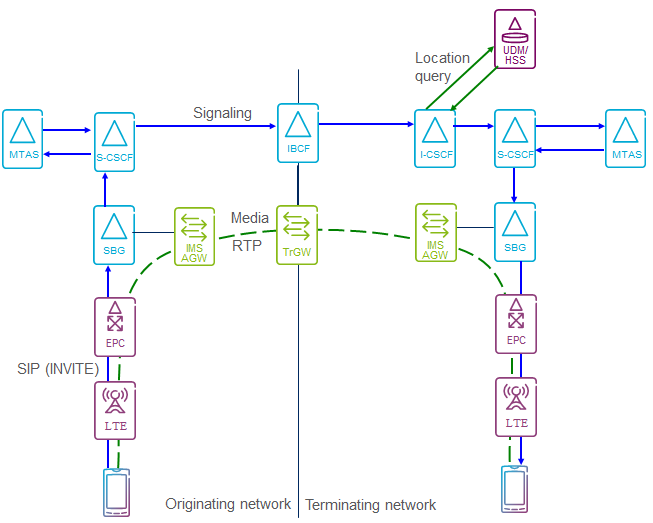
A VoLTE to VoLTE call occurs when both users are in LTE coverage supporting VoLTE. This process includes call setup on both originating and terminating ends, involving LTE, EPC, IMS, and UDM domains. For unexpected call drops, refer to the VoLTE Call Drop case.
The following logic applies for an originating call.
Media issues like one-way speech or poor quality are addressed in future releases.
- UE Connection Activation: UE sends an RRC Connection Establishment request to LTE, which triggers NAS Service Request to EPS. This initiates internal signaling for call setup with IMS.
- SIP Communication: The UE sends a SIP INVITE to IMS (via SBG/P-CSCF), which is forwarded to CSCF and MTAS. Communication between IMS and the UE follows.
- Bearer Establishment: Assuming SIP Precondition and QoS are applied, a bearer is established between the EPS domain (MME) and the UE.
- Final SIP Signaling: After bearer establishment, the last part of SIP signaling occurs between UE and IMS.
The troubleshooting flow aligns with the overall VoLTE-to-VoLTE call establishment flow.
Health Check
When VoLTE-to-VoLTE call establishment fails, a comprehensive health check is required for LTE, EPC, IMS, and UDM. Based on the symptoms, such as the number of affected users, dependency on access, and LTE data status, further analysis should target the suspected domain. Below are examples assuming no handset issues:
- If users face both VoLTE and LTE data failures, focus the health check on the originating RAN and EPC.
- For specific users with VoLTE call failures, verify provisioning and status in EPC (SAPC), UDM (HSS, IPWorks), and IMS (SBG, MTAS).
- For failures in specific areas, investigate terminating RAN/EPC for incoming calls and originating RAN/EPC for outgoing ones.
- For area-independent failures in receiving calls, check terminating IMS and UDM.
- For area-independent failures in making calls, check originating IMS and UDM.
E2E Trace Analysis
Once the E2E trace at the subscriber level is collected, compare the call flow with the acceptance test specifications for this VoLTE deployment. Other reference traces can also be found on the provided wiki. Keep in mind that the E2E trace may vary due to site-specific designs, affecting call flow, message content, and header values. For single-user trace analysis within a domain, refer to the “Troubleshooting Workflow” section in the relevant Domain Troubleshooting Guides.
Performance Indicators
At the E2E VoLTE level, this abstract KPI is defined, covering E2E VoLTE originating and terminating voice calls. However, it does not focus on long call setup time or supplementary services. A successful call setup means that the INVITE to 180 Ringing is executed correctly, and 180 Ringing is received by the UE. The call setup success KPI helps identify problems with VoLTE to VoLTE call establishment.
The formula for call setup success is:
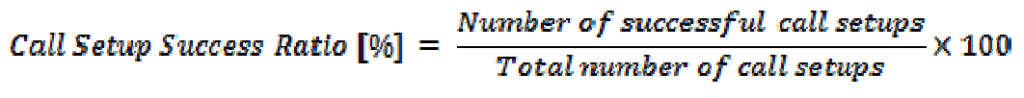
Depending on KPI assessment, issues may exist in the Handset, LTE RAN, EPC, IMS, UDM, or a combination. A good KPI baseline or reference is needed to diagnose the faulty domain. VoLTE call establishment issues are typically found in IMS, EPC, or RAN. IMS is prioritized in troubleshooting because its KPIs are more direct, allowing quicker identification of issues. EPC and RAN KPIs are often undifferentiated, making it harder to pinpoint problems. Troubleshooting starts from the IMS domain, followed by UDM, Packet Core, and RAN.
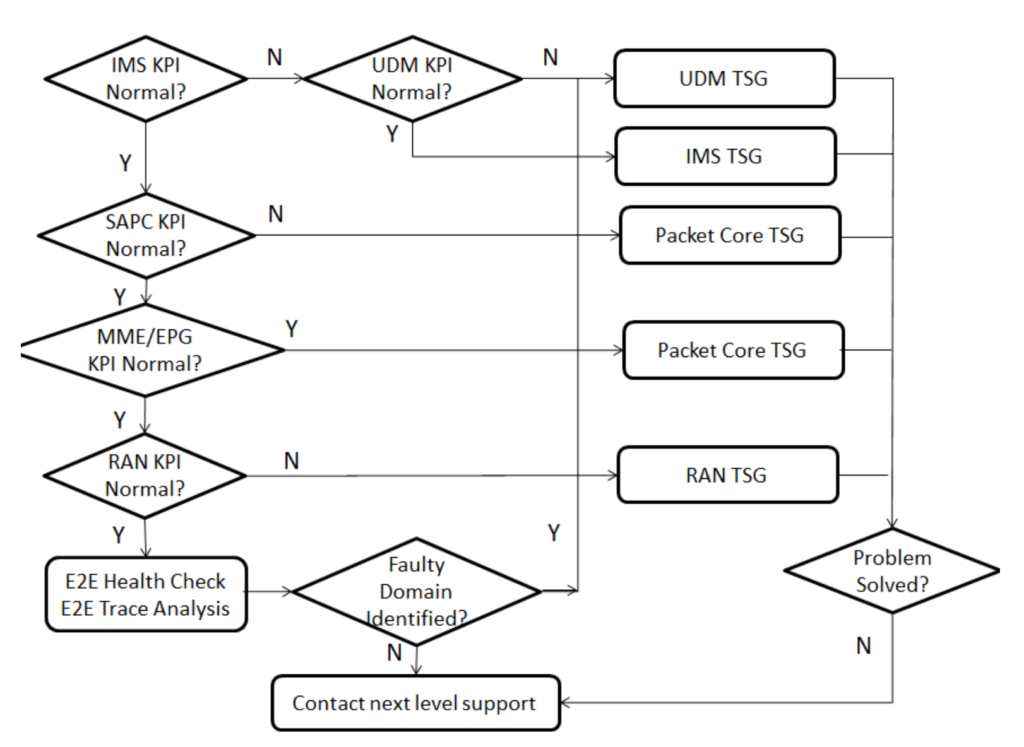
Step1: Check KPIs in IMS
- IMS CSCF Originating Session Set-up Success Ratio.
- IMS CSCF Terminating Session Set-up Success Ratio.
- IMS MMTEL AS Originating Session Set-up Success Ratio.
- IMS MMTEL AS Terminating Session Set-up Success Ratio.
- IMS SBG Incoming Session Set-up Success Ratio.
- IMS SBG Outgoing Session Set-up Success Ratio.
If one or some of the KPIs indicate lower success rate, then the faulty domain is probably IMS. To further troubleshoot IMS, please follow IMS Troubleshooting Guide.
Especially when CSCF and MTAS KPI indicate lower success rate, it probably indicate fault in UDM. To further troubleshooting in UDM, please follow UDM Troubleshooting Guide. Otherwise if all IMS KPIs indicate normal values, the problem is probably before IMS. Continue with the Step 2 on KPIs in Packet Core.
Step2: Check KPIs in SAPC in EPC
SAPC is a key element in EPC which interact with IMS (SBG) during VoLTE call establishment. The KPIs below on SAPC need to be checked.
SAPC: Rx AAR Failure Ratio
SAPC: Gx RAR Failure Ratio.
The first KPI (Rx AAR Failure Ratio) keeps track of communication errors between SAPC and IMS. The second KPI (Gx RAR Failure Ratio) keeps track of communication errors between SAPC and EPG.
If any of these shows a high value there are probably connectivity problems in the network. To further troubleshoot packet core, please follow VoLTE Packet Core Troubleshooting Guide.
If all SAPC KPIs show normal values, continue with Step 3.
Step3: Check KPI in MME and EPG in EPC
Following KPI’s keep track of failures handling the dedicated bearers for the VoLTE call.
- MME: GBR Bearer Activation Failure Ratio.
- SGW: SGW Create Dedicated Bearer Failure Ratio.
- SGW: SGW Update Dedicated Bearer Failure Ratio.
- SGW: SGW S4/S11 Modify Bearer Failure Ratio.
- PGW: PGW S5 Update Dedicated Bearer Failure Ratio per APN.
- PGW PGW S5 Create Dedicated Bearer Failure Ratio.
- PGW: PGW S5 Modify Bearer Failure Ratio.
If any of these KPI’s shows a high value, please further troubleshoot in packet core, follow VoLTE Packet Core Troubleshooting Guide.
If following KPIs also show abnormal values, the failure would probably due to LTE RAN issue, please start Step 4 at the meantime.
- MME: Service Request Failure Ratio.
- MME: Paging Failure Ratio.
- SGW: Downlink S4/S5/S11 data notification ratio.
The first KPI (MME: Service Request Failure Ratio) indicates that the calling UE has issues connecting to the network. The other two KPIs (MME: Paging Failure Ratio, SGW: Downlink S4/S5/S11 data notification ratio) indicate issues for the network to locate and connect the called UE.
Step 4: Check KPI in LTE RAN
Added E-RAB Establishment Success Rate per QCI.
If this KPI is showing less than normal value, the problem is probably in LTE, then go to LTE Troubleshooting Guide.
Step 5: If the problem domain is not identified by KPI analysis, please further troubleshoot by E2E Health Check and E2E Trace Analysis, please follow Domain Troubleshooting Guide.
Step 6: If problem is not solved, please contact next level technical support.