ADSB stands for Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast. Do you know, what is ADSB?
ADS-B, or Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast, is a surveillance technology used in aviation that enables aircraft to broadcast their identity, position, altitude, velocity, and other information to other aircraft and ground stations. It relies on GPS technology to determine the aircraft’s precise position and then broadcasts this information at regular intervals.
What is ADSB?
Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) is a surveillance technology used for tracking aircraft, which is being developed to potentially replace radar as the primary surveillance system.
ADS-B Out and ADS-B In
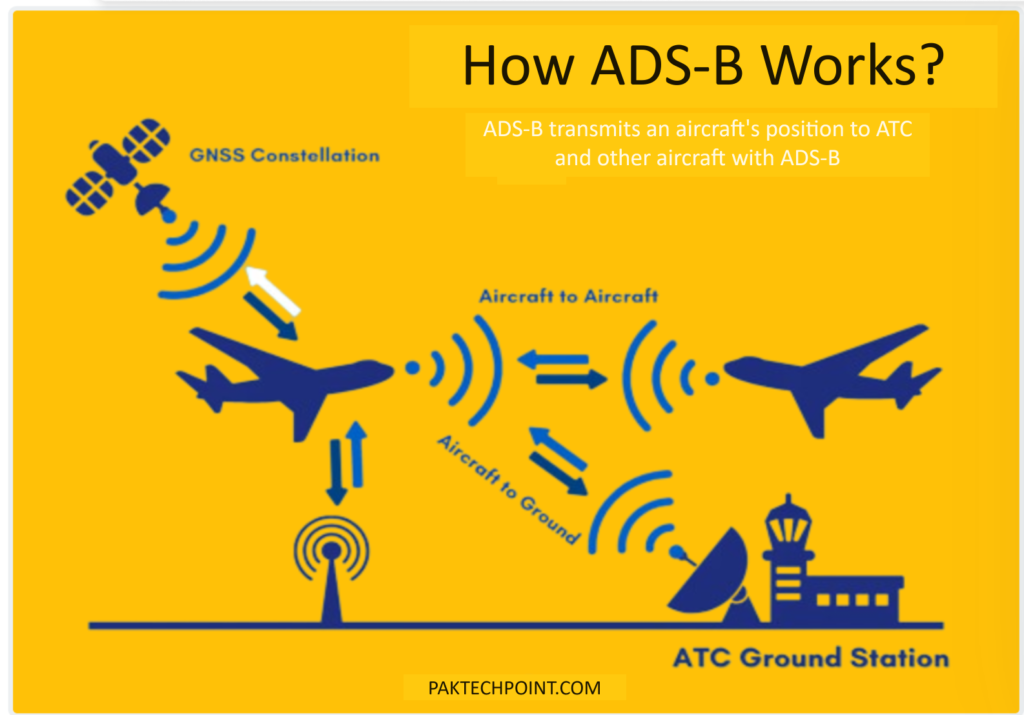
ADS-B technology comprises two distinct services: ADS-B Out and ADS-B In.
ADS-B Out involves an aircraft periodically broadcasting information, including its identification code, position, course, and velocity, through an onboard transmitter. This broadcasted information is then received by ground stations or other aircraft equipped with ADS-B receivers.
On the other hand, ADS-B In refers to the reception of traffic information, flight information, weather data, and other ADS-B data by aircraft. This allows pilots to receive direct communication from nearby aircraft, enhancing their situational awareness.
The ADS-B system relies on two main components: a satellite navigation system, such as GPS (Global Positioning System), and a datalink, typically an ADS-B unit installed onboard the aircraft. The GPS provides accurate position information, while the ADS-B unit transmits and receives data via radio waves.
By utilizing ADS-B technology, air traffic controllers can more precisely track and separate aircraft, thanks to the improved accuracy and timing of the information provided. Additionally, pilots benefit from increased situational awareness, as they receive real-time updates on nearby traffic, weather conditions, and other relevant data. Overall, ADS-B has the potential to enhance both airspace management and flight safety.
Benefits
The potential benefits of ADSB technology are significant and varied:
- Improved situational awareness: Pilots equipped with ADS-B technology have access to real-time information on other aircraft operating in the airspace, as well as detailed weather updates. This allows them to make more informed decisions and enhances safety during flight. Additionally, pilots can receive updates on temporary flight restrictions and runway closures, helping them plan their routes more effectively.
- Enhanced visibility: Air traffic controllers can more accurately monitor the position of aircraft equipped with ADSB technology. This improved surveillance enables controllers to identify and avoid conflicts between aircraft more efficiently. Furthermore, ADSB provides better coverage in areas with limited radar coverage, increasing overall airspace visibility.
- Environmental impact reduction: ADSB facilitates more efficient flight trajectories, leading to reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions. By optimizing flight paths and reducing unnecessary deviations, ADSB contributes to environmental sustainability in aviation.
- Increased safety: The enhanced situational awareness provided by ADS-B helps prevent mid-air collisions and other safety incidents. Pilots can better anticipate and respond to potential hazards, while air traffic controllers can provide more precise guidance and instructions to pilots.
- Capacity and efficiency improvements: ADSB enables various operational enhancements, such as visual approaches, closely spaced parallel approaches, and reduced spacing on final approach. By streamlining air traffic management processes and enabling more flexible routing options, ADS-B helps increase airspace capacity and optimize the efficiency of air traffic services.
Overall, the adoption of ADS-B technology offers multifaceted benefits for aviation stakeholders, ranging from improved safety and efficiency to environmental sustainability and operational flexibility.
Challenges
Indeed, while many airliners have already adopted ADS-B technology, its widespread implementation across all aircraft, including regional ones, is still pending due to the high cost of equipment. As a result, ADS-B cannot yet serve as the primary surveillance system due to its limited coverage. However, there are initiatives in both Europe and the US to encourage the installation of ADS-B on all aircraft by 2020, aiming to enhance airspace surveillance and safety.
Another challenge with ADSB is the reliance on GPS, which currently serves as the main satellite navigation system. GPS’s low integrity poses a concern for the accuracy and reliability of ADS-B data. To address this issue, the implementation of GNSS-2 (the next generation of Global Navigation Satellite System) is planned, which is expected to provide higher integrity and reliability, thereby improving the performance of ADS-B technology. This transition to GNSS-2 will help overcome the limitations associated with GPS and further enhance the effectiveness of ADS-B as a surveillance system in aviation.