Testing a Ring Main Unit (RMU) is crucial to ensure its proper functioning, reliability, and safety in an electrical distribution system. Below is a general test procedure for a Ring Main Unit. Please note that specific procedures may vary based on the manufacturer’s guidelines and equipment specifications. Always refer to the manufacturer’s documentation for the most accurate and detailed information.
To guide the responsible persons in conducting Ring Main Unit Tests.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS – The following Safety precautions shall be taken in consideration prior, during and after conducting the test measurements.
- Safety tagging shall be implemented.
- Isolate the Area by Safety Warning Tape.
- Keep a Safe Distance from the device being tested.
- Wear Appropriate Personal Protective Equipment(PPE) Prior to starting any testing activity.
- Implementation of Proper Grounding.
TEST EQUIPMENTS: Megger IR test Kit; Contact Resistance Test Kit, Breaker Analyzer Test Kit.
Ring Main Unit (RMU) Test Procedure
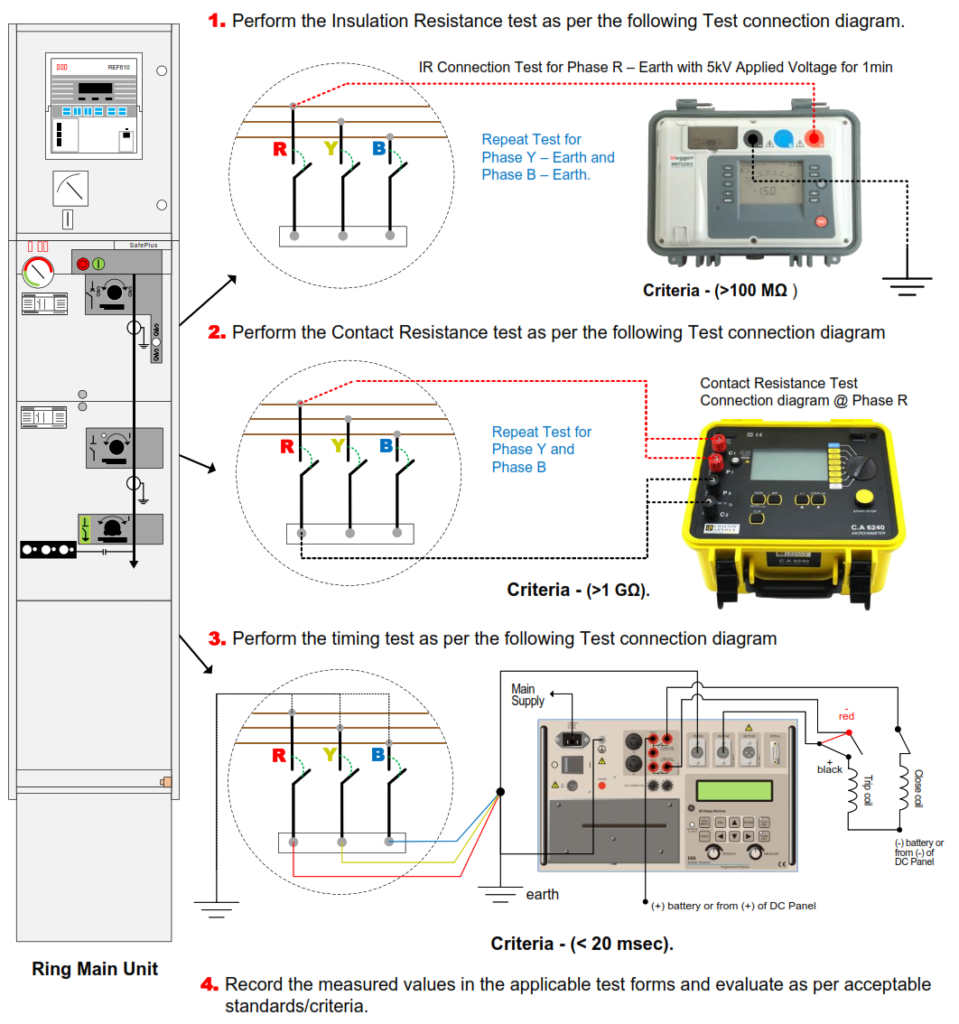
1. Perform the Insulation Resistance test as per the following Test connection diagram.
2. Perform the Contact Resistance test as per the following Test connection diagram.
3. Perform the timing test as per the following Test connection diagram.
4. Record the measured values in the applicable test forms and evaluate as per acceptable
standards/criteria.
General Instruction Points:
- Visual Inspection:
- Inspect the RMU for any visible signs of damage, wear, or loose connections.
- Verify that the RMU is properly grounded.
- Check for proper labeling and signage.
- Insulation Resistance Test:
- Measure the insulation resistance using an insulation resistance tester.
- Measure resistance between phases and between each phase and ground.
- Ensure that insulation resistance values meet or exceed specified limits.
- Contact Resistance Test:
- Perform a contact resistance test using a contact resistance tester.
- Measure the resistance of each main and auxiliary contact.
- Compare the measured values with the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Functional Test:
- Verify the functionality of the RMU by simulating various operating conditions using a secondary injection test set.
- Check the operation of circuit breakers, switches, relays, and other control devices.
- Verify the proper functioning of interlocks and alarms.
- Micro-Ohmmeter Test:
- Measure the resistance of critical connections using a micro-ohmmeter.
- Ensure that the resistance values are within acceptable limits.
- Earth Resistance Test (if applicable):
- Perform an earth resistance test to ensure proper grounding.
- Verify that the earth resistance values comply with specifications.
- Thermal Imaging:
- Use a thermal imaging camera to identify any hotspots or abnormalities in the RMU.
- Pay special attention to connections, busbars, and any components under load.
- High Voltage Test (if applicable):
- If specified by the manufacturer, perform a high voltage test to ensure the insulation can withstand higher-than-normal voltages.
- Verification of Protection Settings (if applicable):
- Check and verify the settings of protection relays.
- Ensure that the protection system operates as intended during fault simulations.
- Documentation:
- Record all test results, including measurements and observations.
- Compare the results with the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Document any deviations from specifications and actions taken to address them.
- De-Energization:
- Safely de-energize the RMU.
- Restore any safety devices or barriers that were removed for testing.
- Report:
- Prepare a comprehensive test report summarizing the procedures, results, and any recommended actions.
- Include any deviations from specifications and actions taken to address them.
Always prioritize safety during testing, and follow all safety guidelines and procedures. If you are not familiar with the testing procedures or if there are any doubts, consult with qualified personnel or the equipment manufacturer.