Dual Connectivity Overview
Dual Connectivity (DC) was introduced in LTE (Release 12) to allow User Equipment (UE) to connect to two eNodeBs (eNBs) simultaneously. This feature enhanced data throughput and mobility. With the advent of 5G (Release 15), DC evolved into Multi-Radio Dual Connectivity (MR-DC), enabling UE to connect to both LTE E-UTRA and 5G NR nodes. This enhances network performance and smoothens the transition from 4G to 5G.
Why Do We Need MR-DC?
- Increased Throughput: Aggregates resources from multiple nodes, significantly boosting data speeds.
- Improved Mobility: Enhances handover and mobility robustness in macro/micro-cell deployments.
- Seamless Transition from 4G to 5G: Allows operators to extend the life of 4G equipment while deploying 5G networks.
This is achieved through:
- UL/DL Separation: Uplink and downlink can be managed separately across nodes.
- User/Control Plane Separation: Control functions are handled by a stable LTE node while user data is managed by both LTE and 5G nodes.
- Traffic Duplication for Redundancy: Essential for Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC).
How Can MR-DC Help Operators in Their 4G-to-5G Migration?
- Option 3 (NSA): Deploy 5G gNodeBs (gNBs) connected to the existing 4G core network (EPC) via eNodeBs (eNBs). This path requires minimal investment.
- Option 4/7: Gradually migrate the core network from EPC to 5G Core (5GC).
- Option 2 (SA): Fully transition to a standalone 5G network with all gNBs.
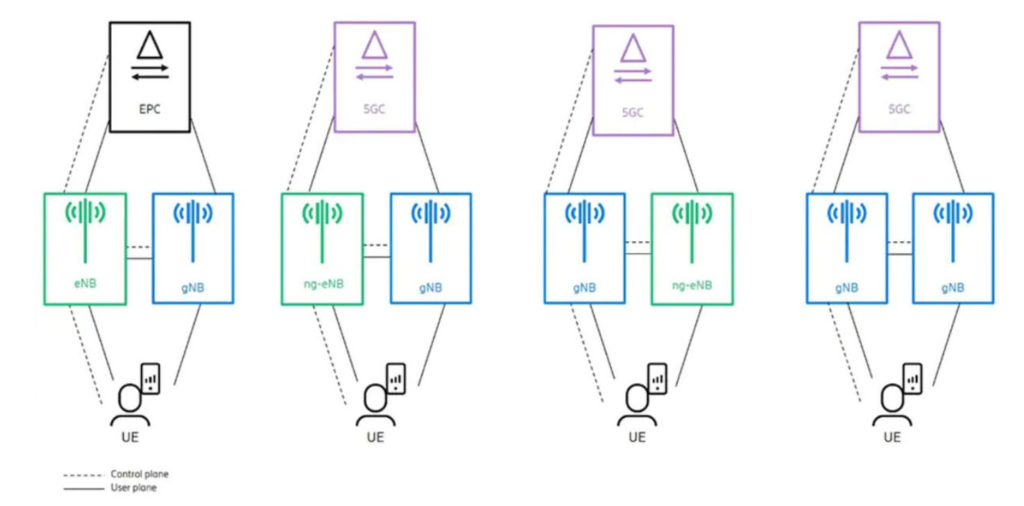
Different Configuration Options in MR-DC
- EN-DC: LTE eNB as Master Node (MN) and 5G en-gNB as Secondary Node (SN) with LTE EPC.
- NGEN-DC: ng-eNB as MN and gNB as SN with 5GC.
- NE-DC: gNB as MN and ng-eNB as SN with 5GC.
- NR-DC: gNB as both MN and SN with 5GC.
Engineering Challenges with Implementing MR-DC
- Self-Interference: Managing intermodulation products to avoid interference.
- Power Control: Balancing power across multiple carriers and nodes.
MR-DC represents a critical step forward in 5G deployment, providing a robust framework for integrating LTE and NR networks, ensuring a seamless user experience, and supporting the future of mobile connectivity.
Key Terminology
- eNB: LTE base station.
- gNB: 5G base station.
- en-gNB: 5G base station operating alongside LTE eNB.
- ng-eNB: LTE base station compatible with 5G core.
- MN: Master Node
- SN: Secondary Node
- 5GC: Core network for 5G.
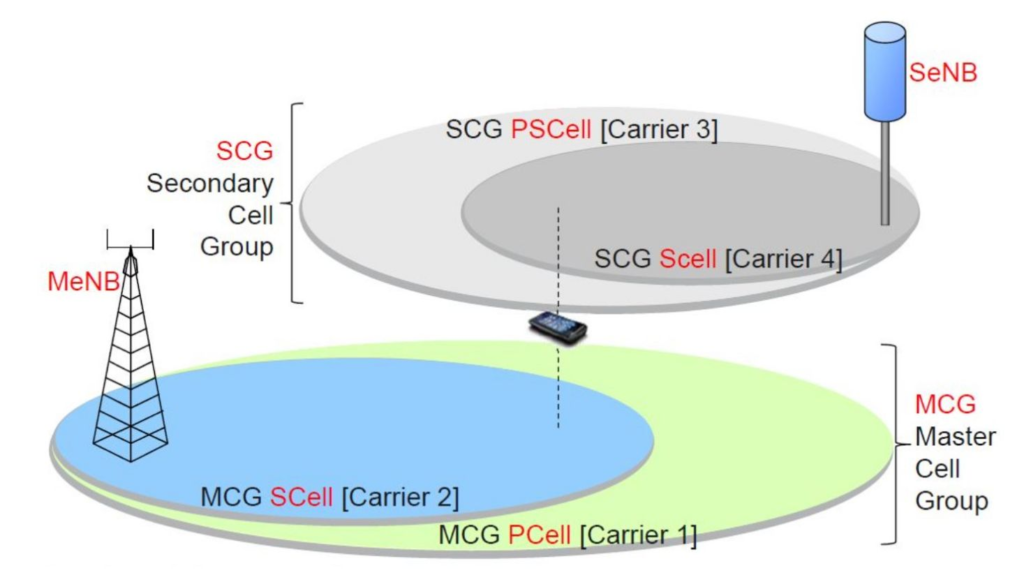
- MCG: Master Cell Group
- SCG: Secondary Cell Group
- PCell: Primary cell in MCG.
- PSCell: Primary cell in SCG.
- MCG Bearer: Radio bearer within the MCG.
- SCG Bearer: Radio bearer within the SCG.
Multi-Radio Dual Connectivity is pivotal for ensuring the seamless integration of LTE and 5G networks, significantly enhancing data throughput, mobility, and overall network performance.