CAS Tracker is a system used for monitoring and tracking aircraft equipped with Collision Avoidance Systems (CAS). It allows operators to visualize the position, trajectory, and status of aircraft equipped with collision avoidance technology in real-time. The CAS Tracker system collects data from aircraft transponders, which transmit information such as identification, altitude, speed, and position. This data is then processed and displayed on a tracking interface, providing operators with a comprehensive view of the airspace and facilitating the management of air traffic to prevent collisions and ensure safe operations. CAS Tracker is an essential tool for air traffic control, aviation authorities, and aircraft operators to enhance situational awareness and maintain the safety of airspace.
CAS Tracker Working Principle
The CAS Tracker function within the Collision Avoidance System (CAS) utilizes information such as range, altitude, and bearing received from nearby aircraft through the Surveillance function. This data allows CAS to establish and maintain a track on each aircraft in the vicinity. By processing successive range reports, CAS computes the range rate of each aircraft. Altitude information is used to estimate the vertical speed of altitude-reporting aircraft, which can be provided in increments of either 25 or 100 feet.
The CAS tracking function is capable of monitoring aircraft with vertical rates of up to 10,000 feet per minute (fpm). It utilizes the tracked information to determine the time to Closest Point of Approach (CPA) and the altitude of each aircraft at CPA.
Additionally, CAS incorporates data from its own aircraft’s pressure altitude to determine its altitude, vertical speed, and the relative altitude of nearby aircraft. The CAS logic prioritizes altitude data from its own aircraft, selecting the source that provides the finest resolution. Own aircraft data can be provided in either fine altitude reports with quantization less than 10-foot increments, or coarse altitude reports with quantization up to 100-foot increments.
The outputs generated by the CAS tracking algorithm, including range, range rate, relative altitude, and vertical rate, are then utilized by the Traffic Advisory and Threat Detection logic to assess whether a Traffic Advisory (TA) or Resolution Advisory (RA) is necessary.
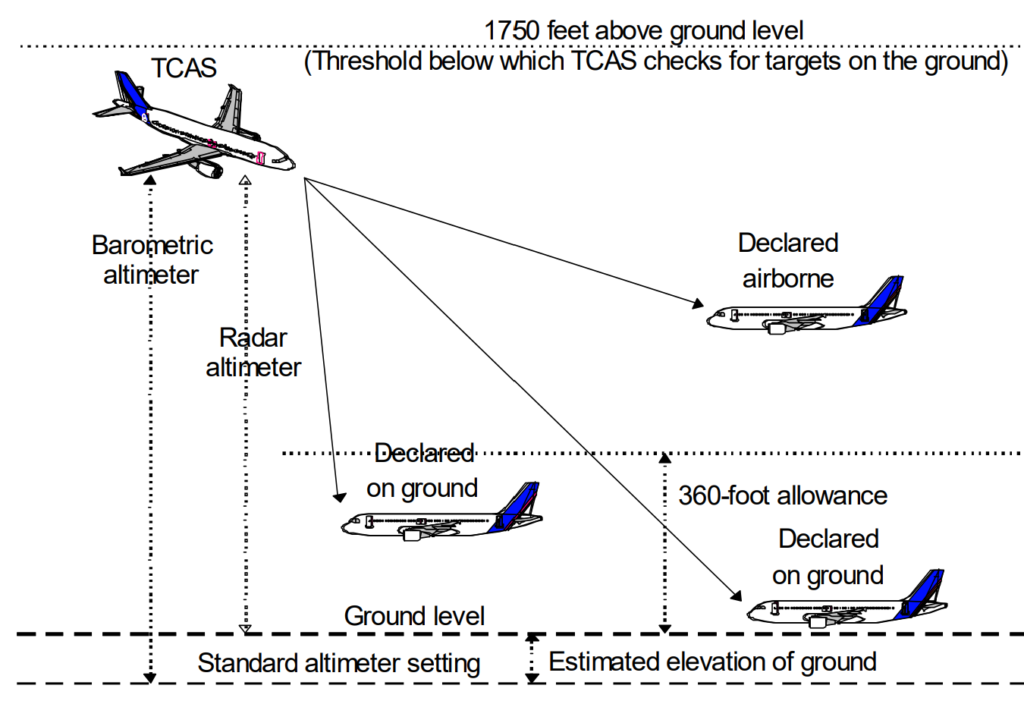
The CAS tracker incorporates a ground estimation logic that utilizes the disparity between its own aircraft’s pressure altitude and radar altitude to approximate the elevation of the ground above mean sea level. This functionality is activated when the own aircraft’s altitude is below 1750 feet Above Ground Level (AGL).
Using this estimated ground level, the CAS tracker subtracts it from the pressure altitude received from nearby Mode C-equipped aircraft. This calculation allows CAS to determine the approximate altitude of each nearby aircraft above the ground. If the difference between the two altitudes is less than 360 feet, TCAS interprets the reporting aircraft as being on the ground. In such cases, TCAS suppresses the generation of advisories against these aircraft to avoid unnecessary alerts.
This methodology is visually represented in Figure 16. For Mode S-equipped aircraft, the on-the-ground status bit contained in either the squitter or transponder reply is utilized to determine if the aircraft is considered to be on the ground.