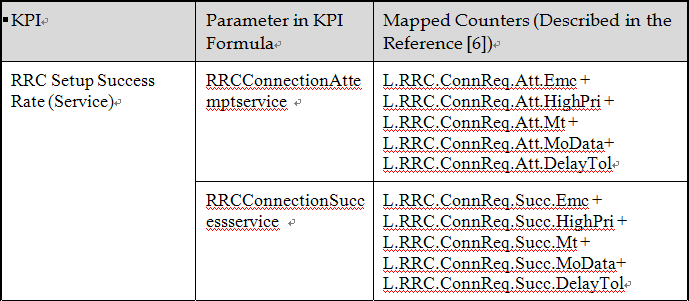
1. RRC Setup Success Rate (Service)
The RRC (Radio Resource Control) setup procedure in LTE is initiated for various reasons, identified by the establishmentCause field in the RRCConnectionRequest message. These reasons include:
- emergency
- highPriorityAccess
- mt-Access (mobile terminating access)
- mo-Signaling (mobile originating signaling)
- mo-Data (mobile originating data)
- delayTolerantAccess-v1020
The UE (User Equipment) sets the establishmentCause and this is received by the eNodeB (Evolved Node B). For KPI (Key Performance Indicator) purposes, causes other than mo-Signaling are categorized as service-related, while mo-Signaling is categorized as signal-related.
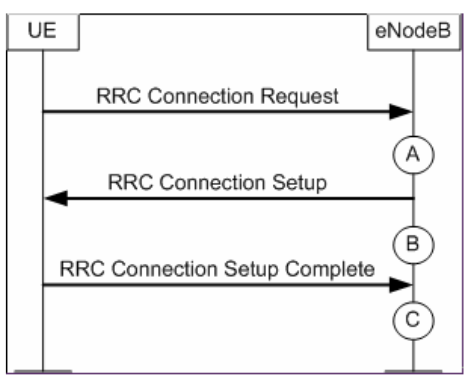
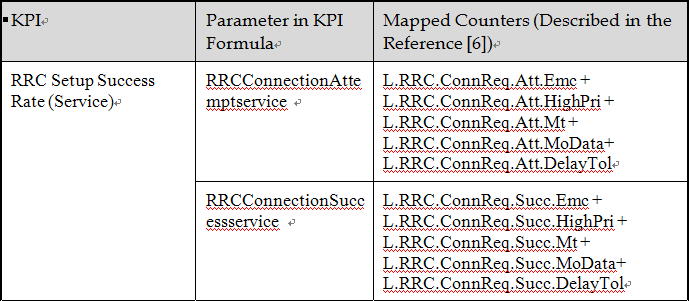
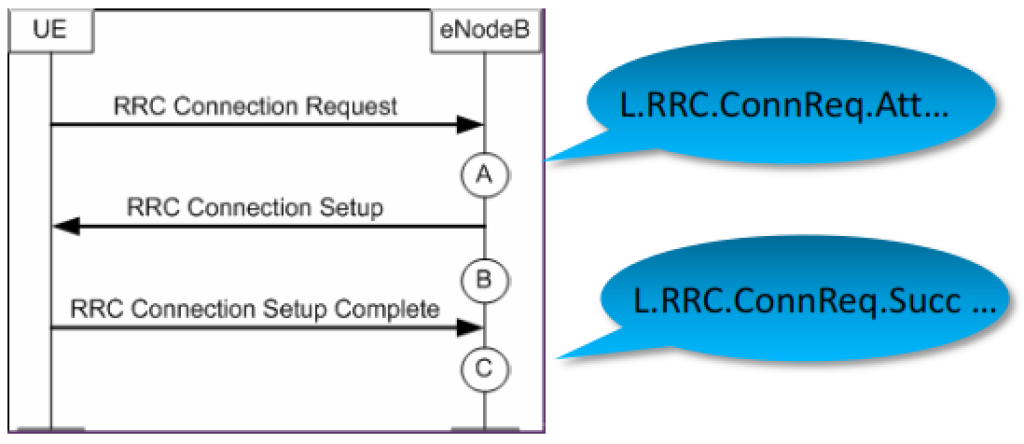
The RRC Setup Success Rate (Service) KPI evaluates the success rate of RRC setups with service-related causes in a specific cell or cluster.
RRC Setup Success Rate (Signal)
This KPI evaluates the RRC setup success rate specifically for the signal-related cause (mo-Signaling) in a cell or cluster.
These two KPIs help in assessing the performance of the RRC setup process by distinguishing between service-related and signal-related causes, providing valuable insights for network optimization.
2. Counter Mapping for RRC SSR.
LTE-SAE QoS Class Identifier
In LTE, there are nine QCIs (QoS Class Identifiers) defined by 3GPP TS 23.203. Each QCI has its own QoS requirements, and each E-RAB (Evolved Radio Access Bearer) is assigned a QCI attribute.
| QCI | Resource type. | Priority | Packet delay budget (ms). | Packet error loss rate. | Example services. |
| 1 | GBR | 2 | 100 | 10−2 | Conversational voice. |
| 2 | GBR | 4 | 150 | 10−3 | Conversational video (live streaming) |
| 3 | GBR | 5 | 300 | 10−6 | Non-conversational video (buffered streaming). |
| 4 | GBR | 3 | 50 | 10−3 | Real time gaming. |
| 5 | Non-GBR | 1 | 100 | 10−6 | IMS signalling. |
| 6 | Non-GBR | 7 | 100 | 10−3 | Voice, video (live streaming), interactive gaming. |
| 7 | Non-GBR | 6 | 300 | 10−6 | Video (buffered streaming). |
| 8 | Non-GBR | 8 | 300 | 10−6 | TCP-based (e.g. WWW, e-mail) chat, FTP, p2p file sharing, progressive video, etc. |
| 9 | Non-GBR | 9 | 300 | 10−6 |
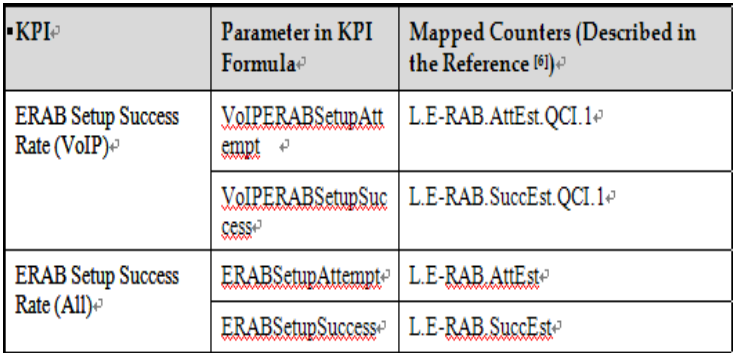
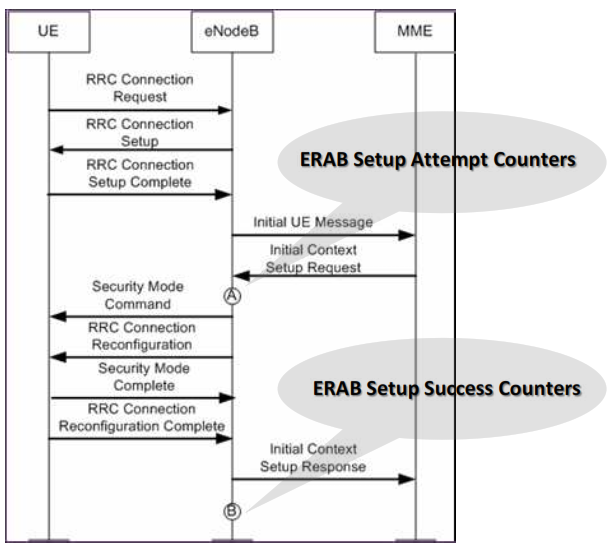
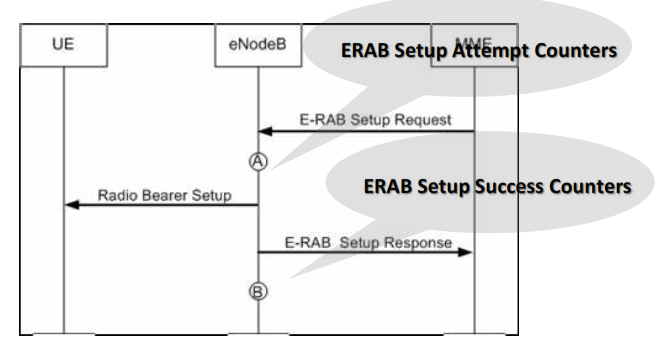
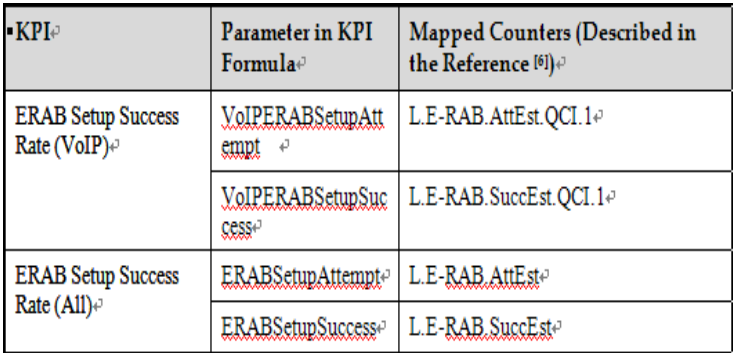
3. ERAB Setup Success Rate.
VoIP ERAB Setup Success Rate: This KPI measures the success rate of ERAB setups for VoIP services (QCI 1) in a specific cell or cluster. The formula for calculating this KPI is:
ERAB Setup Success Rate (All): This KPI measures the success rate of ERAB setups for all services, including VoIP, in a specific cell or cluster. The formula for this KPI is:

4. Counter Mapping for ERAB SSR.
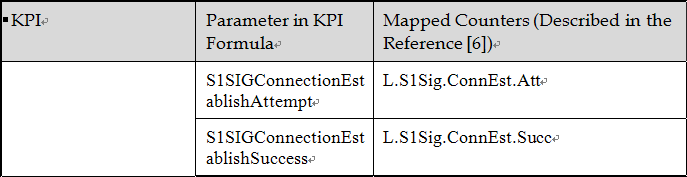
Call Setup Success Rate.
VoIP Call Setup Success Rate (VoIP CSSR): This KPI evaluates the success rate of the entire call setup procedure for VoIP services (QCI 1) in a cell or cluster. This procedure includes three main phases: RRC setup, S1 signaling connection establishment, and VoIP E-RAB setup. The formula for calculating VoIP CSSR is:
Call Setup Success Rate (All): This KPI measures the call setup success rate for all services, including VoIP, in a cell or cluster. It also includes the three main phases: RRC setup, S1 signaling connection establishment, and service E-RAB setup. The formula for calculating CSSR (All)
These KPIs are critical for evaluating and optimizing the performance and reliability of LTE networks, ensuring high-quality service for end users.
Counter Mapping for CSSR.