This article is about Fieldbus Fundamentals and Difference between fieldbus and HART and focusing to the engineers, technicians and supervisors. You will find lot of documents related to this article. Just navigate our website www.paktechpoint.com and find more articles. Please! Do not forget to subscribe our You tube channel also. Thanks in Advance.
Fieldbus Fundamentals and Difference between fieldbus and HART
Trends In Process Automation
Process Automation has long been a playground of closed systems and proprietary solutions. This scheme has mostly been argumented using technological issues, such as reliability. Amazing development and popularity seen in standard PC-technologies, both in hardware and software, is also changing interest and development efforts towards open systems.
Introduction :
Process automation has long been a playground of closed systems and proprietary solutions. This scheme has mostly been argumented using technological issues, such as reliability. There is however no doubt that strategies based on economical
aspects have played a very strong role in this development as well as lack of suitable and commonly accepted standards.
aspects have played a very strong role in this development as well as lack of suitable and commonly accepted standards.
The situation is now changing quite rapidly. In the field of digital communication there are nowadays both standard as well as de-facto standard solutions available. Amazing development and popularity seen in standard PC-technologies,
both in hardware and software, is also changing interest and development efforts towards open systems.
both in hardware and software, is also changing interest and development efforts towards open systems.
Process Automation Systems
The modern Process Automation Systems handle many tasks. Disadvantage of Current Control Systems is the diagnostics, which covers only the automation system not the field devices. The field device is diagnosed based on the Process Problems which results in unnecessary inspection, maintenance or servicing.
The modern Process Automation Systems handle many tasks, the most obvious one being the process control. In addition to this, they take care of numerous other tasks as well. These include handling huge amount of information and knowledge concerning the process and production, disturbance handling, diagnostics and analysis of abnormal situations.
One big disadvantage in most current systems is that diagnostics covers thoroughly only the automation system itself and huge number of field devices are diagnosed only through the process.So, if process behaves in abnormal
way, one of the reasons might be a non-functional field device in the process.
Due to this uncertainty, many critical field devices have been inspected or serviced on regular basis, whether they need maintenance or not. For
some years the automation system and instrument manufacturers have been providing field management systems for configuration, document and maintenance management of field devices based on the digital technologies. The drawback of
these kind of system is the integration level is quite low as they work parallel. This is often a result of non-standard or poorly supported digital communication techniques.
way, one of the reasons might be a non-functional field device in the process.
Due to this uncertainty, many critical field devices have been inspected or serviced on regular basis, whether they need maintenance or not. For
some years the automation system and instrument manufacturers have been providing field management systems for configuration, document and maintenance management of field devices based on the digital technologies. The drawback of
these kind of system is the integration level is quite low as they work parallel. This is often a result of non-standard or poorly supported digital communication techniques.
The concept of total management has become very popular, meaning integration of whole field. This concept is possible only if standard, open and commonly accepted techniques, especially communication techniques, are used.
Even beyond this concept, there is a move in industry to implement enterprise wide connectivity, networking all systems producing and consuming data and distributing real-time control data all the way up to the boardroom. The critical thing is access to all the data, any time, from any place.
Field Devices Digital Technology Advantages
• Flexible configuration
• Easier and calibration
• On-device linearization
• Compensation Capabilities
• Device diagnostics functions
Field Devices :
There are many kind of field devices used in the process industry. Correspondingly the requirements and
expectations vary. Some very basic properties expected from all field devices are solid performance as well as reliability. Both of these areas have been lately improved by utilizing digital technology.
expectations vary. Some very basic properties expected from all field devices are solid performance as well as reliability. Both of these areas have been lately improved by utilizing digital technology.
In addition to improved performance and reliability, the field device digitalization has made it possible to embed many new features into field devices. These features include more flexible and easier configuration and calibration, on-device linearization and compensation capabilities and device diagnostics just to name some of them.
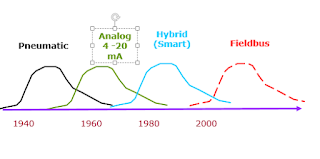
The above Figure shows the increasing functionality seen in field devices. This trend clearly decreases the amount of devices needed in the field, which also inevitably increases the reliability. The 1990’s has been the decade of field device digitalization and there is no way back.
The above Figure shows the increasing functionality seen in field devices. This trend clearly decreases the amount of devices needed in the field, which also inevitably increases the reliability. The 1990’s has been the decade of field device digitalization and there is no way back.
Why Digital Communication ?
Increase in the functionality of the Field Devices increases the amount of Data flowing in and out of device.
Benefit of Digital Communication
• Basic measurement
• Accuracy of measurement
• Less noise in measurement.
• Operating status,
• Ease of Maintenance
• advance diagnostic function.
• Process efficiency
Digital communication :
The need for digital bus is clearly a result from the development trends seen both in automation systems and field
devices. As the functionality of field devices increases, so does the amount of data needed and provided by them.
devices. As the functionality of field devices increases, so does the amount of data needed and provided by them.
One obvious benefit of two way digital communication bus is that it can provide more and any kind of data; data also beyond basic measurement values, such as operating status, maintenance and diagnostic information. As field devices will
be digital any way, a key to process efficiency is the effective use of the wealth of information that’s available from modern field devices. Also the accuracy of measurement information is improved as no unnecessary AD/DA-conversions are performed and interference on bus does not result as noise in measurements.
be digital any way, a key to process efficiency is the effective use of the wealth of information that’s available from modern field devices. Also the accuracy of measurement information is improved as no unnecessary AD/DA-conversions are performed and interference on bus does not result as noise in measurements.
In order to fully utilize all the features in new digital field devices and fulfill the requirements of total management concept, a two way digital communication is a must.
Field Signal Transmission
Technologies and products experience generation change. We have witnessed three generations for field transmission,… they are pneumatic transmission, analog 4-20mA and hybrid of analog and digital (often called “smart”). A new generation of full-digital transmission is in reality now.
Difference between fieldbus and HART
HART Protocol
HART is a open communication protocol, most commonly used in digital field devices connected to 4-20 mA current loop.
In late 80’s Rosemount developed a hybrid solution in which the digital signal was superimposed on a 4-20 mA analog signal. This communication protocol, based on BELL-202 FSK technique with 1200 bit/s, is known as HART.
In early days of digital field devices most manufacturers had proprietary solutions for communication protocols as well as for Human Machine Interface (HMI). Many of these solutions required also additional wires for communication to work. This scheme was greatly changed as communication protocol known as Highway Addressable Remote Transducer (HART) became popular.
In late 80’s Rosemount developed a hybrid solution in which the digital signal was superimposed on a 4-20 mA
analog signal. This communication protocol, based on BELL-202 FSK technique with 1200 bit/s, is known as HART. Later the supervision and further development of HART was handed over to non-profit HART Communication Foundation (HCF).
Nowadays HART is a open communication protocol, most commonly used in digital field devices connected to 4-20 mA current loop. Many of the benefits of digital Fieldbus are available already with HART.
analog signal. This communication protocol, based on BELL-202 FSK technique with 1200 bit/s, is known as HART. Later the supervision and further development of HART was handed over to non-profit HART Communication Foundation (HCF).
Nowadays HART is a open communication protocol, most commonly used in digital field devices connected to 4-20 mA current loop. Many of the benefits of digital Fieldbus are available already with HART.
In HART message definition is divided into three categories; universal commands, common practice commands and
device specific commands. Lot of the functionality, especially all the most advanced features, of field devices is commonly realized by device specific commands. Thus a standardized way to describe this functionality was needed.
For this purpose a Device Description Language (DDL) was created. Standardized DDL used to describe field device capabilities in form of Device Descriptions (DDs) was thought to become one of the key features in HART communication.
device specific commands. Lot of the functionality, especially all the most advanced features, of field devices is commonly realized by device specific commands. Thus a standardized way to describe this functionality was needed.
For this purpose a Device Description Language (DDL) was created. Standardized DDL used to describe field device capabilities in form of Device Descriptions (DDs) was thought to become one of the key features in HART communication.
Fieldbus
Fieldbus in general is a bi-directional communication protocol and can be thought as a Local Area Network (LAN) for factory floor instrumentation and control devices.
Fieldbuses in general are bi-directional communication protocols and can thought as Local Area Network (LAN) for factory floor instrumentation and control devices. Communication in automation systems has been traditionally divided into three levels.
Benefits of using digital bus
include of course all benefits of digital communication mentioned earlier. In addition to those, digital bus in general means savings in space needed (enclosures, cross connection), labour costs (design, installation, maintenance) and HW (cabling, enclosures).
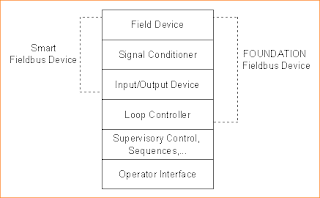
Fieldbus System Overview
The Fieldbus application architecture supports distribution of automation tasks to the devices in the field which are interconnected by a network.
The Fieldbus interconnection architecture is based on a three-layer subset of the architecture from the OSI (open systems interconnect) reference model developed by ISO (International Organization for Standardization).
The Fieldbus application architecture supports distribution of automation tasks to the devices in the field which are interconnected by a network. The most basic functions performed by a device are modeled as blocks. The blocks cooperate and are interconnected with each other, supporting the propagation parameters between devices, and the
operator.
The Fieldbus interconnection architecture is based on a three-layer subset of the architecture from the OSI (open systems interconnect) reference model developed by ISO (International Organization for Standardization). The OSI application and system management, and likewise the Fieldbus application architecture, models are based on Object Oriented programming (OOP) concepts. Both OSI and OOP use models to simplify understanding of functionality. Both are also briefly introduced in this tutorial to achieve a better understanding of Fieldbus.
operator.
The Fieldbus interconnection architecture is based on a three-layer subset of the architecture from the OSI (open systems interconnect) reference model developed by ISO (International Organization for Standardization). The OSI application and system management, and likewise the Fieldbus application architecture, models are based on Object Oriented programming (OOP) concepts. Both OSI and OOP use models to simplify understanding of functionality. Both are also briefly introduced in this tutorial to achieve a better understanding of Fieldbus.