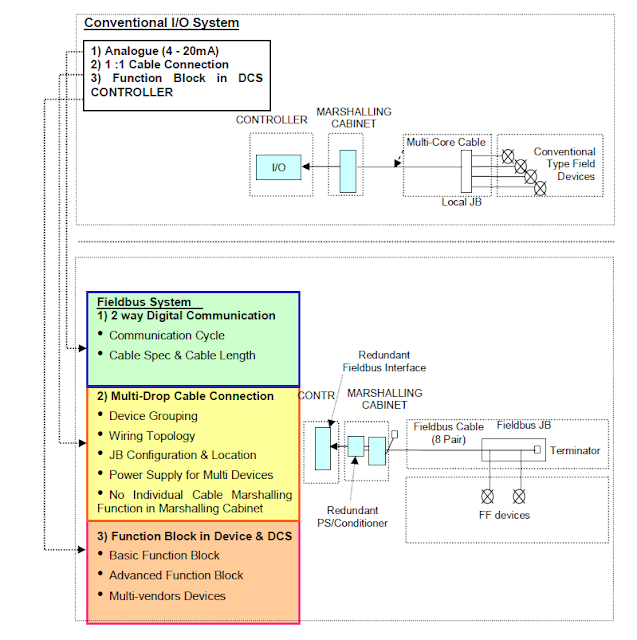
Differences between a Fieldbus and a Traditional Installation
Hardware Difference between Traditional and Fieldbus
The power and communication is provided over the same cable in FF with some exceptions such as magnetic type flow meters.
The network configuration results in less I/O cards, I/O interface racks and marshalling cabinets required both in the CCR’s and Process Interface Building (PIB). Also more sensors can be integrated in one FF device leading toa reduction in field devices and/or enhanced diagnostic features.
Communication Difference between Traditional and Fieldbus
Since FF technology is tag driven, whereby the host will check and commission devices on basis of tags in the database with auto addressing of devices, a reduction in the loop check effort can be realised.
Data transfer shall be fully digital eliminating the need for re-ranging and recalibration against drift.
Protocol Difference between Traditional and Fieldbus
The FF protocol enables the adequate transfer of a variety of information such as, Process Variable, status, diagnostics, etc. The host is to convert this basic data into information which leads to higher plant
availability and reduced maintenance costs.
availability and reduced maintenance costs.
Engineering Difference between Traditional and Fieldbus
The Fieldbus system shall be designed in a similar manner to the traditional system design, whereby the device layouts and cable schedules are used mainly for marshalling cabinet design and the DCS system will be designed based on I/O lists and process operation procedures, irrespective of the cable
schedule or the location of the devices and junction box.
schedule or the location of the devices and junction box.
However, in a Fieldbus based system, the field side details, i.e. segment design, do affect the DCS system design. This means that the DCS system design is dependent on device layout, cable detail, i.e. segment design details.
The segment design shall be simplified and where possible, be based on default values as specified
The basis shall therefore be to mimic a traditional implementation approach of a HART based system to minimize the design effort.
Nice article and good explanation.