Packet Data Protocol (PDP) context activation is a procedure in GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) and later mobile communication technologies like UMTS and LTE. It establishes a data session between the mobile device (User Equipment – UE) and the packet data network, enabling data transfer services.
PDP Context Activation Procedure (Session Management).
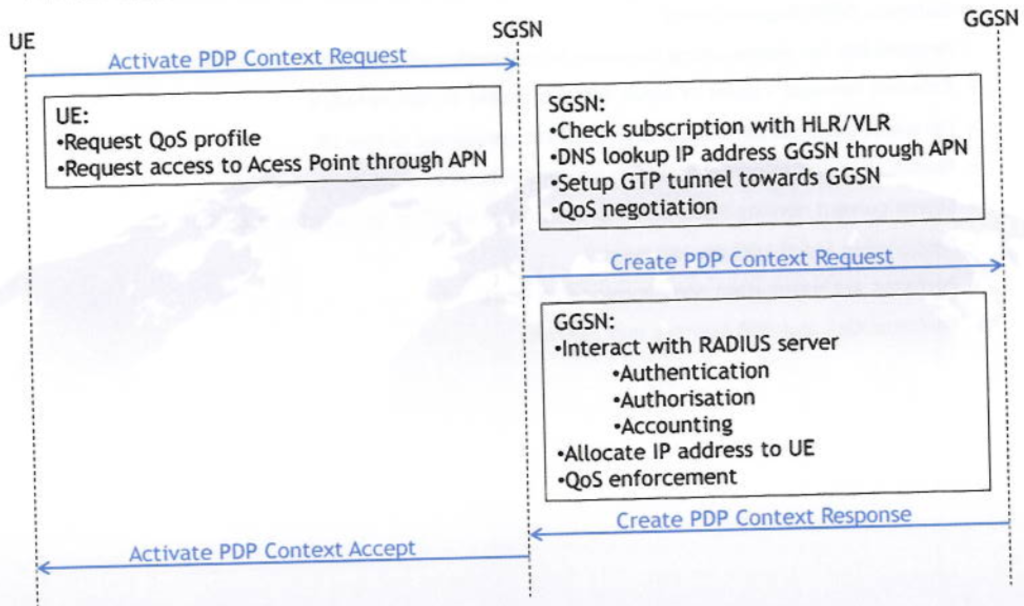
With the NAS message Activate PDP Context Request, the UE is requesting a Quality of Service profile and access to a specific Access Point (APN: Access Point Name, an IP network to which a mobile can be connected ) related to the service to be used. When receiving this message the SGSN will check the UE subscription with the HLR/VLR, and a DNS lookup will be performed to translate the APN name to the IP address of the concerned GGSN.
Next a GTP (GPRS Tunnelling Protocol) tunnel is setup towards the concerned GGSN and QoS negotiation is started by sending the following message from SGSN to GGSN: Create PDP Context Request.
The GGSN will interact with the RADIUS server to perform authentication, authorisation and accounting. The GGSN allocates an IP address to the UE and takes final decision on the allocated Quality of Service level. A response (Create POP Context Response) is sent back to the SGSN, and the procedure is completed with the downlink NAS message Activate PDP Context Accept.
The PDP context is a data structure present on both the SGSN and GGSN which contains the subscriber’s session information when the subscriber has an active session. When a mobile wants to use PS data, it must first attach and then activate a PDP context. This allocates a PDP context data structure in the SGSN that the subscriber is currently visiting and the GGSN serving the subscribers access point.
PDP Context Activation Procedure (SM) – GGSN.
- Gateway GPRS Support Node.
- Responsible for interworking between 3G network and external PS networks (e.g. internet).
- External network’s point of view: GGSN is router to sub-network.
- Forwards external data to serving SGSN for concerned active UE.
- Routes UE originating data packets to right external network.
- Stores current serving SGSN address and profile of UE in its location register.
- Responsible for IP address assignment.
- Performs authentication and charging functions.
- Performs QoS and PDP Context enforcement.
The above brief points gives a complete overview of the tasks performed by the GGSN. As can be seen, the GGSN is not only responsible for QoS negotiation and UE IP address allocation, but many other tasks are performed by this network element.
PDP Context Activation Procedure (SM)
- Used to manage QoS profile between UE and SGSN/GGSN.
- Allocates IP address to UE.
- Trigger for RAB setup.
- Data transfer can start upon completion of PDP Context activation procedure.
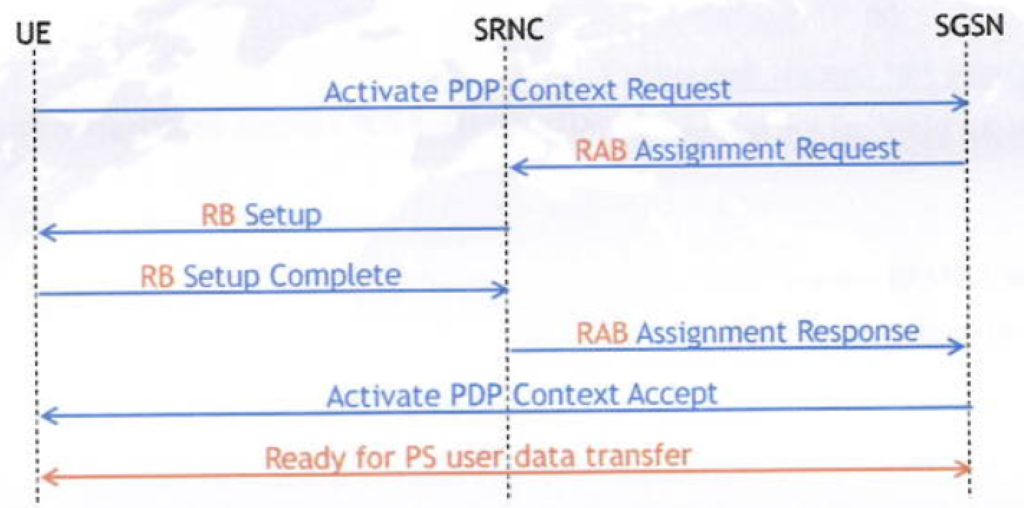
As mentioned before the PDP Context activation procedure is used to manage the QoS profile between UE and SGSN/GGSN, and to allocate an IP address to the UE. This procedure is also triggering the RAB (Radio Access Bearer) Setup procedure, resulting in a bit pipe between UE and SGSN. The data transfer can only start upon completion of the PDP Context activation procedure.
PDP Context deactivation procedure (SM).
- Trigger for RAB/RB release.
- Can be initiated by UE or SGSN.

The PDP Context deactivation procedure is used to release the QoS profile and UE allocated IP address. This procedure triggers the release of RAB/RB, and can be initiated by UE or SGSN. The procedure consists of two messages: Deactivate PDP Context Request and Deactivate PDP Context Accept.
Key Functions
- Establish Data Session: Sets up a data connection for internet access, email, and other data services.
- Allocate Network Resources: Ensures appropriate network resources are allocated for the data session.
- Assign IP Address: Assigns an IP address to the UE for data communication.
Steps in PDP Context Activation Procedure
- PDP Context Activation Request: The UE sends a PDP Context Activation Request to the Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN). This request includes information such as the PDP type (IPv4, IPv6), requested QoS (Quality of Service), and Access Point Name (APN).
- SGSN Processing: The SGSN processes the request and checks the subscription data to verify if the requested APN and QoS are allowed for the user. If the subscription check passes, the SGSN proceeds with the next steps.
- GGSN Interaction: The SGSN sends a Create PDP Context Request to the appropriate Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) based on the APN. The GGSN is responsible for interfacing with the external packet data network.
- IP Address Allocation: The GGSN assigns an IP address to the UE and allocates necessary resources for the data session. It then sends a Create PDP Context Response back to the SGSN, confirming the successful setup.
- SGSN Updates: Upon receiving the response from the GGSN, the SGSN updates its records with the PDP context information, including the IP address assigned to the UE.
- PDP Context Activation Accept: The SGSN sends a PDP Context Activation Accept message to the UE, including the allocated IP address, the agreed QoS parameters, and other relevant details.
- UE Confirmation: The UE receives the activation accept message, confirms the details, and establishes the data session using the allocated IP address and QoS settings.
Key Messages in PDP Context Activation
- PDP Context Activation Request: Sent by the UE to initiate the activation procedure.
- Create PDP Context Request: Sent by the SGSN to the GGSN to allocate resources and assign an IP address.
- Create PDP Context Response: Sent by the GGSN to the SGSN confirming resource allocation and IP address assignment.
- PDP Context Activation Accept: Sent by the SGSN to the UE confirming successful activation.
Example Scenario
- User Requests Data Service: A user initiates a data session by opening a web browser or any data application on the UE.
- PDP Context Activation Request Sent: The UE sends a PDP Context Activation Request to the SGSN.
- SGSN Verifies Subscription: The SGSN checks if the user is allowed to access the requested APN and QoS.
- SGSN Contacts GGSN: The SGSN sends a Create PDP Context Request to the GGSN.
- GGSN Allocates IP Address: The GGSN assigns an IP address and allocates resources, then sends a Create PDP Context Response to the SGSN.
- SGSN Updates Context: The SGSN updates its records and sends a PDP Context Activation Accept message to the UE.
- UE Establishes Data Session: The UE uses the allocated IP address and QoS settings to establish the data session.
Conclusion
The PDP Context Activation procedure is essential for establishing data sessions in mobile networks. It involves multiple steps, including requesting activation, verifying subscription data, allocating IP addresses, and confirming resource allocation. This procedure enables the UE to access data services and communicate with external networks efficiently.