5G New Radio (NR) inherits and expands upon the frame structure of LTE, providing greater flexibility to meet diverse service requirements. Understanding the 5G NR frame structure is essential for telecommunications engineers to effectively design and implement 5G networks.
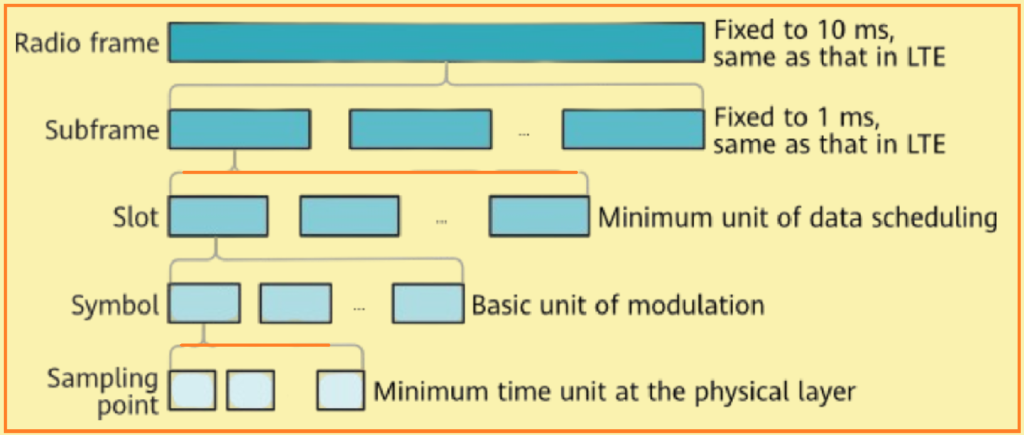
This figure illustrates the hierarchical organization of the 5G NR frame structure, comprising frames, subframes, slots, and symbols.
Frame:
- Length: 10 ms
- Frame Number Range: 0 to 1023
Subframe:
- Length: 1 ms
- Subframe Number Range: 0 to 9
Slot:
- A slot typically consists of 14 symbols with normal Cyclic Prefixes (CPs). The slot length varies with the symbol length, which is determined by the Subcarrier Spacing (SCS).
Symbol:
- The length of a symbol is not fixed and is related to the SCS.
Key Points to Remember:
In LTE, the time unit for data scheduling is a subframe (1 ms). In 5G NR, the time unit is a slot, with the slot length varying based on the SCS.
When the SCS is 60 kHz with extended CPs, a slot consists of 12 symbols.
Relationships Between Frame, Subframe, Slot, and Symbol.
The relationships between these units change with different SCS values. The following tables summarize the numbers of symbols per slot, slots per frame, and slots per subframe for various SCS configurations, as defined in 3GPP TS 38.211.
Table 1 Numbers of symbols per slot, slots per frame, and slots per subframe with normal CPs.
| μ | Number of Symbols per Slot | Number of Slots per Frame | Number of Slots per Subframe |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 14 | 10 | 1 |
| 1 | 14 | 20 | 2 |
| 2 | 14 | 40 | 4 |
| 3 | 14 | 80 | 8 |
| 4 | 14 | 160 | 16 |
Table 2 Numbers of symbols per slot, slots per frame, and slots per subframe with extended CPs.
| μ | Number of Symbols per Slot | Number of Slots per Frame | Number of Slots per Subframe |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 12 | 40 | 4 |
Explanation of Symbol and Slot Variability.
- Symbol Length and SCS: In 5G NR, the symbol length varies with the SCS. The SCS can be 15 kHz, 30 kHz, 60 kHz, 120 kHz, or 240 kHz, allowing the system to adapt to different use cases and channel conditions.
- Slot Structure: Each slot contains a fixed number of symbols, but the duration of a slot changes based on the SCS. Higher SCS values result in shorter symbol and slot durations, enabling lower latency and more efficient spectrum usage.
Conclusion
The 5G NR frame structure is designed to provide flexibility and efficiency, accommodating a wide range of services and deployment scenarios. By understanding the detailed relationships and parameters of frames, subframes, slots, and symbols, telecommunications engineers can optimize 5G networks for enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC), and massive machine-type communications (mMTC).
References
- 3GPP TS 38.300, NR and NG-RAN Overall Description; Stage 2 (Release 16)
- 3GPP TS 38.101-1, User Equipment (UE) radio transmission and reception; Part 1: Range 1 Standalone (Release 16)
- 3GPP TS 38.101-2, User Equipment (UE) radio transmission and reception; Part 1: Range 2 Standalone (Release 16).
- 3GPP TS 38.104, Base Station (BS) radio transmission and reception (Release 16).
- 3GPP TS 36.211, Physical channels and modulation (Release 14).
- 3GPP TS 38.213, Physical layer procedures for control (Release 16).
- 3GPP TS 38.211, Physical channels and modulation (Release 16).
- 3GPP TR 38.912 (Release 15).
- 3GPP TR 38.802, Physical Layer Aspects (Release 14).
Following questions are asked during interview of 5G NR RAN, RF and Microwave on topic of Time Domain Resources.
- Where do the basic time units Tc and Ts in the 5G system come from?
- What are intersymbol interference (ISI) and inter-subcarrier interference (ICI)?
- Why can extended cyclic prefixes (CPs) avoid the interference?
- What are slot formats?
- What is mini-slot?
- How do 3GPP specifications describe mini-slot?