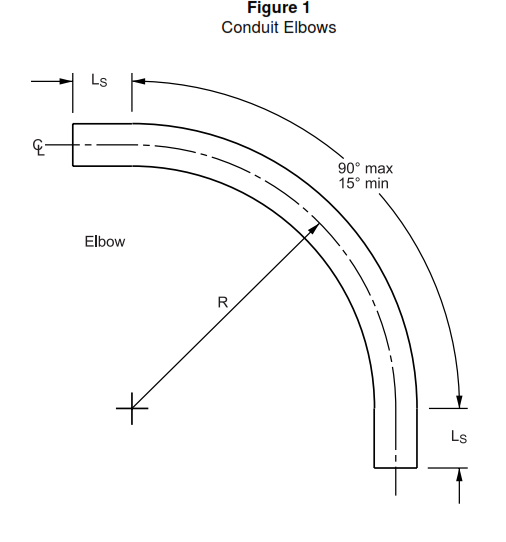
Elbow and Bend.
An elbow or bend is a curved section of metal conduit threaded on one end.
Nipple.
A nipple is a straight section of rigid conduit threaded on each end.
Threaded Coupling.
A threaded coupling for a metal conduit is an internally threaded cylinder for connecting two sections of metal conduit.
Types of Conduits and Tubing
Rigid Metal Conduit
- The rigid metal conduits covered by this section are rigid galvanized and PVC coated RGS steel conduits, and rigid aluminum conduits. The application of these conduit systems is for indoor and outdoor use in accordance with NFPA 70.
- Rigid galvanized or PVC coated metal conduit, nipples, elbows, and couplings shall be manufactured in accordance with either UL 6 or 6A. Each component of the conduit system shall be constructed of the same metal material as the conduit.
- For PVC-coated galvanized RGS conduit, the conduit shall be coated internally and externally. The PVC external coating nominal thickness on conduit shall be 1.02 mm (0.04 in) and the internal coating
nominal thickness shall be 0.18 mm (0.007 in) thick, as specified in NEMA RN 1. - For the purpose of understanding the dimensions of elbows, see Figure 1.
- The minimum dimensions for RGS conduit elbows shall be as specified in UL 6, as shown in Table I
- The minimum dimensions for aluminium couplings shall be as specified in UL 6, as shown in Table II
- The minimum dimensions for aluminium conduit elbow shall be as specified in UL 6A, as shown in Table III.
- The minimum dimensions for RGS couplings shall be as specified in UL 6A, as shown in Table IV.
- The conduit shall have a circular cross section sufficiently accurate to allow the uniform cutting of threads as specified in UL 6 and 6A.
- Trade sizes for rigid metal conduit shall be as specified in Table V.
- The wall thickness, internal diameter and the external diameter of rigid metal conduit (RGS), shall be as specified in UL 6, as shown in Table V.
- The nominal wall thickness, internal diameter and the external diameter of rigid metal conduit, for example aluminum, shall be as specified in UL 6A, as shown in Table VI.
- The galvanized coating on RGS conduit shall be a minimum thickness of 0.02 mm (0.0008 in), in accordance with ANSI C80.1. The inside surface coating shall be free of burrs or other injurious defects.
Intermediate Metal Conduit IMC
- Intermediate metal conduit (IMC) is a thin walled rigid metal conduit, used as detailed in NFPA 70 Section 345.
- IMC conduit, nipples, elbows, and couplings shall be manufactured in accordance with UL 1242.
- Elbows shall not be sharper than 90° nor shallower than 15°. The minimum dimensions of elbows shall not be less than as specified in UL 1242, as shown in Table VII.
- The length of couplings shall be as specified in UL 1242, as shown in Table VIII.
- IMC conduit shall have a circular cross section sufficiently accurate to allow the uniform cutting of threads, as specified in UL 1242.
- The available trade sizes for IMC are as detailed in Table IX.
- The wall thickness, internal diameter and the external diameter of straight runs of IMC conduit shall be as specified in UL 1242, as shown in Table IX.
- The galvanized coating on the outside of steel conduit shall be a minimum thickness of 0.02 mm (0.0008 in), in accordance with ANSI C80.1.
Electrical Metallic Tubing EMT
- Electrical metallic tubing (EMT) is a thin walled metallic tubing, used as detailed in NFPA 70 Section 348. EMT conduit shall be constructed in accordance with UL 797.
- EMT shall be of steel, or aluminum-base alloy. The tubing shall be straight and shall have a circular cross-section. The walls shall be of uniform thickness through its full length.
- EMT conduit shall not be threaded. Sections of tubing shall be connected using sleeved couplings and fittings provided with set screws.
- The maximum length of EMT shall be as specified in UL 797, as shown in Table X.
- The nominal trade size, external diameter, internal diameter and the wall thickness in inches shall be as specified in UL 797, as shown in Table XI.
- The trade size, external diameter, internal diameter and the wall thickness shall be as specified in UL 797, as shown in Table XII.
- The nominal inner radius of bends shall be as specified in UL 797, as shown in Table XIII.
PVC Conduit
- PVC conduit is a rigid non-metallic conduit, used as detailed in NFPA 70 Section 347. PVC conduit shall be constructed in accordance with UL 651A.
- Limits on the wall thickness and outside diameter of PVC and PE conduit shall be as specified in UL 651A, and are shown in inches in Table XIV and in millimeters in Table XV.
- PVC Binding Properties
Properties of PVC coating for conduit shall be as specified in NEMA RN 1, as shown in Table XVI.
Conduit Inspection
Conduit shall be visually inspected to ensure that it is straight and not deformed. Conduit and fittings shall be visually inspected for surface defects, for example cracks, flakes, rough edges, and internal surface obstructions, which would cause damage to cable to be installed. Any conduit or fittings which are found to be not in conformance with the requirements of this specification shall be rejected and returned to the supplier at his expense.
Check all tables mentioned of this post in this attachment conduit tables
Conduit References
American National Standards Institute (ANSI)
C80.1 Rigid Steel Conduit, Zinc Coated
American Society for Testing and Material(ASTM)
D 149 Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and Dielectric Strength of Solid Electrical Insulating
Materials at Commercial Power Frequencies
D 638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastic
D 1790 Test Method for Brittleness Temperature of Plastic Sheeting by Impact
D 2240 Test Method for Rubber Property – Durometer Hardness
National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA)
RN1 Polyvinyl-Chlorine (PVC) Externally Coated Galvanized RGS Conduit and Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC)
National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
70 National Electrical Code
Underwriters’ Laboratory (UL)
6 Electrical Rigid Metal Conduit-Steel
6A Electrical Rigid Metal Conduit-Aluminum, Bronze, and Stainless
651A Types EB and A Rigid PVC Conduit and HDPE Conduit
797 Electrical Metallic Tubing
1242 Intermediate Metal Conduit