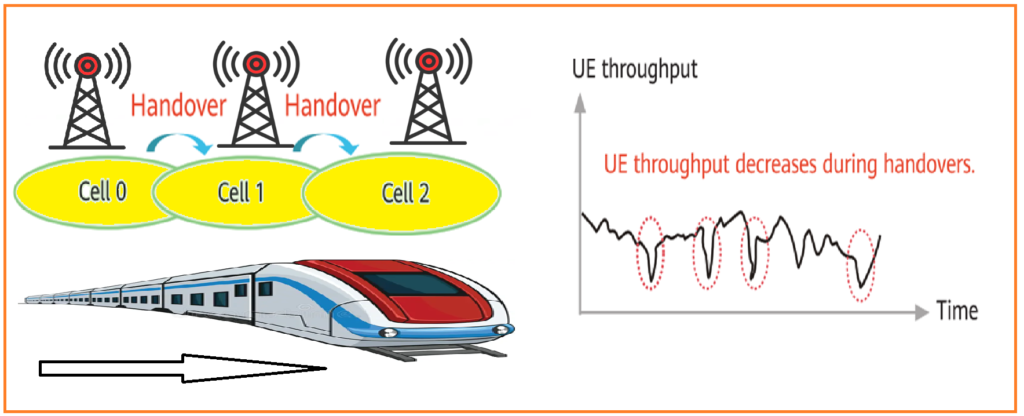
Hyper Cell is a 5G feature designed for high-speed linear coverage scenarios like subways or railways. It minimizes frequent handovers caused by UEs moving quickly through traditional cell areas. By reducing handovers, Hyper Cell enhances user experience by lowering service drops and improving throughput, especially in low-frequency TDD bands. This feature ensures stable connectivity and consistent service quality in high-mobility environments.
Hyper Cell Definition.
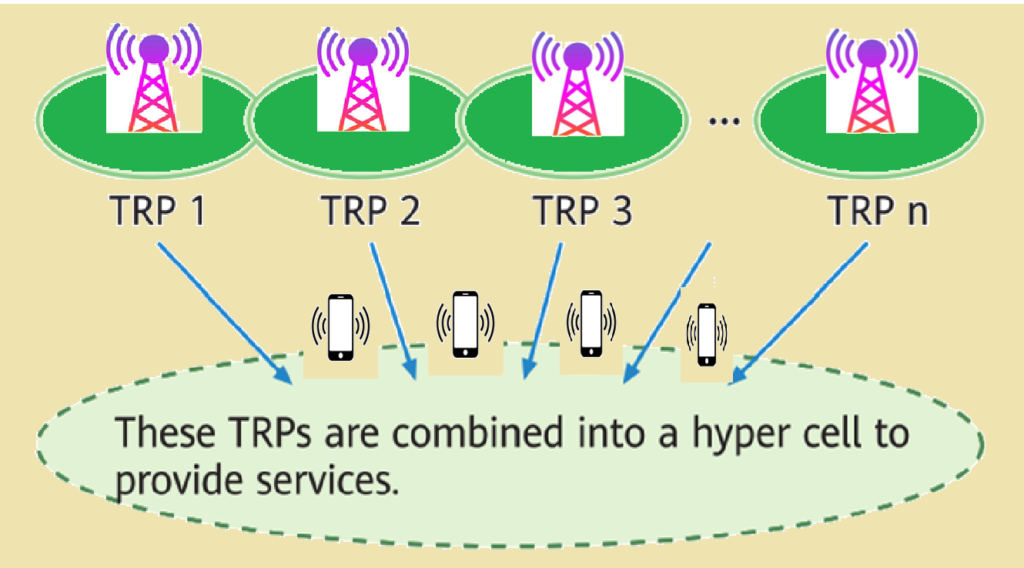
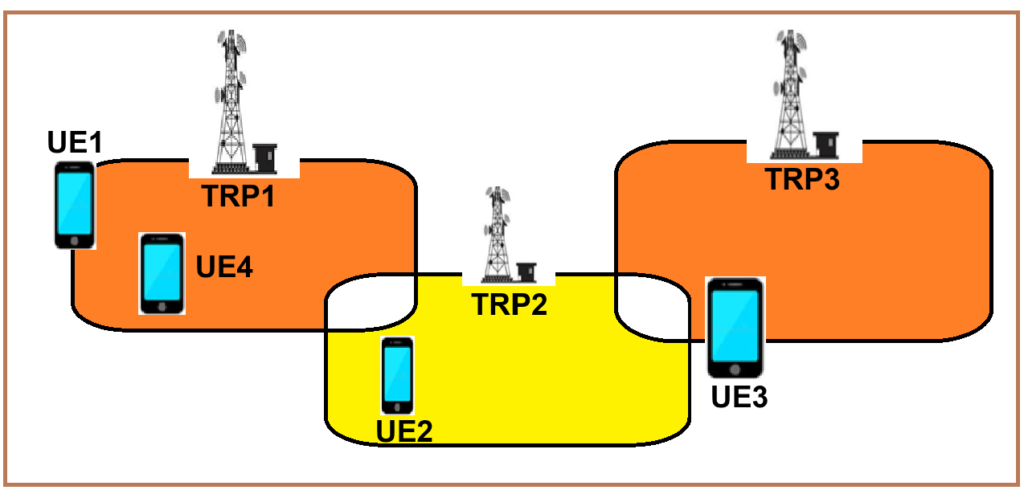
A Hyper Cell is formed by combining multiple Transmission and Reception Points (TRPs) operating on the same frequency and bandwidth, creating a unified coverage area. Each TRP, equipped with an antenna array, corresponds to an individual coverage area and is located at a specific geographical point. In linear coverage scenarios like subways or railways, this configuration reduces handovers and improves connectivity by treating multiple TRPs as a single logical cell, ensuring seamless mobility and consistent service quality for UEs moving at high speeds.
What are Benefits of Hyper Cell?
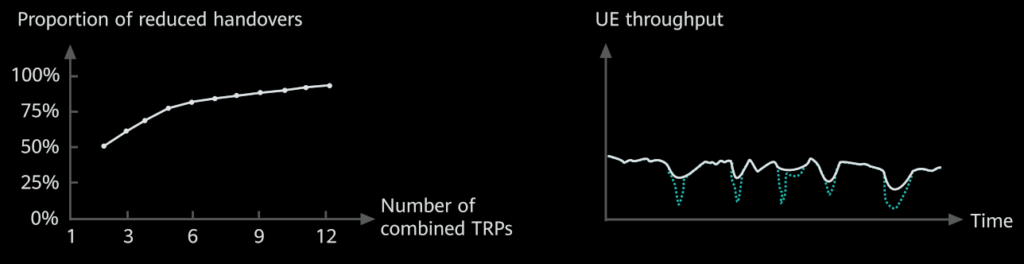
Fewer Handovers: UEs experience significantly fewer handovers during movement, especially in linear coverage areas like subways or railways. The more TRPs are combined, the fewer handovers occur.
Improved Throughput: UE throughput during movement is enhanced due to the reduced handover events and seamless connectivity offered by the unified cell structure.
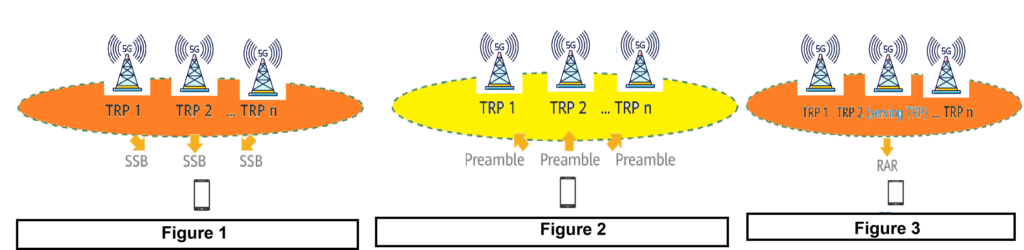
1. Serving TRP Selection in Hyper Cell.
When a UE accesses the network within a hyper cell, the gNodeB evaluates the preamble RSRP values of all TRPs. It selects the TRP with the highest preamble RSRP value as the serving TRP for the UE. The selected TRP facilitates the UE’s network access, ensuring optimal signal strength and connectivity. This process enhances efficiency and user experience within the hyper cell environment.
Figure-1. All TRPs transmit the same SSBs.
Figure-2. The UE sends preambles to all TRPs after receiving the SSBs.
Figure-3. The gNodeB selects a TRP with the highest preamble RSRP value as the serving TRP, and sends an RAR to the U E through the TRP.
2. Handover Between TRPs
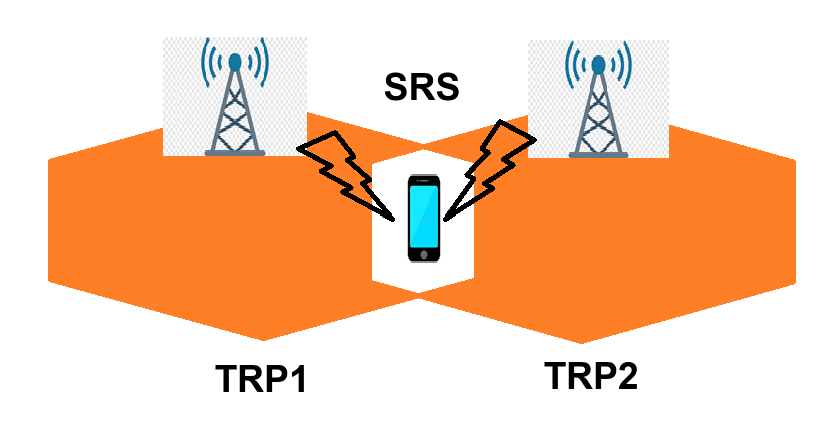
When a UE moves across TRPs within a hyper cell, the gNodeB measures the SRS RSRP for each TRP. If a candidate TRP has an SRS RSRP exceeding the serving TRP’s by more than a configurable margin (default: 1 dB), the gNodeB selects it as the new serving TRP. This handover involves no RRC procedures, minimizing service interruption. The UE sends SRS periodically, enabling the gNodeB to evaluate and update the serving TRP dynamically.
3. Inter-TRP Coordinated Scheduling.
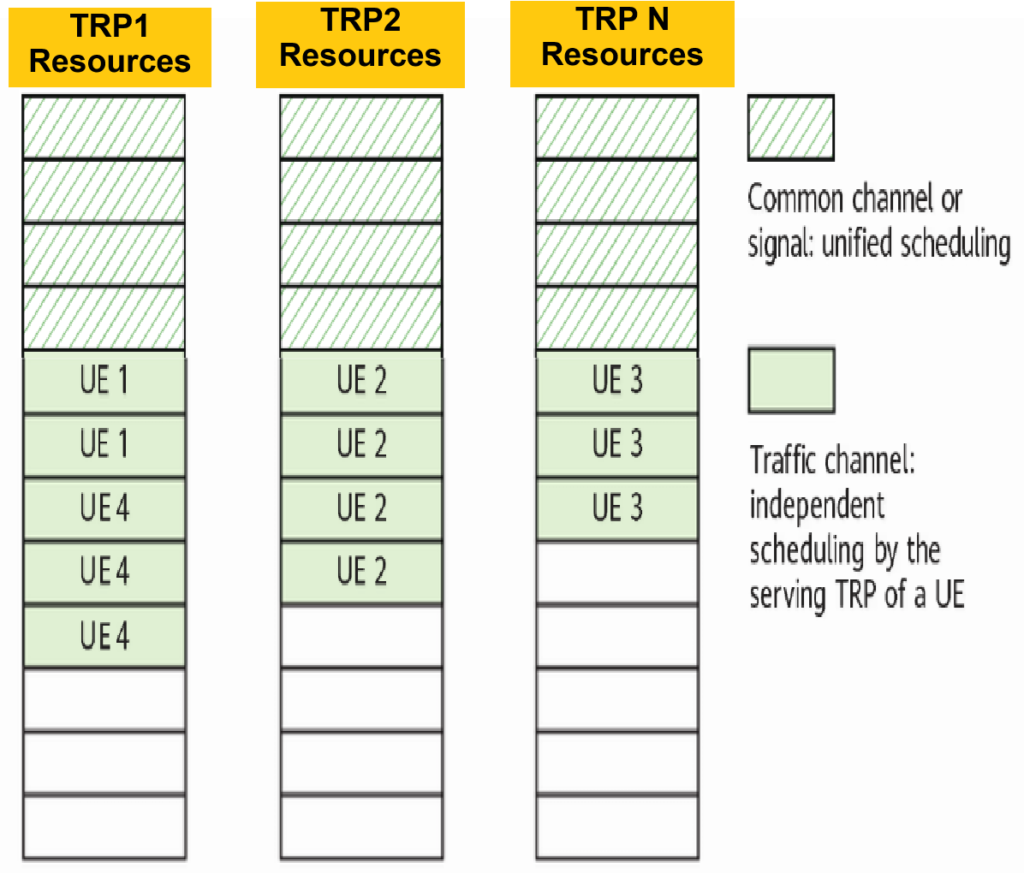
In a hyper cell, inter-TRP coordinated scheduling ensures unified resource allocation for common channels or signals across all TRPs, as directed by the gNodeB. Each TRP allocates resources collectively for these shared channels or signals. Conversely, traffic channel resources are managed independently by the gNodeB for each TRP. Only the serving TRP allocates traffic channel resources to the UE, ensuring efficient resource utilization and tailored service delivery.
Engineering Deployment
1. Hardware
The hyper cell feature in 5G systems supports up to 12 TRPs per hyper cell, configured within the same baseband processing unit (BBU). Specific requirements include:
- Compatible with 3900/5900 series and DBS3900/DBS5900 base stations.
- UBBPfw1 boards support one hyper cell, with all TRPs under the same board.
- UBBPg units allow TRPs from two identical boards to form a hyper cell.
- TRPs must share antenna configurations (e.g., 2T2R or 64T64R).
- Common and hyper cells cannot coexist on the same baseband processing unit.
2. Networking
Hyper cell networking is ideal for linear coverage scenarios, such as railways and subways. It supports combining common and RF combination cells into a hyper cell but excludes combined-RRU cells, multi-carrier sector cells, and uplink/downlink decoupling cells. To minimize interference, it is recommended that adjacent TRPs have different NRDUCellTrp.NrDuCellTrpld values modulo 6.
3. Software
The hyper cell function requires the TRS rate matching feature to be active. It cannot work alongside mutually exclusive functions such as Carrier Aggregation (CA), uplink and downlink decoupling, power-saving bandwidth parts (BWP), remote interference avoidance, energy-saving features, Super Uplink Phase 1, or LTE TDD and NR Flash Dynamic Power Sharing. These exclusions ensure the optimized operation and resource allocation required for hyper cell deployment.
4. How to activate Hyper Cell?
To activate a hyper cell:
- Add the hyper cell configuration to the network.
- Include all desired TRPs in the hyper cell setup.
- Set the RSRP threshold difference that determines handovers between TRPs within the hyper cell.
- Activate the hyper cell to begin operations.