Prerequisite of following article to start reading this article Hazardous Area Classification NEC.
Principles of Class I Areas – Hazardous Area Classification NEC
Class I areas are areas in which the combustible material is a gas or vapor.
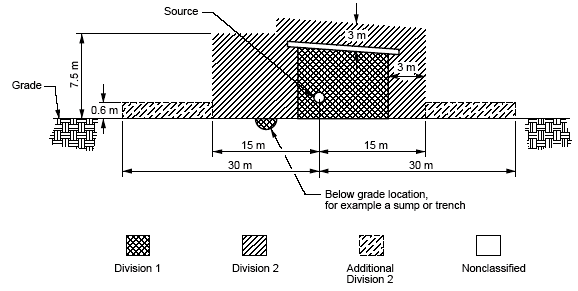
Division 1
- In Division 1 locations, an explosive or ignitable mixture of gas or vapor may be continuously present under normal conditions of operation.
- Electrical installations in Division 1 areas shall be designed in a way that under normal operating conditions, as well as under failure, the system shall not release flame, sparks or hot gases, nor will it result in surface temperatures high enough to ignite the surrounding atmosphere.
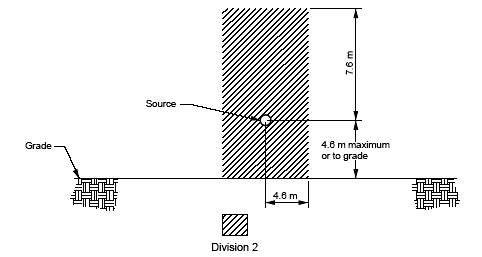
Division 2
- In Division 2 locations, an explosive or ignitable mixture of gas or vapor may be present only under abnormal conditions of operation, for example process equipment failure.
- Electrical installations in Division 2 areas shall be designed in a way that under normal operating conditions they shall not provide a source of ignition, and that protection from ignition during an electrical malfunction shall not be required.
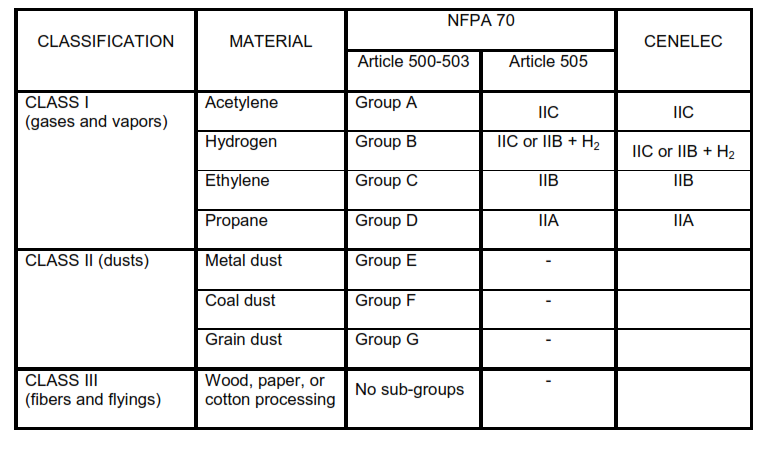
Groups
See .
Enclosures
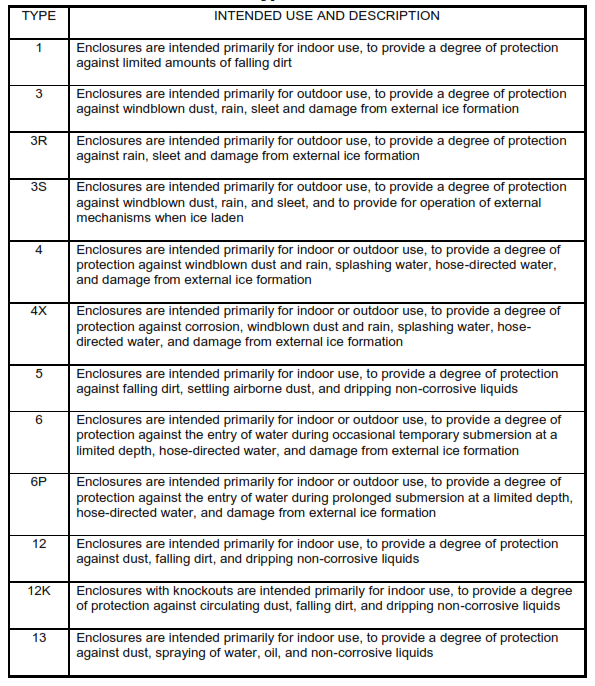
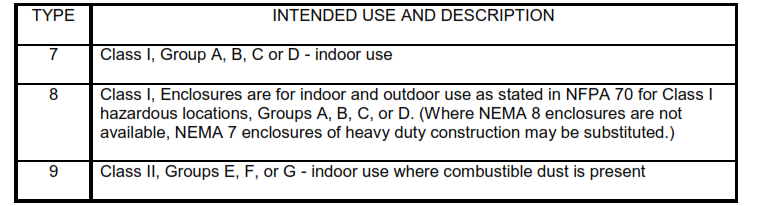
NEMA enclosure types for hazardous and non-hazardous location shall be selected from Tables I and II.
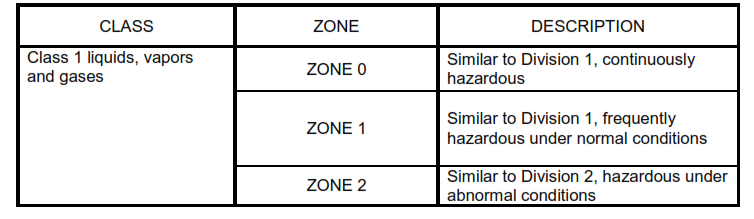
Zone System
- NFPA 70, Article 505 presents an alternative Zone Classification system, similar to but not the same as the three zone system of IEC 60079-10. Table III compares the area classification of zone system with NFPA 70 Division system. See Tables V, VI and VII for further comparisons between NFPA 70 Zone classifications system, and other international classification systems.
- Equipment meeting any of the conditions described in NFPA 70, Article 505 shall be marked with following information in the order shown:
a. Class
b. Zone
c. Symbol ‘Aex’ – Symbol for equipment built to American standards
d. Types of protection designation, in accordance with NFPA 70, Article 505, Table 505-10(b)(1)
e. Applicable gas certification group(s) in accordance with NFPA 70, Article 505, Table 505-10(b)(2)
f. Temperature classification in accordance with NFPA 70, Article 505, Table 505-10(b)
Figure 9 – Lighter Than Air Flammable Gas or Vapor in an Adequately Ventilated Area
Figure 10 – Heavier Than Air Flammable Gas or Vapor Indoors in an Inadequately Ventilated Area
Conditions Necessary for Ignition
In Class I locations three conditions have to be satisfied simultaneously to cause ignition:
a. A combustible gas or vapor has to be present in an atmosphere surrounding electrical equipment
b. The gas or vapor has to be mixed with the correct proportion of air to cause ignition
c. An energy release or temperature rise from electrical or other equipment, intense enough to cause ignition of the gas or vapor, has to occur
Characteristics of Flammable and Combustible Materials
- Flammable Mixtures. Flammability is defined as follows:
a. The range of concentrations of vapors or gases where ignition can occur is defined as the flammability range
b. Concentrations of vapors or gas too lean to support ignition are defined as being below the lower flammable limit (LFL)
c. Concentrations of vapors or gases too rich to support ignition are defined as being above the upper flammable limit (UFL)
d. See Figures 9 and 10 for illustrations of the above described principles - Flash Point. This is the lowest temperature at which the liquid gives off sufficient vapor to produce an ignitable concentration with air in the vapor space above the liquid. The lower the flashpoint, the higher the risk of ignition.
- Ignition Energy. This is the minimum energy required for ignition, which requires a spark of sufficient intensity and duration to ignite flammable gas or vapor mixtures.
Gas or Vapor Mixtures of Different Ignition Temperatures
The ignition temperature of the mixture shall be that of the individual gas or vapor with the lowest individual ignition temperature as specified in NFPA HAZ10.
Gas or Vapor Mixtures of Different Densities
- Mixtures composed entirely of heavier-than-air gases or vapors shall be classified as heavier-than-air.
- For mixtures composed of both heavier-than-air and lighter-than-air gases or vapors: a. If the density of the mixture is greater than 75 percent of the density of air at standard conditions, it shall be classified as heavier-than-air
b. If the density of the mixture is less than 75 percent of the density of air at standard conditions, it shall be classified as lighter-than-air - Mixtures composed entirely of lighter-than-air gases or vapors shall be classified as lighter-than-air.
Gas or Vapor Mixtures of Different Groups
Where the mixture contains different Groups, as defined by NFPA 70, Article 500, the area classification requirements of every Group which constitutes 30 percent or more of the total mixture shall be fulfilled. (See section 3, Class I Group Definitions).
Ventilation
- Ventilation shall be used for the prevention of fire and explosion, and shall be considered adequate if capable of preventing the formation of significant quantities of a gas or vapor in air at concentrations above 25 percent of the lower flammable limit.
- Facilities where combustible gases and vapors may be present shall be located outdoors whenever possible, in areas with adequate natural ventilation.
- When facilities where combustible gases or vapors may be present have to be located indoors, natural ventilation should be achieved by the use of open walls, fixed open louvers and open gratings.
- In enclosed indoor areas where combustible gases or vapors may be present, and natural ventilation cannot be achieved, artificial means of ventilation should be used to reclassify the area to a less severe classification, but not as unclassified.
- For flammable liquids with heavier-than-air vapors, ventilation shall be arranged to ventilate all areas (particularly floor areas) where flammable vapors might collect.
- For lighter-than-air gases, roof or wall openings shall be arranged to ventilate all areas (particularly ceiling areas) where gases might collect.
- Enclosed areas (rooms, buildings, or spaces) that are provided at least 1.0 cubic foot of air volume flow per square foot of floor area per minute, but at least six (6) air changes per hour, shall be considered as adequately ventilated. This ventilation rate may be accomplished by either natural or mechanical means.
Air Purging
Where practical, purging or pressurization of electrical equipment enclosures, to unclassify the interiors and allow operation in combustible atmospheres shall be permissible. Equipment shall be in conformance with NFPA 496.
TABLE I – NEMA Enclosure Types for Non-Hazardous Locations
TABLE II – NEMA Enclosure Types for Hazardous Locations
Table III – Area Zone Classification NEC 505
TABLE V – Comparison of NFPA 70 and European Hazard Categories
TABLE VI – Classification Based on Hazard Type
Note: The table may be used to convert NEMA type numbers to nonhazardous IEC classification designations. This table cannot be used to convert IEC classification designations to NEMA type numbers.
TABLE VIII – Auto Ignition and Flammability of Combustible Mixtures in Air – Check following documents
TABLE IX – Electrical Conductivity of Liquids – Check following documents
Hazardous Area Classificatio Tables 8 and 9
Subsequent Articles for this post are
Principles of Class II Areas – Hazardous Area Classification NEC
Principles of Class III Areas – Hazardous Area Classification NEC