The rubber lining types that are covered in this guideline are:
SOFT NATURAL RUBBERS.
EBONITES (HARD RUBBERS).
NEOPRENE.
HYPALON.
EPDM.
BUTYL.
CHLOROBUTYL.
NITRILE.
How To Select The Proper Lining
A careful analysis of all the details of the service conditions must be identified before selecting the right lining material. The following data must be taken into consideration:
Composition and concentration of the chemical.
Impurities, if any.
Temperature, maximum, minimum and time cycle.
Pressure or vacuum or alternating cycle.
If abrasives present, percentage, size and velocity.
Size and shape of equipment or tank to be lined.
Indoor or outdoor service.
The information given in Tables 1 and 2 must be used by SABIC and its contractors when designing, specifying and installing chemical and/or abrasion resistant rubber linings.
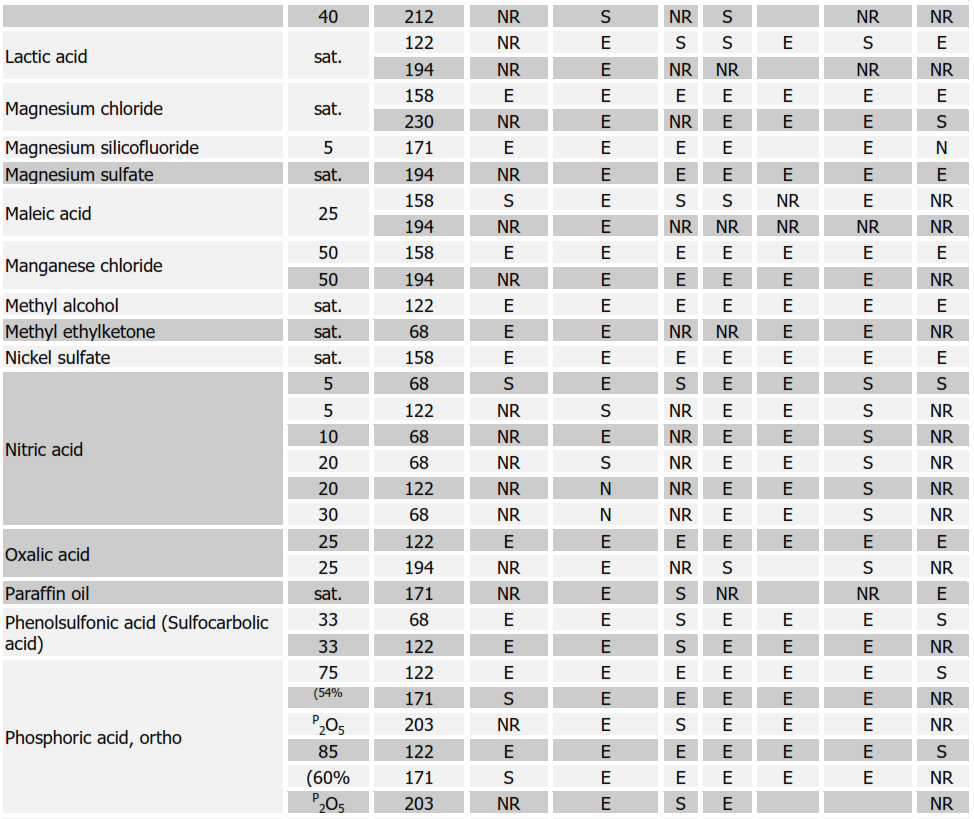
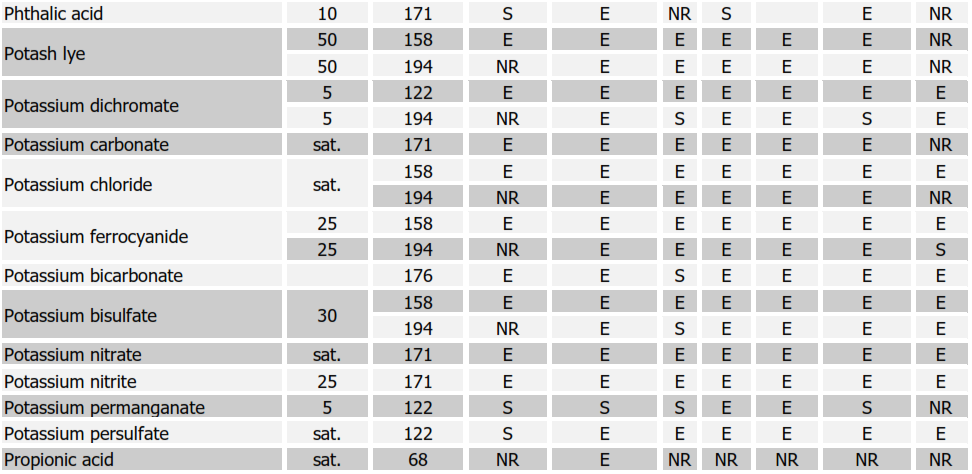
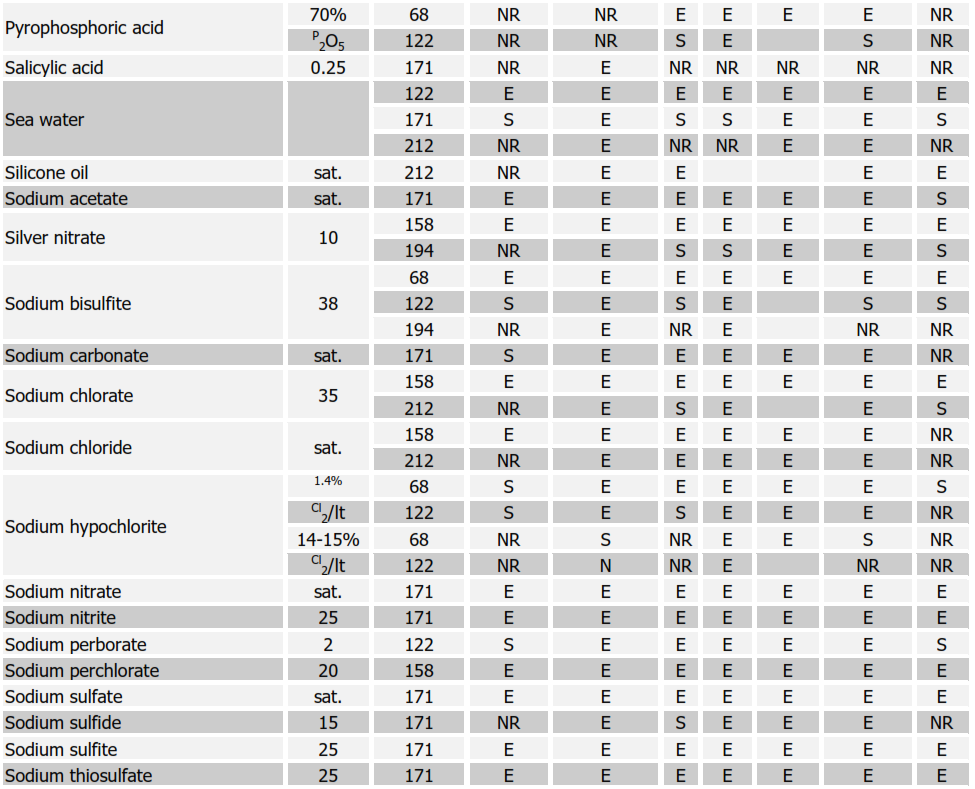
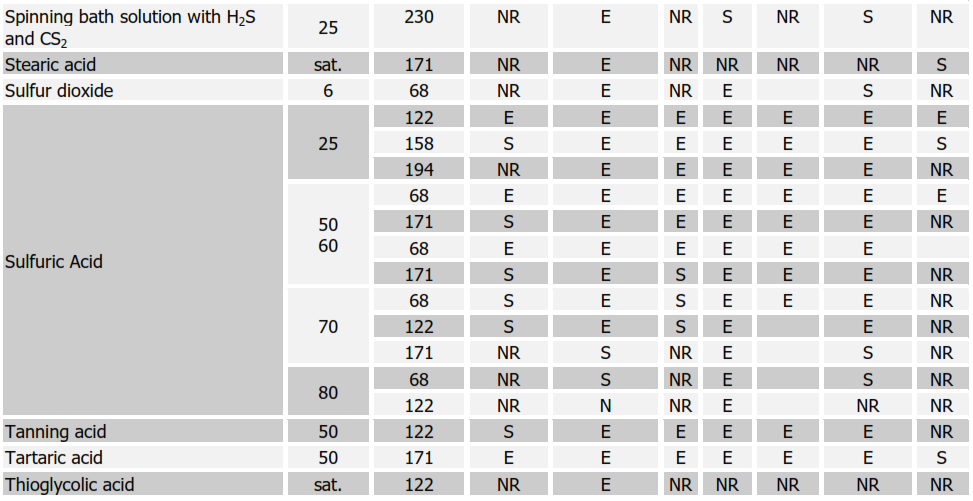
Table 1. Characteristics and typical uses of the different types of rubber linings
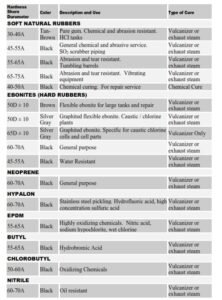
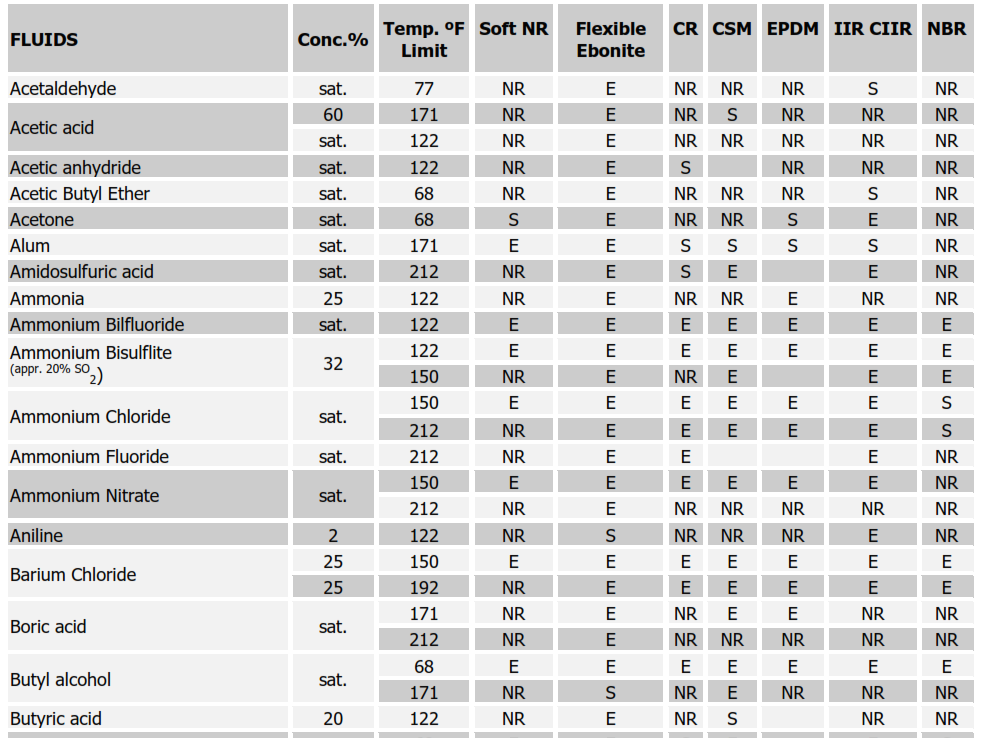
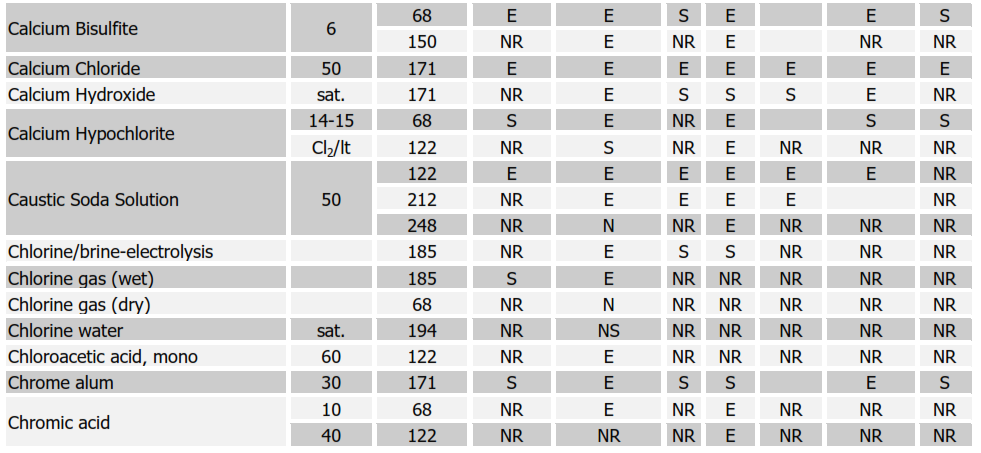
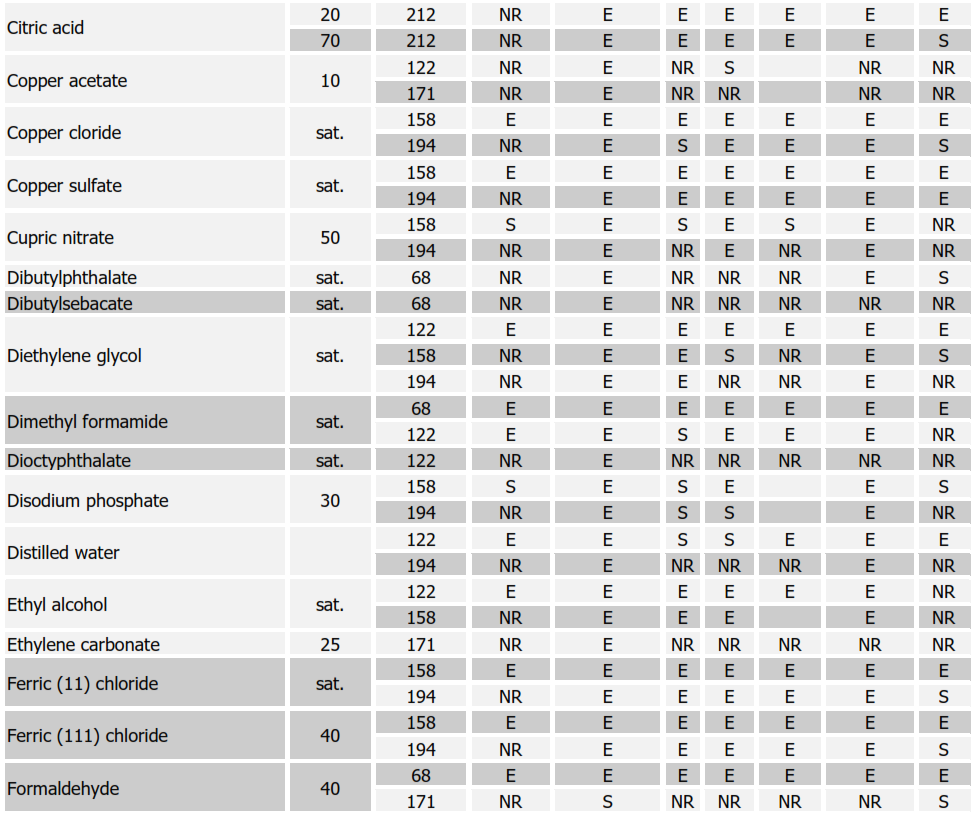
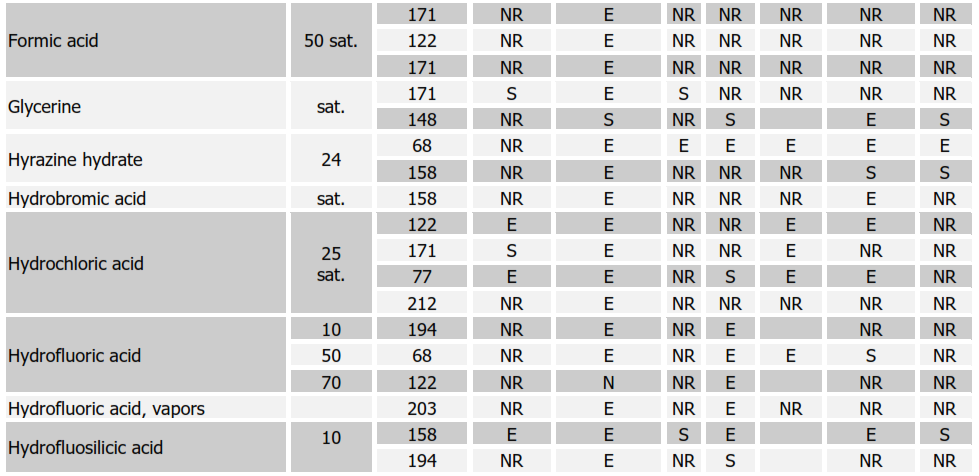
Chemical Resistance Chart for Rubbers
SYMBOLS:
E = EXCELLENT, S = SATISFACTORY, NR = NOT RECOMMENDED Soft Natural Rubber (NR); Nitrile (NBR); Neoprene (CR); Butyl (IIR); Chlorobutyl (CIIR); Hypalon (CSM)
Vessel Fabrication
All welded joints shall be continuous and ground smooth to a minimum of 1/8″ radius for convex corners and to a minimum of 1/4″ radius for concave corners.
All surfaces shall be free of weld splatter of foreign material.
Voids, gaps, holes, pockets or undercut welds are not permitted.