This article is about Bolt tightening, torquing and tensioning procedure and method statement for structural steel works. Here explained sequence wise of bolt tightening.
1. Purpose
2. Scope of Work
3. References
4. Man Power
5. Tools and Equipment
6. Procedures
7. Quality Control
8. Safety
9. Attachment
BOLT TIGHTENING PROCEDURE AND METHOD STATEMENT
1. Purpose
The purpose of this procedure is to provide the methodology and testing of bolt tightening (bolt torqueing) of structural steel work in all supply mechanical equipment to the commercial buildings, plants and refinery project and its equipment structures.
2. Scope of Work
The scope of work covers the requirement of bolt tightening of all mechanical equipment structural joints and sections showing the required bolt size, field inspection and implement safety precautions to be taken to prevent accident occurrence during work execution.
3. References
All works shall be executed according to project applicable standards:
3.1 SAIC-M-2007 Inspection of Structural Alignment during Erection.
3.2 SAIC-M-2008 Repair/Correction of Errors of Structural Alignment.
3.3 SATIP-M-001-01 Structural Steel-Pipe Rack, Steel Support & Miscellaneous Steel Structures(including pipe supports per specification).
3.4 SAIC-M-2009 High Strength Bolt Tightening Inspection and Testing (ASTM A325 or A490 Bolts).
3.5 SATR-M-2002 Pre-Installation Procedure Verification Testing Turn-of-Nut Method (ASTM A325 or ASTM A490 bolts).
3.6 SATR-M-2004 Pre-Installation Procedure Verification Testing of Calibration Wrench (ASTM A325 or ASTM A490 bolts).
4. MAN POWER
4.1 Foreman Steel Structure /Mechanical.
4.2 Man lift Operator (ARAMCO Certified).
4.3 Mechanical Worker.
4.4 Flagman.
4.5 QC Inspector.
5. TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT
5.1 Calibrated Torque Wrench.
5.2 Hammer Wrench.
5.3 Spud Wrench.
5.4 Impact Wrench.
5.5 Torque Calibrator.
5.6 Man lift.
6. Procedure.
6.1 Site and Materials preparation.
6.1.1 Determine which type of bolt materials are to be used, unless otherwise specified by the contract documents.
6.1.2 All primary structural frames and some secondary framing require high strength A-325 or A490 Bolts.
6.1.3 Requisition of pre-determined bolts.
6.1.4 Steel members to be jointed must be free from oil, grease or any loose adherent materials.
6.1.5 Any circumstances discovered by the DEC that affect progression, performance, or completion of work activities such as discrepancies between drawings and delivered steel members to be jointed, incorrect fabricated steel members, incomplete or unacceptable material shall be reported in writing.
6.1.6 Before bolt tightening DEC shall check the connection points to confirm their location, orientation, elevation and condition.
6.1.7 Contractor shall place a scaffolding access, ladder, wood boards or floor plates for the people who will conduct the activity to prevent injury while commencing the work.
6.2 Structural Stability
6.2.1 DEC shall at all times be responsible for the adequacy and installation of any temporary bracing or guy cables required to counteract loadings imposed. This responsibility shall also extend to temporary bracing required to ensure safe and stable conditions of partially completed structural assemblies.
6.2.2 The structure shall be plumbed, levelled and braced before final bolting connections are made.
6.3 Bolt Connections
6.3.1 Where structural joints are made using high-strength bolt assemblies, the materials, method of installations, tension control, types of wrenches to be used and inspection methods shall conform to AISC Specification for Structural Joints using ASTM A325 or A490 Bolts.
6.3.2 When used, direct tension indicator washer shall be installed according to the manufacturer’s given specifications.
6.3.3 All bolts shall be as noted on the shop drawing, erection drawings or other contract documents.
6.4 Bolt Tightening
6.4.1 After aligning the holes in a joint; sufficient bolts shall be placed and brought to a SNUG – TIGHT condition to ensure that all parts of the joints are brought to full contact with each other.
6.4.2 “SNUG-TIGHT” as defined is the effort of a person using SPUD WRENCH or tightness attained by a few impacts of an IMPACT WRENCH.
• Manual operation using SPUD Wrench Method
In this case, full efforts of a man using an ordinary spud wrench would bring the bolt to a snug tight position. No wrench extension or long wrenches should be used to avoid tensioning; the normal spud wrench is usually 12 inches (300mm) long.
• Using IMPACT Wrench Method.
Few impacts of an impact wrench should be sufficient to bring the bolts into snug tight position. If the impact wrench is strong enough, this operation should not take more than 30 seconds of application to bolt which already tightened to full contact with the steel connection plates.
6.4.3 Once the SNUG tight position is achieved a straight line shall be marked by metal marker or pentel pen on the bolt head continue to nut location. This will indicate the initial position of nut prior to its final tightened position.
6.4.4 In critical-slip connection where the joint is subject to vibratory or fatigue loading, chance of bolt to be loosened is very high. In this case, after bolts has fully tensioned an additional jamb-nut maybe provided. Alternately, the threads can be spiked or marred or the nut can be tack-weld to the base metal to prevent it from turning.
6.5 Operations
6.6 Following the initial tightening operation all bolts in the joints shall be further tightened using either turn-off-nut or calibrated wrench method.
6.6.1 Turn-Of-Nut-Method
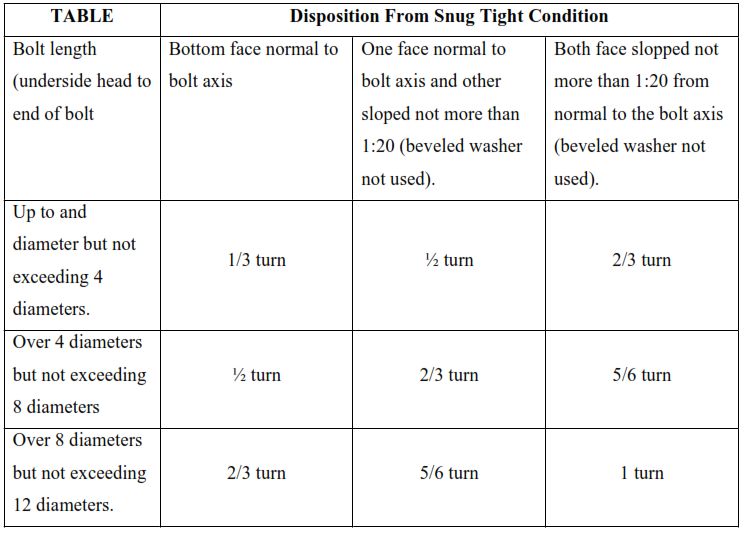
• After all the bolt have reached the snug tight condition it shall be further tightened by the amount of rotation as specified in the table below.
6.6.2 Calibrated Wrench Method.
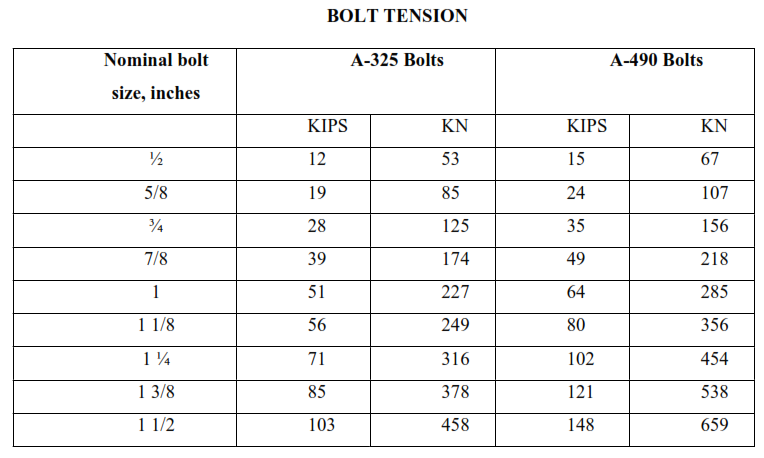
• Following the initial tightening specified under paragraph 4.4, calibrated torque wrench shall be used to tighten bolts to provide a tension at least 5% more than the minimum bolt tension specified in the table below (as per ASTM A325) and SAIC-M-2009.
• The wrench shall be calibrated at least once every year working day for each bolt diameter, length and grade being installed. Calibration shall be accomplished by tightening in a device capable of indicating actual bolt tension. Three typical bolts shall be tightened for each diameter from the bolts being installed.
7. Quality Control
7.1 Check the physical appearance and the material specifications to be used for bolting prior to the work execution.
7.2 Ensure to follow IFC drawings for bolt specification requirements including sizes and manufacturer’s recommendation. Observe as always SATIP activity, SAIC and SATR standard requirements for compliance.
7.3 Check, verify and continuously monitor bolting works activities at site and lay down yard where assembly and bolt tightening is on progress.
7.4 Request for SAUDI ARAMCO inspection for final acceptance.
8. Safety
8.1 Ensure that all personnel involved in the work are wearing standard personnel protective equipment (PPE).
8.1.1 Maintain warning devices such as warning tapes, signboards and barriers around the work area to prevent injury to all personnel affected by the operations.
8.1.2 Tools (Hand Tools and Machined Operated tools) and Safety Harnesses shall be monitored and coded as per safety monthly monitoring guidelines for acceptance and compliance of these equipment to daily site activities.
9. Attachment
9.1 JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS
ERECTION STEEL STRUCTURE PROCEDURE | METHOD STATEMENT
High Strength Bolts Tightening Procedures