In 5G NR, slot configuration is more dynamic and flexible compared to LTE. Unlike LTE, where the number of slots in a frame is fixed, the slot configuration in 5G NR is influenced by the Subcarrier Spacing (SCS). This allows for adaptable downlink (DL) and uplink (UL) transmission configurations within a frame.
Key Points to Remember:
- Switch-point Period: The period within which the switch between uplink and downlink transmissions occurs. A guard period (GP) must be configured between these transitions to ensure proper signal transmission.
- Guard Period (GP): A time interval reserved to avoid interference between uplink and downlink transmissions.
5G Slot Configuration Layers.
The slot configurations in 5G NR are defined across four layers as per 3GPP TS 38.213:
Layer 1: Cell-specific Slot Configuration
- Characteristics: Static or semi-static configuration.
- Configuration Delivery: Delivered by System Information Block Type 1 (SIB1).
- Switch-point Periods: {0.5, 0.625, 1, 1.25, 2, 2.5, 5, 10} ms.
- Priority: Highest. The DL and UL parts cannot be modified by other layers.
Layer 2: UE-specific Slot Configuration
- Characteristics: Static or semi-static configuration tailored for individual UEs.
- Configuration Delivery: Delivered by Radio Resource Control (RRC) signaling.
- Switch-point Periods: {0.5, 0.625, 1, 1.25, 2, 2.5, 5, 10} ms.
- Priority: Relatively high. Can modify flexible (F) parts of the cell-specific configuration but not the DL and UL parts.
Layer 3: UE-group-specific Slot Configuration
- Characteristics: Periodic dynamic configuration for groups of UEs.
- Configuration Delivery: Delivered by Slot Format Indicators (SFIs).
- Switch-point Periods: {1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 20} slots.
- Priority: Relatively low. Can modify F parts of layer-1 or layer-2 configurations but not DL and UL parts.
Layer 4: UE-specific Slot Configuration
- Characteristics: Slot-level dynamic configuration.
- Configuration Delivery: Delivered by Downlink Control Information (DCI).
- Priority: Lowest. Can modify only the F parts of layer-1, layer-2, or layer-3 configurations.
Configuration Modes.
Multiple layers of slot configurations can be applied simultaneously or individually, allowing for fine-tuned adjustments to meet various service requirements and network conditions. When multiple layers are configured:
- Upper Layer Dominance: The DL and UL parts in the cell-specific (layer-1) configuration cannot be altered by lower layers.
- Flexible Part Modification: Lower layers can modify only the flexible (F) parts of the upper layer configurations.
Practical Implications.
- Dynamic Resource Allocation: 5G NR’s flexible slot configuration enables dynamic and efficient resource allocation, adapting to varying traffic demands and service requirements.
- Low Latency and High Throughput: This flexibility supports use cases requiring low latency, such as URLLC, and high throughput scenarios, optimizing network performance.
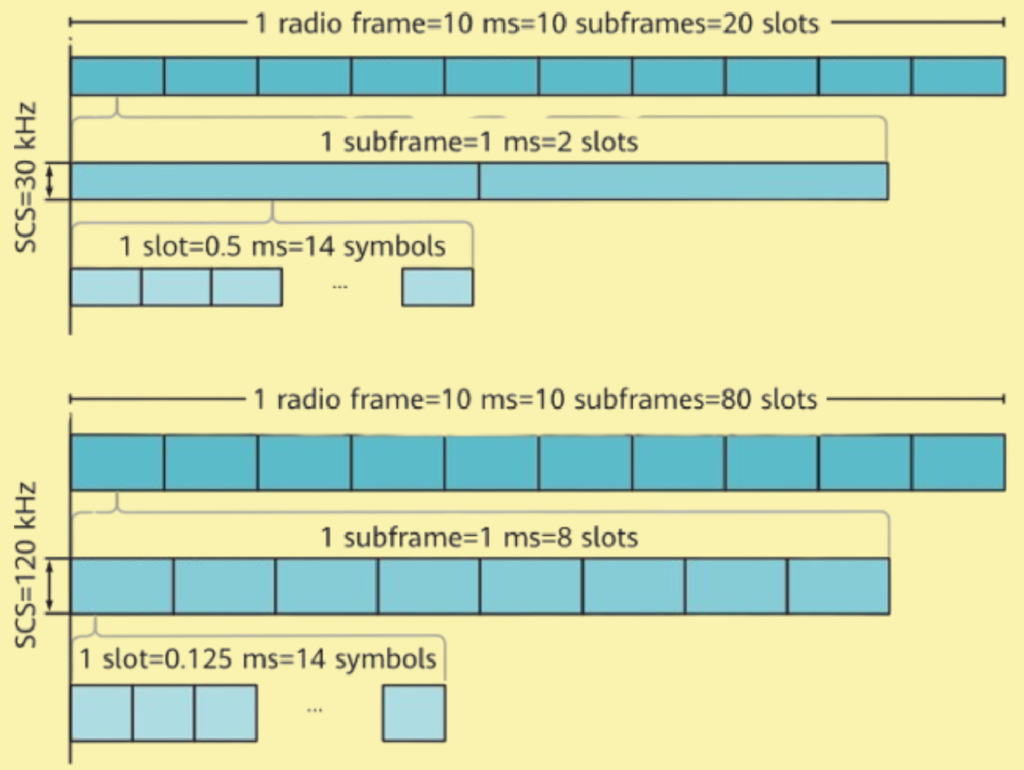
Table – Slot configurations at different layers.
| Slot Configuration | Characteristics and Configuration Priorities |
|---|---|
| Layer 1: Cell-specific + SIB1 | Characteristics: Cell-specific+static or semi-static configurationPriority: Highest. The D and U parts in the cell-specific slot configuration cannot be modified by slot configurations at other layers. |
| Layer 2: UE-specific + RRC signaling | Characteristics: UE-specific + static or semi-static configurationPriority: Relatively high. The slot configuration at this layer can modify the F part in the cell-specific slot configuration. The D and U parts in this slot configuration cannot be modified by the layer-3 or layer-4 slot configuration. |
| Layer 3: UE-group-specific + SFI | Characteristics: UE-specific or UE-group-specific + periodic dynamic configurationPriority: Relatively low. The slot configuration at this layer can modify the F part in the layer-1 or layer-2 slot configuration. The D and U parts in this slot configuration cannot be modified by the layer-4 slot configuration. |
| Layer 4: UE-specific + DCI | Characteristics: UE-specific + slot-level dynamic configurationPriority:Low. The slot configuration at this layer can modify only the F part in the layer-1, layer-2, or layer-3 slot configuration. |
In summary, 5G NR’s slot configuration framework provides a robust and adaptable mechanism for managing radio resources, enhancing the network’s capability to meet diverse service needs efficiently.
References
- 3GPP TS 38.300, NR and NG-RAN Overall Description; Stage 2 (Release 16)
- 3GPP TS 38.101-1, User Equipment (UE) radio transmission and reception; Part 1: Range 1 Standalone (Release 16)
- 3GPP TS 38.101-2, User Equipment (UE) radio transmission and reception; Part 1: Range 2 Standalone (Release 16).
- 3GPP TS 38.104, Base Station (BS) radio transmission and reception (Release 16).
- 3GPP TS 36.211, Physical channels and modulation (Release 14).
- 3GPP TS 38.213, Physical layer procedures for control (Release 16).
- 3GPP TS 38.211, Physical channels and modulation (Release 16).
- 3GPP TR 38.912 (Release 15).
- 3GPP TR 38.802, Physical Layer Aspects (Release 14).
Following questions are asked during interview of 5G NR RAN, RF and Microwave on topic of Time Domain Resources.
- Where do the basic time units Tc and Ts in the 5G system come from?
- What are intersymbol interference (ISI) and inter-subcarrier interference (ICI)?
- Why can extended cyclic prefixes (CPs) avoid the interference?
- What are slot formats?
- What is mini-slot?
- How do 3GPP specifications describe mini-slot?