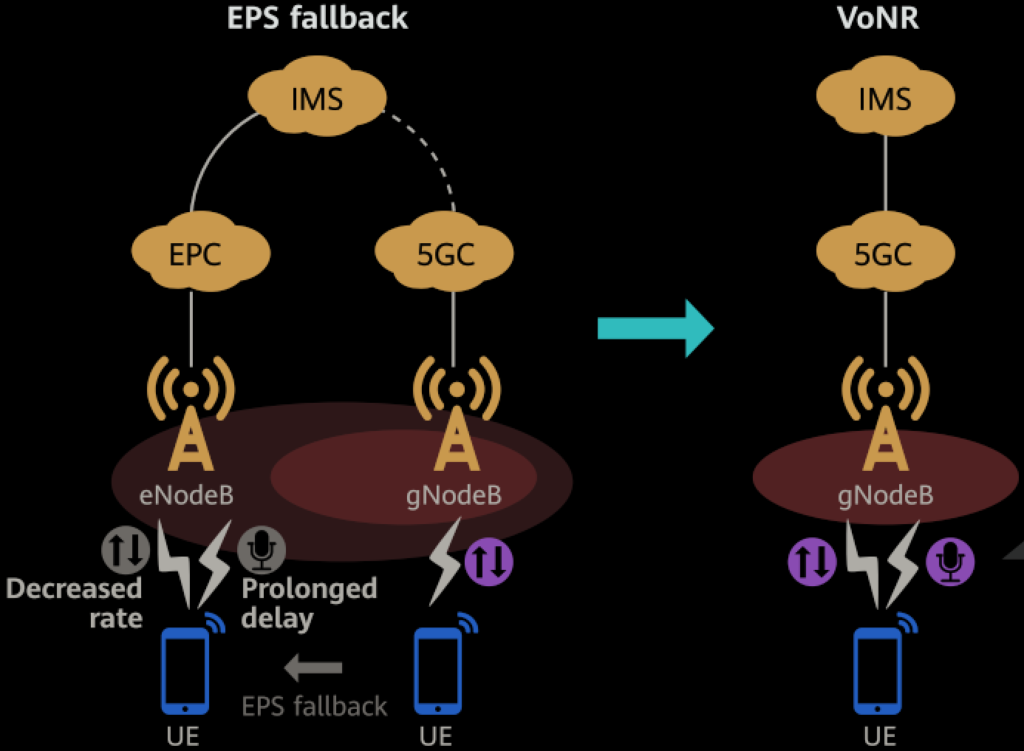
Voice services are a core component of wireless communication networks. During the initial deployment phase of 5G networks, both the coverage of 5G base stations and the availability of 5G-capable devices are limited. In Standalone (SA) 5G networks, voice and data services often fall back from the 5G New Radio (NR) network to the LTE network using a method called EPS fallback. However, this fallback process increases the delay in setting up voice calls and reduces data service speeds.
As 5G networks become more widely deployed, the Voice over New Radio (VoNR) solution can be implemented to address these issues. VoNR allows 5G devices to perform voice services directly on the 5G NR network, eliminating the need to fall back to LTE. This results in improved voice quality and higher data service rates.
What is VoNR?
VoNR enables 5G devices to handle voice calls directly over the 5G NR network. With VoNR, IP-based dedicated voice bearers are established between the devices and the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) on the 5G network.
VoNR Call Flow Process:
- RRC Connection Setup: The Radio Resource Control (RRC) connections are established between the calling and called UEs (User Equipment) and their serving gNodeBs (5G base stations).
- QoS Flow Setup for SIP Signaling: The 5G Core (5GC) sets up Quality of Service (QoS) flows with a QoS Identifier (5QI) of 5 to handle SIP signaling between the UEs and the IMS. The gNodeBs set up the corresponding Data Radio Bearers (DRBs).
- SIP Negotiation: The UEs and the IMS negotiate the codec scheme, IP address, port number, and other relevant call information for the voice service.
- QoS Flow Setup for RTP/RTCP: The 5GC then establishes QoS flows with a 5QI of 1 to carry the Real-Time Protocol (RTP) and Real-Time Control Protocol (RTCP) data flows for the voice call. The gNodeBs set up the corresponding DRBs.
- Release of QoS Flows: Once the call ends, the QoS flows with a 5QI of 1 are released, and the gNodeBs release the corresponding DRBs.
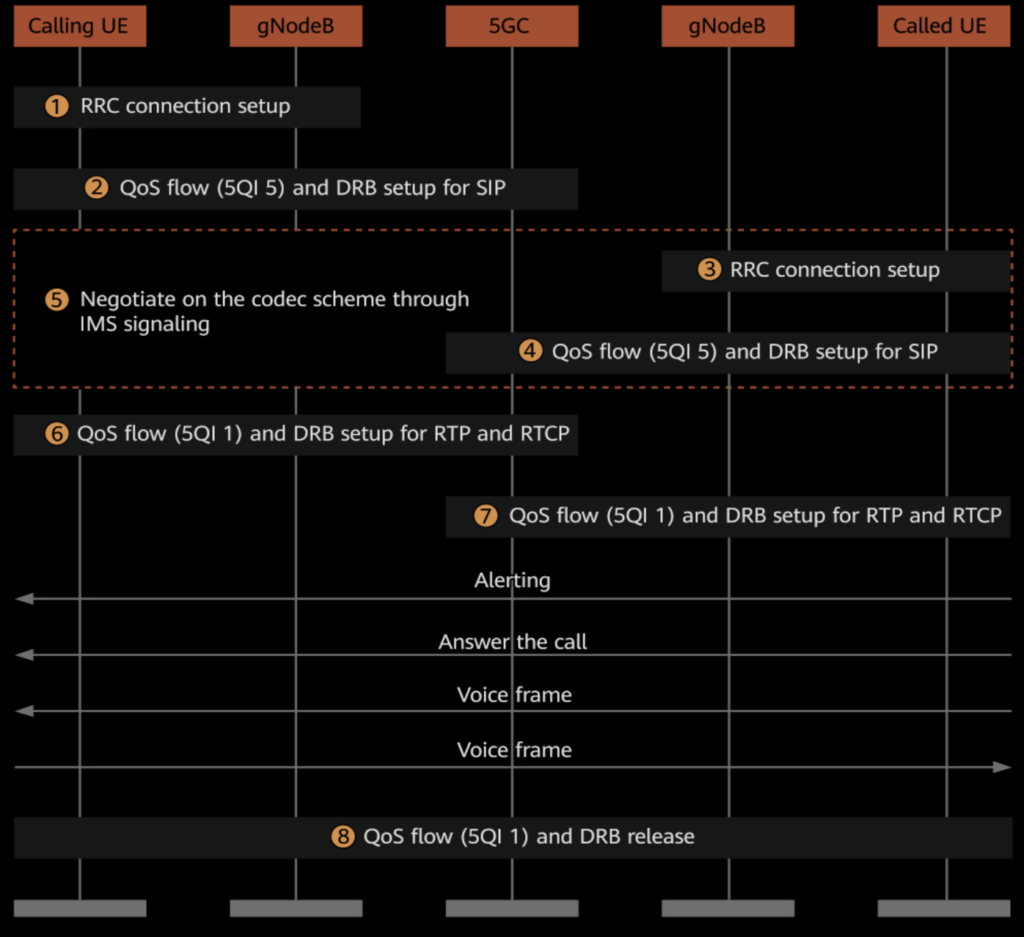
Voice bearers with a 5QI of 1 are released after the call ends.
This process allows for efficient and high-quality voice services directly over the 5G network, enhancing both voice call quality and overall data throughput in the network.
VoNR benefits.
- The voice quality MOS increases by approximately 0.1 to 0.3 points.
- The uplink coverage improves by approximately 0.1 to 1.5 dB.
VoNR Features and Functionalities.
Below of key technologies features and functionalities related to Voice over New Radio (VoNR) in 5G networks:
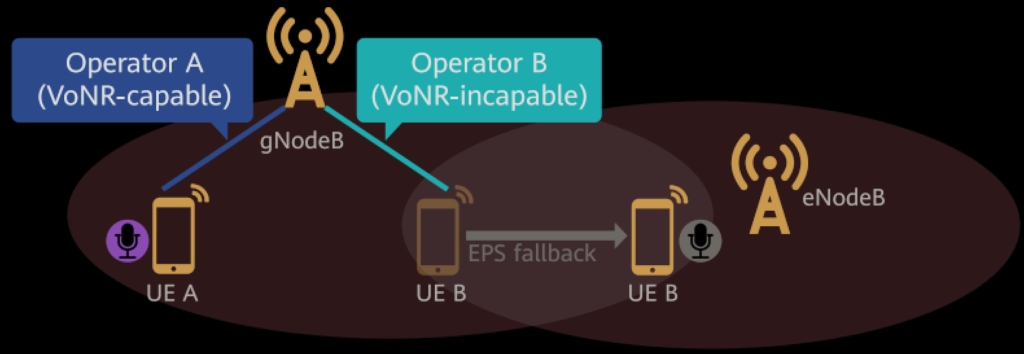
1. RAN Sharing with VoNR
RAN Sharing with Common Carrier: Multiple operators can share a gNodeB (5G base station) and its served cells. In this setup, VoNR can be configured separately for each operator within the shared cell.
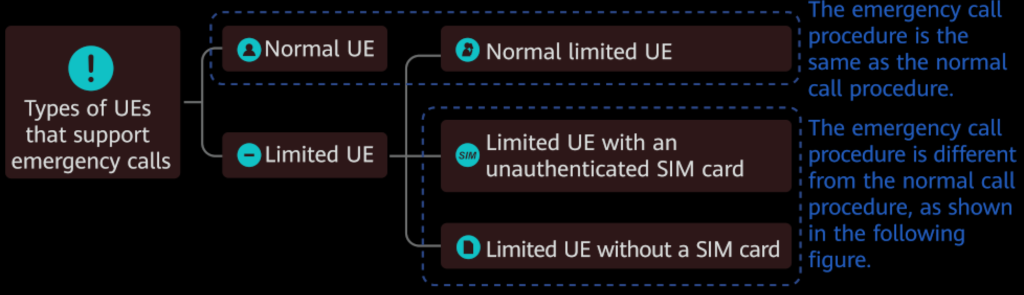
2. VoNR Emergency Call
Emergency Call Functionality: VoNR allows subscribers to make emergency calls during situations like terrorism, medical emergencies, fires, or natural disasters.

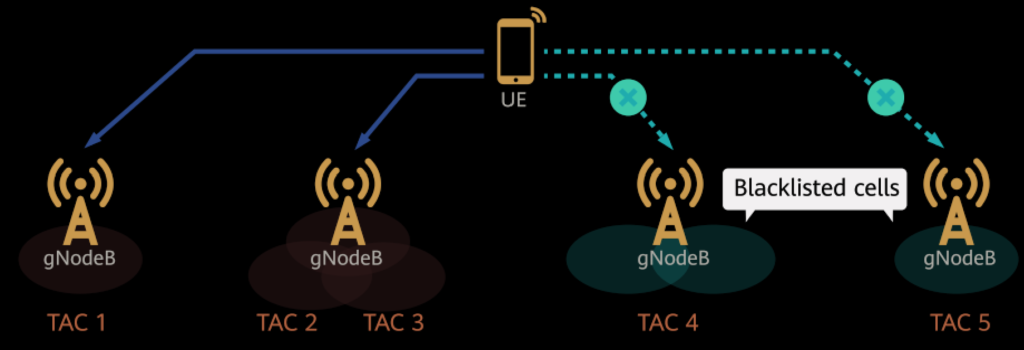
3. VoNR Blacklist
Blacklist Functionality: The gNodeB can blacklist cells identified by Tracking Area Codes (TACs) that do not support VoNR. This prevents devices from being handed over to cells where VoNR services would fail, ensuring stable voice services.
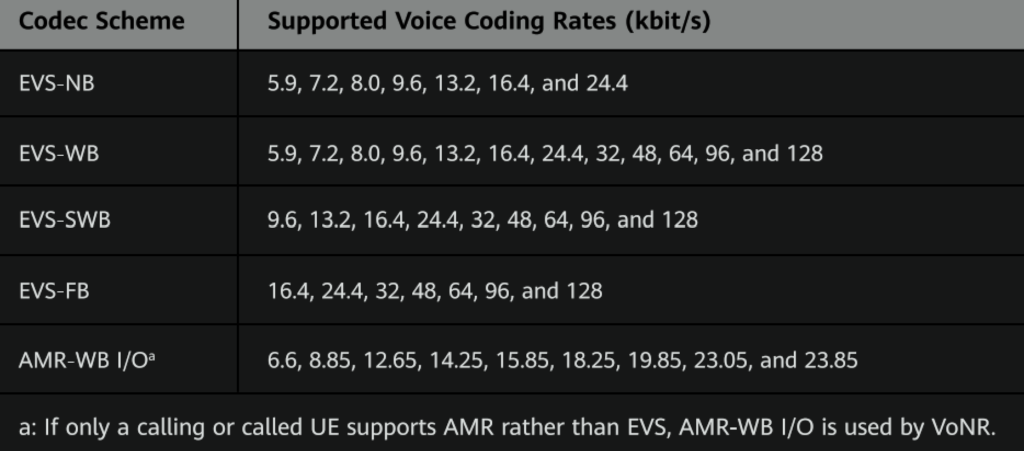
4. Enhanced Voice Services (EVS) Codec
EVS Codec: The EVS codec provides higher voice quality compared to other codecs like AMR-WB, even at similar coding rates. This codec comes in various formats, such as EVS-NB, EVS-WB, EVS-SWB, EVS-FB, and AMR-WB 1/0.
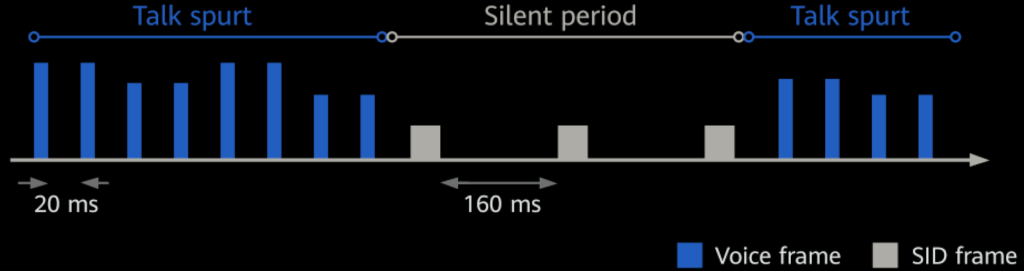
Voice services have two states:
Talk spurts: During talk spurts, UEs transmit voice frames in the uplink or receive voice frames in the downlink. Voice frames are transmitted at 20 ms intervals, and their sizes are determined by the voice coding rate.
Silent periods: During silent periods, UEs transmit SID frames in the uplink or receive SID frames in the downlink. SID frames are transmitted at 160 ms intervals. For the EVS codec, the SID frame sizes are always 64 bits.
5. MAC CE-Based Rate Adjustment
Rate Adjustment Functionality: The gNodeB can suggest optimal air interface rates to UEs (User Equipment) using a MAC Control Element (CE), helping them adjust their rates for better performance.
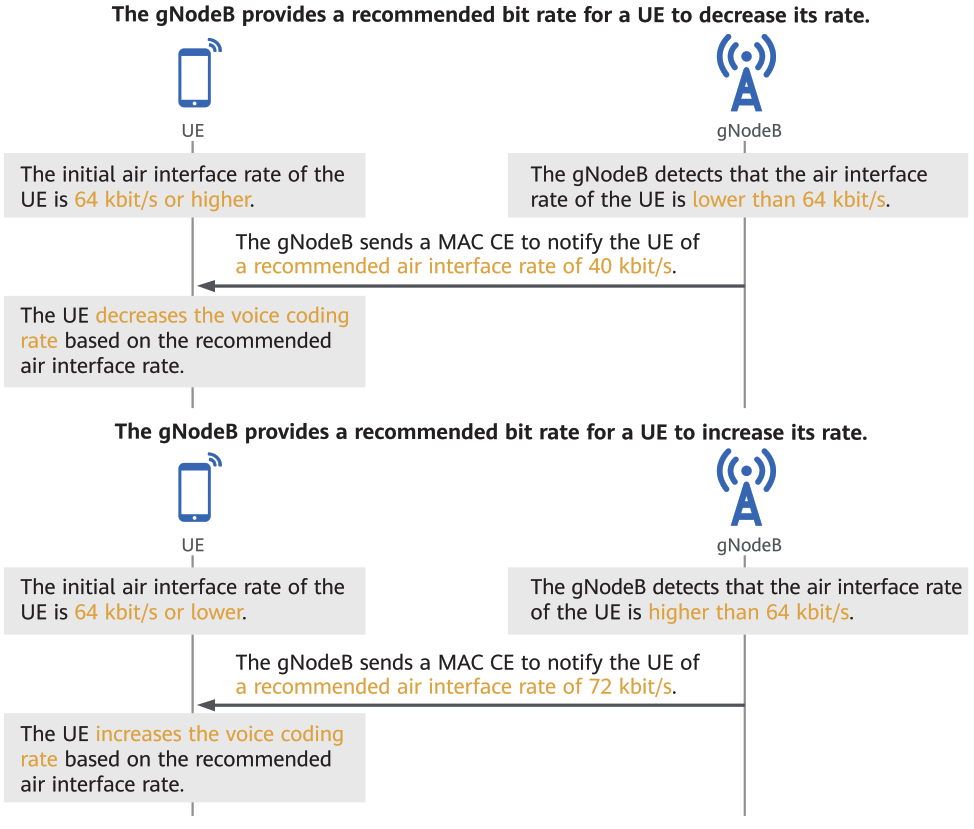
When the uplink air interface capability of a UE is improved, the UE proactively queries a recommended rate from the gNodeB to achieve better rate adjustment.
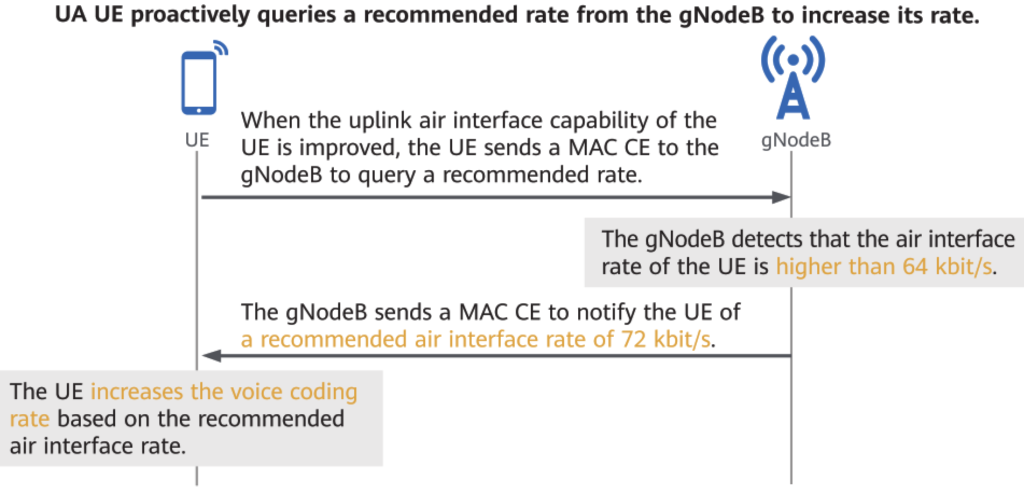
6. Uplink Coverage Optimization
HARQ Retransmissions: To improve uplink success in weak coverage areas, the maximum number of Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest (HARQ) retransmissions is increased from four to eight, specifically in NR TDD (Time Division Duplex) scenarios.
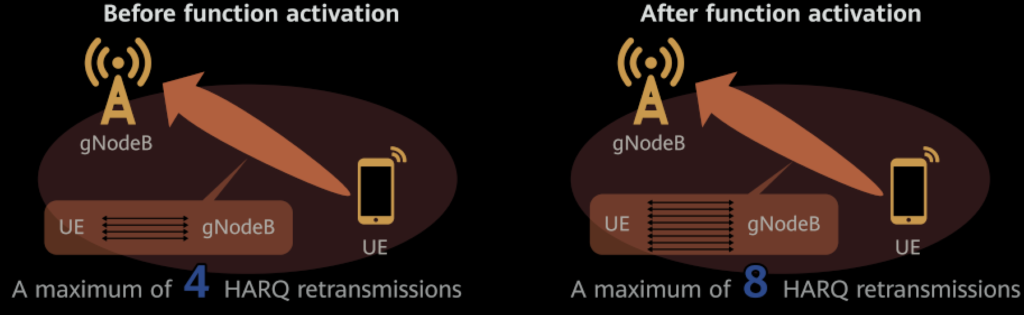
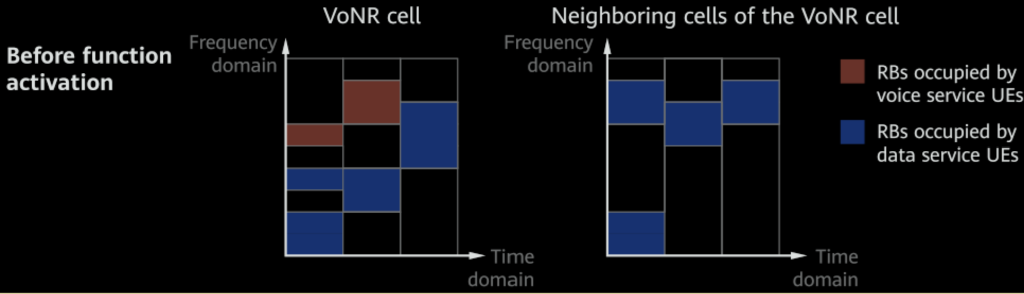
7. Uplink RB Reservation
Resource Block (RB) Reservation: RBs can be reserved for voice services in the uplink, giving them priority over other services. If reserved RBs are full, voice services can use non-reserved RBs. Non-voice services cannot use reserved RBs.
After function activation:
The same RBs must be reserved in the VoNR cell and its neighboring cells.
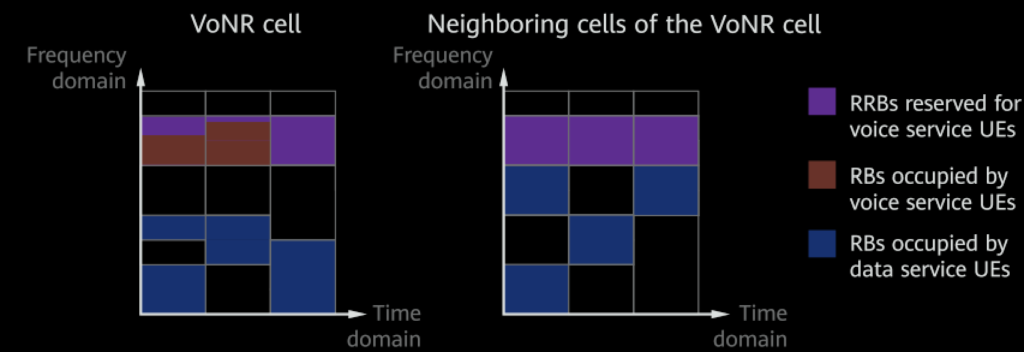
This function allows voice services to preferentially occupy reserved RB resources.
This function allows voice services and data services to occupy different resources, reducing the interference of data services on voice services.
8. Robust Header Compression (ROHC)
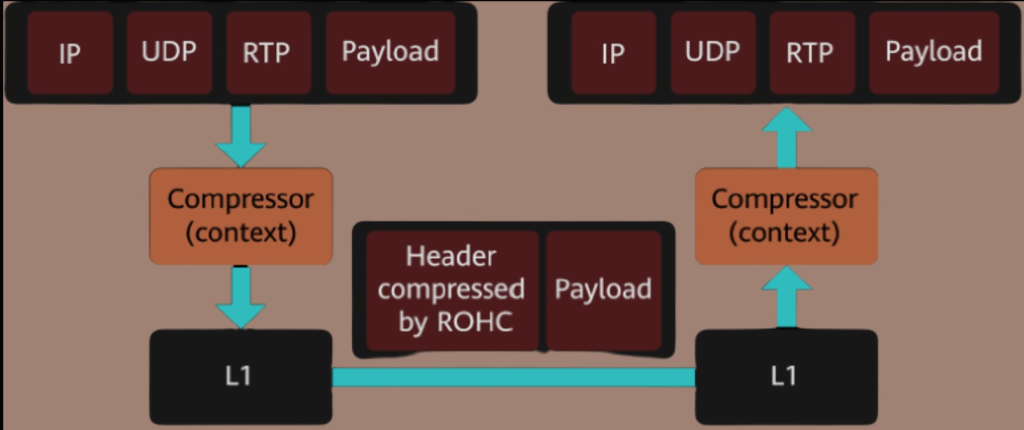
ROHC: This function reduces header overhead in voice packets, which decreases bit error rates (BERs), shortens delays, and conserves radio resources. It is particularly useful for IPv4 and IPv6 headers, and requires UEs to support ROHC.
Data streams that comply with different network layer protocols use various header compression schemes defined by profiles.

After this function is enabled, the gNodeB determines the common profiles supported by the UE before negotiating the maximum number of ROHC contexts with the UE. After the negotiation succeeds, the ROHC procedure starts.
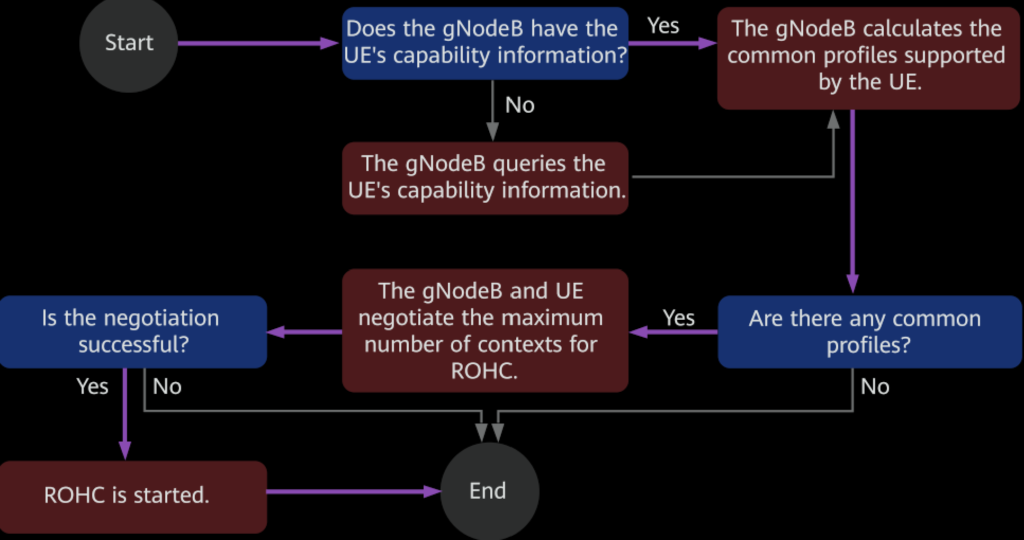
After ROHC is started, the compressor at the transmit end compresses the headers of voice packets, and the decompresser at the receive end restores them. The following figure shows the ROHC process that uses profile 0x0001.
These functionalities ensure that VoNR services are optimized, reliable, and of high quality across different network scenarios and configurations.
Engineering Deployment.
1. Hardware Requirements
- Base Stations:
- Models: 3900 series and 5900 series base stations, including the DBS3900 and DBS5900 LampSite, all using the BBU3910.
- Boards:
- All NR-capable (New Radio-capable) main control boards and baseband processing units.
- RF Modules:
- Not applicable in this context.
2. Networking Setup
- Standalone (SA) networking is used.
- The delay between the gNodeB (5G base station) and the SGC (Session Gateway Controller) must be less than 20 ms.
3. License
Currently, no licenses are required for trial functions.
4. Software
- No prerequisite or mutually exclusive functions.
- User Equipment (UEs) must support VoNR.
- Operators must have deployed IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem), and the SGC must support IMS-based voice services.
5. Activation
To enable VoNR, the following functions need to be activated:
- Cell-Level VoNR
- MAC CE-Based Rate Adjustment
- Operator-Level VoNR
- Uplink Coverage Optimization (based on increased number of retransmissions)
- VoNR Emergency Call
- VoNR Blacklist
- Uplink RB Reservation
- Robust Header Compression (ROHC)
These components and settings ensure that the network is properly configured to support VoNR, providing high-quality voice services directly over 5G networks.