Reduced voltage means a situation where the voltage supplied to an electrical device or system is intentionally decreased from its normal or rated value. This reduction in voltage can be achieved using various methods. It is often done for specific purposes such as starting electric motors, controlling power consumption, or protecting equipment.
Following is an example of Reduced voltage application which is reduced voltage starter or soft starter.
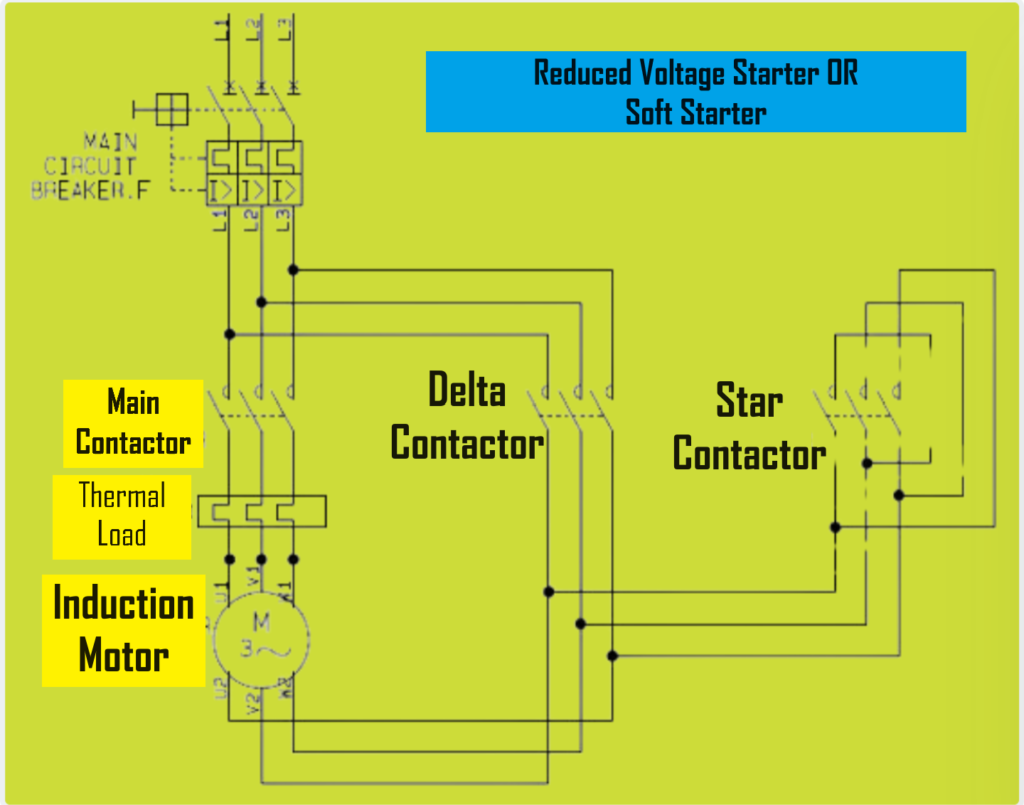
Reduced voltage starting is a common application where the voltage supplied to a motor during startup is intentionally reduced to limit the starting current and torque. This helps prevent mechanical stress on the motor and reduces the likelihood of voltage dips or disturbances in the electrical system. Reduced voltage starting methods include star-delta starters, autotransformer starters, and soft starters, each of which provides a controlled reduction in voltage during motor startup.
In some cases, reducing voltage may be necessary to control power consumption or to ensure compatibility with equipment that has specific voltage requirements. For example, voltage reduction may be used in lighting systems to dim or adjust the brightness of lamps, or in electronic devices to regulate power consumption and extend battery life.
It’s important to note that while reducing voltage can be beneficial for specific applications, it may also affect the performance or operation of electrical devices and systems. Careful consideration and proper engineering design are necessary to ensure that reduced voltage applications meet safety, reliability, and performance requirements.