In many cases, analog inputs use a special 250-ohm resistor to change a 4 to 20 mA current signal into a 1 to 5 V voltage signal. When it comes to 2 wire transmitter, the power for the loop can come from the control system itself (as shown in Figure 21) or from an external source (as shown in Figure 22).
What is 2-Wire Transmitter?
In process control systems, the quest for simplicity and efficiency has led to the evolution of technologies that redefine how industries operate. Among these innovations, 2 wire transmitter stand out for their ability to streamline wiring and enhance overall system simplicity. In this discussion, we delve into the fundamentals, operation, advantages, and applications of 2 wire transmitter.
2 Wire Transmitter Wiring Diagram:
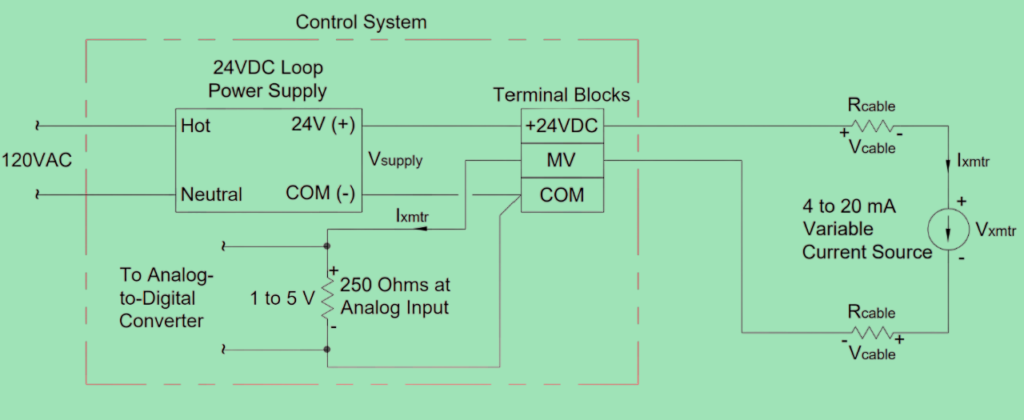
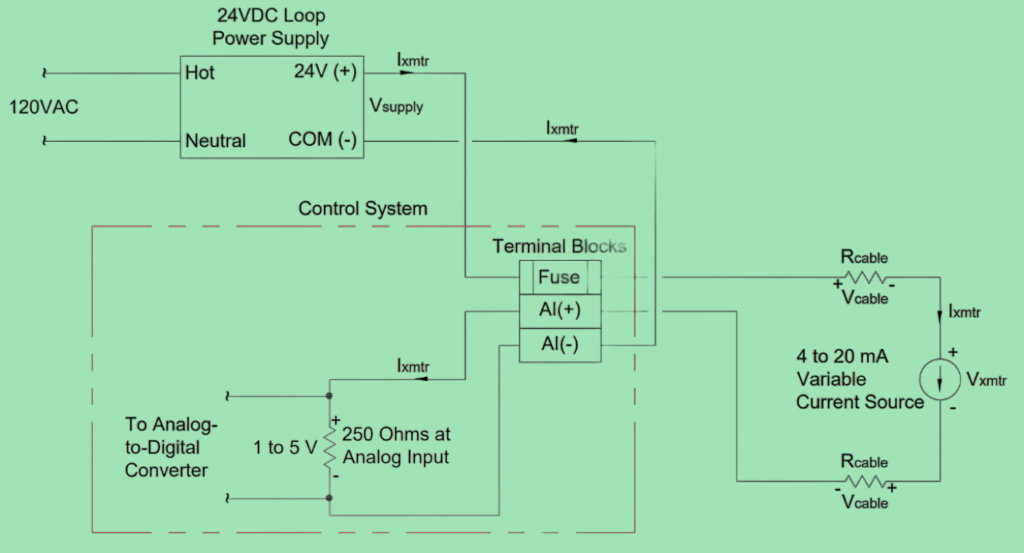
Fundamentals of 2 Wire Transmitter:
At the core of 2 wire transmitter is the ingenious integration of both power supply and signal transmission into a two-wire configuration. Unlike their multi-wire counterparts, 2-wire transmitters utilize a single pair of wires for both energizing the transmitter and conveying the crucial process signal. This unification of functions contributes significantly to the reduction of wiring complexity.
Working Principle
The operational principle of 2-wire transmitters revolves around the concept of loop power. In a 2-wire configuration, the same loop that carries the process signal also provides the necessary power to the transmitter. This is typically achieved by using a loop current, often ranging from 4 to 20 mA, which powers the transmitter while concurrently transmitting the desired signal.
The power required by the transmitter is harnessed from the voltage drop across the device within the loop. This innovative approach eliminates the need for a separate power wiring infrastructure, resulting in a simplified and cost-effective solution.
Advantages of 2-Wire Transmitters:
- Simplified Wiring: The primary advantage is the significant reduction in wiring complexity. With only two conductors needed, the installation process becomes more straightforward, minimizing the likelihood of errors during setup.
- Cost-Effective Installation: The streamlined wiring not only simplifies the installation process but also contributes to cost savings, making 2 wire transmitters an economically viable choice for various applications.
- Suitability for Short to Moderate Distances: While ideal for applications with shorter to moderate distances between the control system and the transmitter, 2-wire configurations may pose challenges for longer-distance installations.
Considerations:
- Voltage Drop: Engineers must consider the potential voltage drop along the loop, especially in longer-distance installations, to ensure the effectiveness of 2 wire transmitters.
- Power Limitations: Certain types of transmitters may have specific power requirements, and the available power from the loop must be sufficient to meet these needs.
- Common Ground: The shared conductors for power and signal result in a common ground. Engineers need to account for this shared ground in system design to prevent interference issues.
Applications of 2-Wire Transmitters:
- Industrial Monitoring and Control: 2 wire transmitters find extensive use in industrial settings for monitoring and controlling various processes.
- Situations Prioritizing Wiring Simplicity: They are particularly suitable for situations where wiring simplicity is a priority, and the benefits of reduced complexity outweigh potential limitations.
- Short to Moderate-Distance Installations: Ideal for applications where the distance between the control system and the transmitter falls within the suitable range for 2-wire configurations.
In conclusion, 2 wire transmitters represent a paradigm shift in process control by embracing simplicity without compromising functionality. Their streamlined design, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for specific distance ranges make them an invaluable component in industrial automation. As industries continue to evolve, the role of 2 wire transmitters is poised to expand, offering enhanced solutions for optimizing process control systems.
Read Also:
What is 3-Wire Transmitter? Wiring Diagram, Working Principle, Connection to PLC
What is 4-Wire Transmitter? Wiring Diagram, Working Principle, Connection to PLC