Surge and Compressor Choke in Compressor Control System
What is Surge?
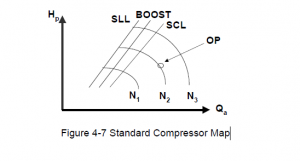
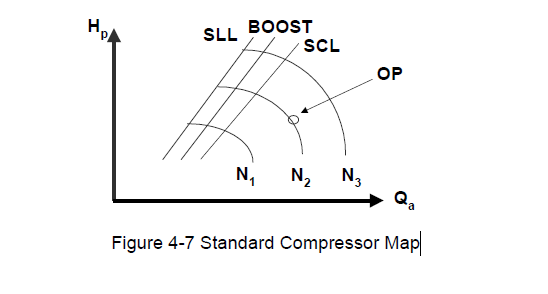
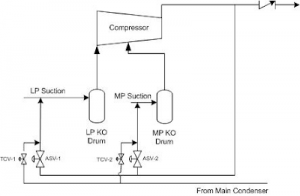
Since the fundamental purpose of any compressor control is to prevent or limit the effects of surge, it is appropriate to review the phenomenon itself. Surge occurs when the low flow operation limit of a compressor has been exceeded, resulting in flow reversal.
It is an unstable, pulsating condition that is usually evident by an audible boom, piping vibration, rapid increase in discharge temperature and oscillation of flow and discharge pressure. Violent surging may cause the following compressor damage:
• Open internal clearances which damage impeller seals and balance piston seals.
• Damage the compressor shaft end seals.
• Damage the compressor thrust bearings.
• Damage the compressor radial bearings.
• Cause impellers to rub against stationary diaphragm.
• Cause a shaft coupling failure.
• Possible shearing of drive shaft.
Along with compressor damage, the process flow and pressure can become very unstable contributing to upstream and downstream process upsets.
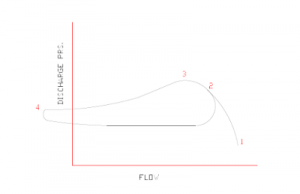
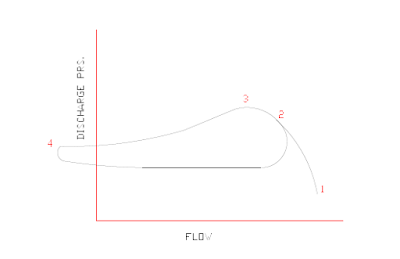
Figure shows a simple surge cycle at a constant speed and constant suction pressure. At point 1 of surge cycle we have low discharge point and high flow rate. As the system resistance increases (e.g. discharge valve closes, downstream processes shutdown or decrease load, series units drop off-line, or parallel units come on-line), the compressor flow decreases, and discharge pressure increases.
At point 2 of surge cycle is very near to surge limit and here flow countinues to decreas and discharge pressure will be increase. At point 3 of surge cycle finally stage comes where by due to system resistance compressor can not increase discharge pressure.
If the system resistance increases further, the discharge pressure becomes greater than the machine’s capability. This initiates a surge that spans between points 3 and 4. Flow may actually reverse through the compressor, as shown at point 4. A now reduced system resistance will allow increased flow back through the compressor that brings the operation back to point 2.
Read more