The S1 Application Part (S1AP) is a protocol used for communication between the Mobility Management Entity (MME) and the eNodeB (eNB) in an LTE network. Its primary role is to establish and manage the connection between these two network elements through a process known as the S1 setup procedure. S1AP messages maintain this connection, adjust configuration parameters, handle errors and overload situations, balance the load, and reset, re-establish, or release the connection when necessary.
Here i am giving example of LTE eNodeB startup and UE setup signalling and eNodeB initiates an S1 connection with the MME. S1AP Protocol used in below picture.
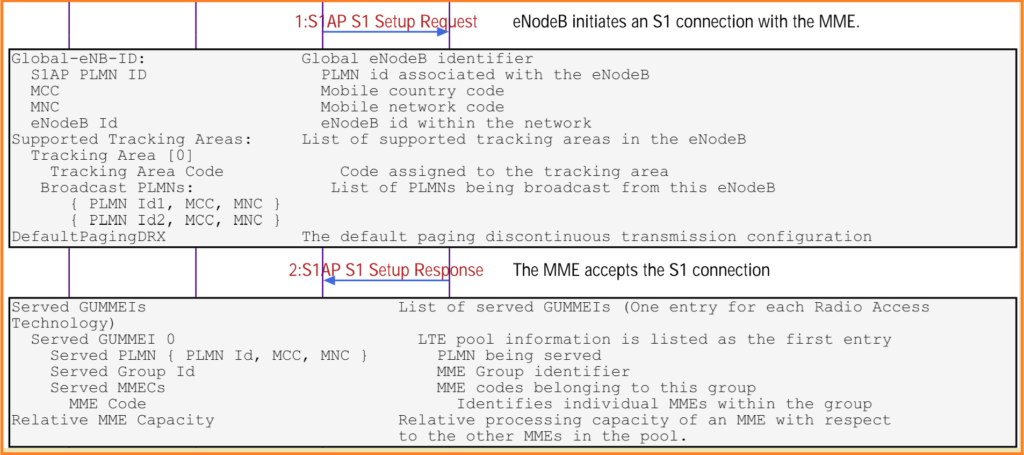
S1 Application Part (S1AP) Protocol.
Once the connection between the eNB and MME is set up, the User Equipment (UE) that camp on the eNB’s cells can be paged via S1AP for mobile terminating connections or can initiate calls themselves. During these processes, S1AP helps forward Non-Access Stratum (NAS) messages transparently. Additionally, S1AP manages the S1-U GTP tunnels, which are crucial for data transfer. These tunnels, part of the E-RAB (E-UTRAN Radio Access Bearer), can be established, modified based on Quality of Service (QoS) requirements, and released using S1AP procedures. While the MME typically initiates E-RAB setup and modification, both the MME and eNB can trigger their release.
During initial registration and connection setup, an S1 UE context is created in the eNB. Each S1AP connection for a particular UE is identified by a unique pair of identifiers: the MME UE S1AP ID and the eNB UE S1AP ID. These identifiers are used to link all S1AP messages related to a specific UE, except for paging messages sent before the UE context is established. S1AP also plays a key role in mobility functions, such as handovers between eNBs connected to the same MME (path switch procedure) and handovers between different MMEs or radio access technologies (inter-MME and inter-RAT handovers).
Furthermore, S1AP supports E-RAB management functions, allowing for the setup, modification, and release of E-RABs during an active connection. Separate S1AP messages are provided for these E-RAB management tasks, ensuring efficient and flexible handling of data bearers in the network.
The S1AP is also responsible for different mobility functions.
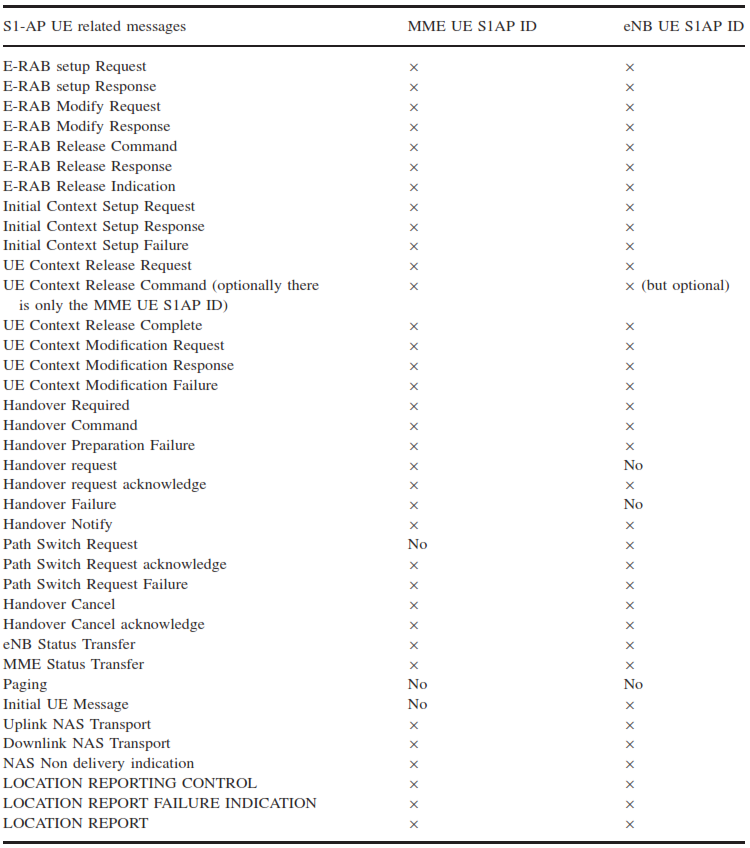
Location Reporting and Broadcast Warning Messages
In addition to connection and bearer management, S1AP includes messages for broadcasting warning messages and for location reporting. The S1AP location report keeps the MME updated about the serving cell ID currently used by the UE.
Protocol Details and Procedures
S1AP procedures are categorized into two classes based on their response requirements:
Class 1 Procedures:
These require a response, either successful or unsuccessful, to the initiating message. Each request must be acknowledged by an appropriate success or failure message. An example is the handover preparation procedure, where the initiating message (Handover Required) must be answered by either a successful outcome (Handover Command) or an unsuccessful outcome (Handover Preparation Failure).

Class 2 Procedures:
These are unidirectional messages that do not require an explicit acknowledgment from the receiving entity.
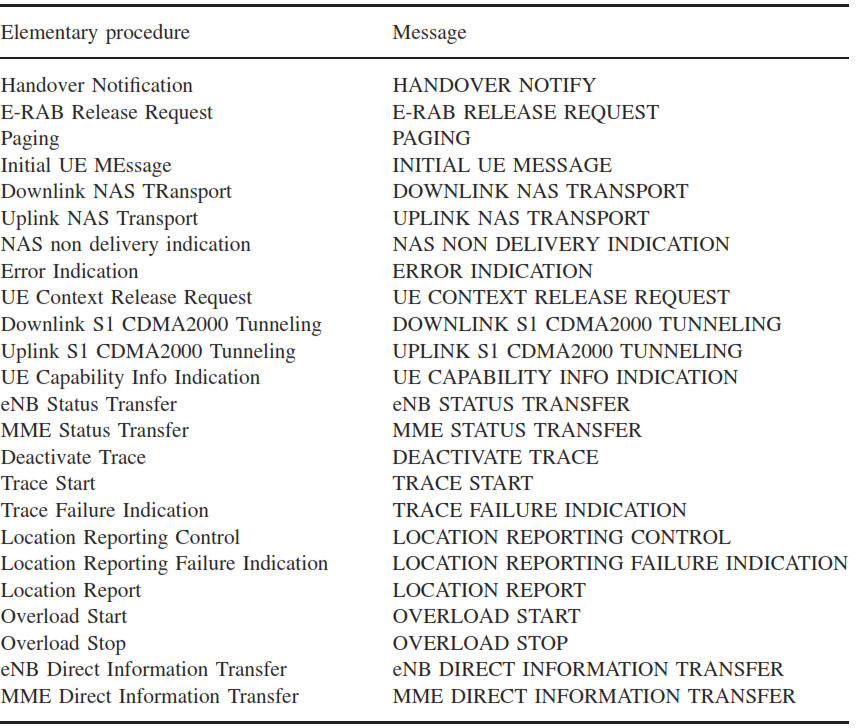
For each procedure, S1AP follows ASN.1 encoding rules, translating standard message names into encoded formats suitable for communication. For example, the “Handover Required” message is encoded as an initiating message with the procedure code “id-HandoverPreparation.”
handoverPreparation S1AP-ELEMENTARY-PROCEDURE ::= {
INITIATING MESSAGE HandoverRequired
SUCCESSFUL OUTCOME HandoverCommand
UNSUCCESSFUL OUTCOME HandoverPreparationFailure
PROCEDURE CODE
id-HandoverPreparation
CRITICALITY
reject
}