You’ve learned that good insulation exhibits high resistance in previous article [What is Good Insulation in Electrical Systems?], while poor insulation demonstrates relatively low resistance. The actual resistance values can vary, depending on factors like temperature and moisture content (as resistance decreases in lower temperatures or higher moisture levels). However, with some basic record-keeping and practical judgment, you can gauge insulation condition based on relative values.
The Megger insulation tester is a compact and portable instrument designed to provide a direct reading of insulation resistance in ohms or megohms. In the case of well-maintained insulation, the resistance typically falls within the megohm range.
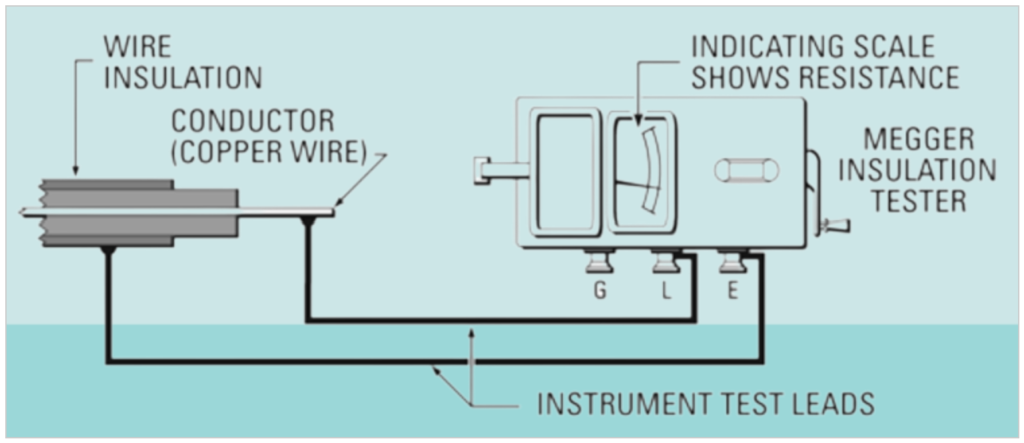
The Megger insulation tester functions as a specialized high-range resistance meter, often referred to as an ohmmeter. It includes an integrated direct-current (DC) generator. This meter is uniquely designed with both current and voltage coils, allowing it to measure true ohms directly, irrespective of the applied voltage. It’s important to note that this testing method is non-destructive, meaning it doesn’t cause any harm to the insulation being examined.
The generator within the Megger insulation tester can be operated either manually by hand-cranking or by connecting it to a power source. It generates a high DC voltage, which induces a small current to flow through and across the insulation surfaces under examination (typically at an applied voltage of 500 volts or higher). This current is then measured by the ohmmeter, which features an indicating scale. A typical scale is depicted in below Figure, where resistance values increase from left to right until reaching infinity or a resistance level too high to be measured.
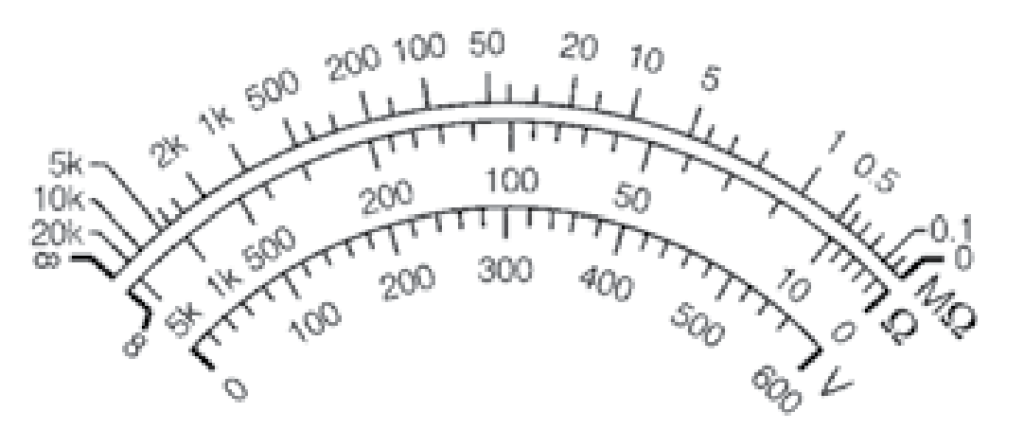
In summary, the Megger insulation tester is a valuable tool for assessing insulation resistance by applying a high DC voltage and measuring the resulting current, providing readings in ohms or megohms. This method is safe for insulation and allows for accurate evaluations of its condition.
Related Articles:
What is Good insulation?
What Makes Insulation Go Bad?
How Insulation Resistance is Measured.
How to Interpret Resistance Readings.
Factors Affecting Insulation Resistance Readings.
Types of Insulation Resistance Tests.
Test Voltage vs. Equipment Rating.
AC Testing vs. DC.
Use of DC Dielectric Test Set.
Tests During Drying out of Equipment.
Effect of Temperature on insulation Resistance.
Effects of humidity.
Preparation of Apparatus to test.
Safety Precautions.
Connections for testing insulation resistance of electrical equipment.
Additional Notes About using A Megger Insulation Tester.
Interpretation-Minimum Values.
Minimum Values for Insulation Resistance.
Tests Using Multi-Voltage Megger Insulation Testers.
Step-Voltage Method.
Use of a Guard Terminal.
Outdoor Oil Circuit Breaker.