A digital communications network refers to a system that allows the exchange of digital information between various devices or nodes. These networks play a crucial role in connecting people, computers, and other devices, enabling them to communicate, share data, and collaborate. Digital communication networks can take various forms, and they can be classified based on their scale, purpose, and the technologies they employ. Here are some key concepts related to digital communications networks:
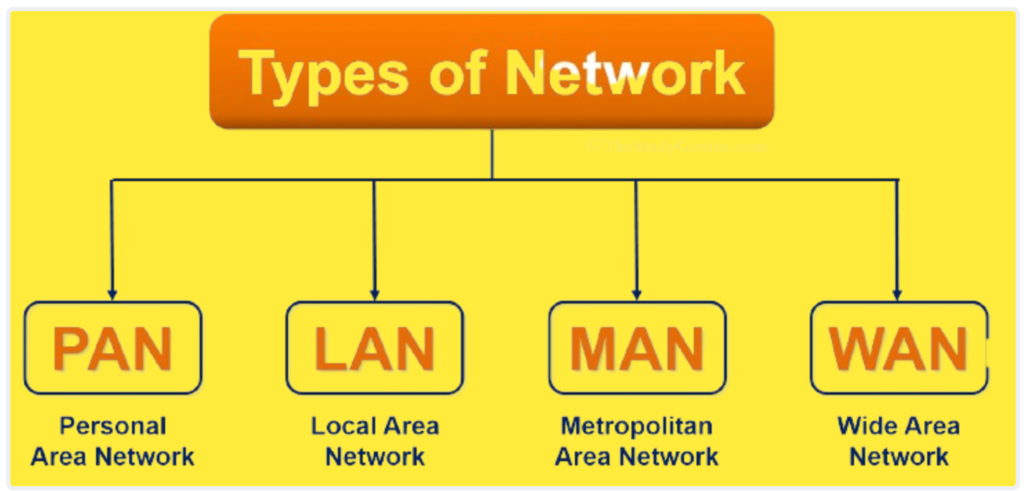
Types of Digital Communication Networks:
- Local Area Network (LAN): A LAN is a network that typically spans a small geographic area, such as a single building or a campus. It enables the connection of computers and devices within this limited area.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): A WAN covers a larger geographic area and connects LANs over long distances. The internet itself can be considered a global WAN.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): A MAN falls between a LAN and WAN in terms of geographic coverage. It typically covers a city or a large campus.
- Personal Area Network (PAN): A PAN is a network for personal devices within the range of an individual person, typically involving connections like Bluetooth or Infrared.
Network Topologies:
- Bus Topology: Devices are connected to a central cable (bus). Data is transmitted along the bus, and devices can access the data they need.
- Star Topology: Devices are connected to a central hub or switch. All communication passes through the central hub.
- Ring Topology: Devices are connected in a circular fashion. Data travels in one direction, passing through each device in the ring.
- Mesh Topology: Devices are interconnected, providing multiple paths for data to travel. This topology offers redundancy and fault tolerance.
Protocols and Standards:
- Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP): The foundation of the internet, TCP/IP is a suite of protocols that governs the exchange of data between devices.
- Ethernet: A widely used LAN technology that defines wiring and signaling standards for the physical layer and the data-link layer of the OSI model.
- Wi-Fi: A set of protocols for wireless LANs based on the IEEE 802.11 standards.
- HTTP/HTTPS: Protocols used for web communication.
Digital Communication Technologies:
- Fiber Optic Communication: Uses optical fibers to transmit data as pulses of light. It offers high bandwidth and is resistant to electromagnetic interference.
- Wireless Communication: Involves the transmission of data without physical cables, utilizing technologies like radio waves, microwaves, or infrared.
- Satellite Communication: Uses satellites to relay signals over long distances.
Network Security:
- Firewalls: Protect networks by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic.
- Encryption: Secures data by converting it into a code that can only be deciphered by authorized parties.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): Provides a secure, encrypted connection over the internet.
Digital communication networks are foundational to the modern world, enabling the internet, telecommunications, and numerous applications across various industries. Their design and implementation are critical to ensuring reliable, efficient, and secure communication.