Traffic KPIs are essential for measuring the traffic volume and user activity on the LTE radio access network (RAN). These KPIs are classified into several categories based on traffic types, including radio bearers, downlink traffic volume, uplink traffic volume, average user number, and maximum user number.
LTE Traffic KPIs.
1. Radio Bearers.
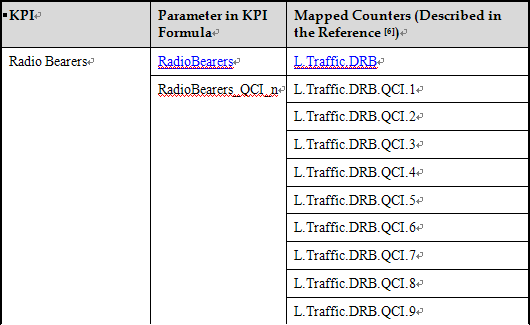
The Radio Bearers KPI consists of ten sub-KPIs. One KPI represents the total number of radio bearers, while the other nine correspond to different QCIs (Quality of Service Class Identifiers). These sub-KPIs indicate the average number of radio bearers in a cell or on a radio network. The radio bearers for each QCI are based on the number of active RRC (Radio Resource Control) connections per QCI, as defined in the QoS (Quality of Service) information.
The Radio Bearers KPIs are detailed in Table below, with each KPI mapped to its corresponding counter.

2. Downlink Traffic Volume.
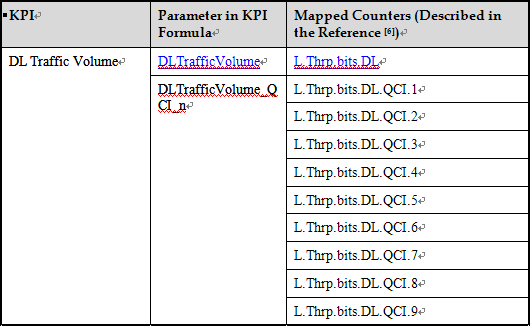
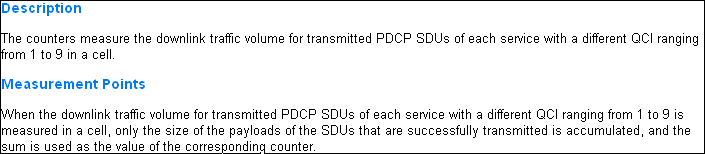
Similar to the Radio Bearers KPI, the Downlink Traffic Volume KPI consists of ten sub-KPIs. One KPI corresponds to the total DRB (Data Radio Bearer) traffic volume, and the other nine correspond to the nine QCIs. These sub-KPIs indicate the downlink traffic volume in a cell, measured at the PDCP (Packet Data Convergence Protocol) layer, excluding the PDCP header.
The Downlink Traffic Volume KPI is detailed in Table below.
3. Uplink Traffic Volume.
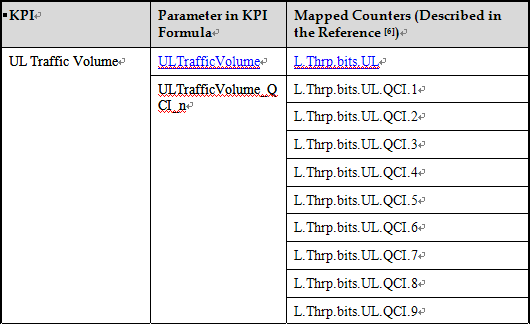
The Uplink Traffic Volume KPI is similar to the Downlink Traffic Volume KPI and also consists of ten sub-KPIs. One KPI represents the total uplink traffic volume for DRBs, and the other nine correspond to the nine QCIs. These sub-KPIs indicate the uplink traffic volume in a cell, measured at the PDCP layer, excluding the PDCP header.
The Uplink Traffic Volume KPI is detailed in Table below.

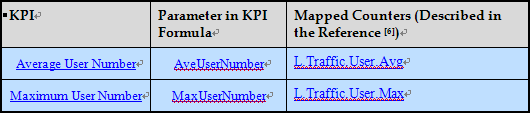
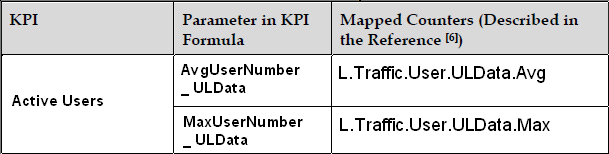
4. Average User Number.
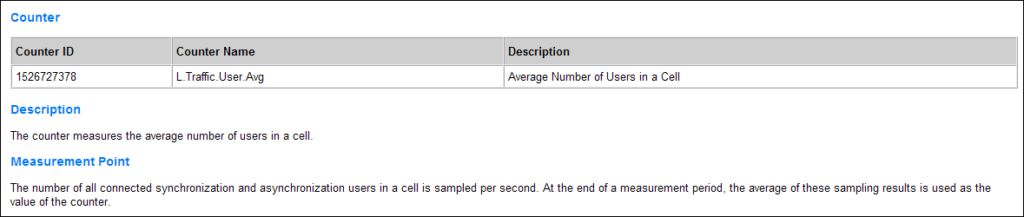
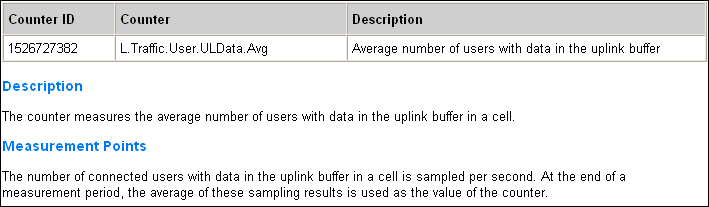
This KPI indicates the average number of users in RRC_Connected mode in a cell. It is calculated based on samples taken every second by the eNodeB, which records the number of users in the cell and then calculates the average value over the measurement period.
The Average User Number KPI is detailed in Table below, with its formula mapped to corresponding counters.
- AvgUserNumber
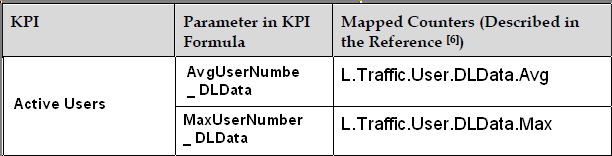
- AvgUserNumber DLData
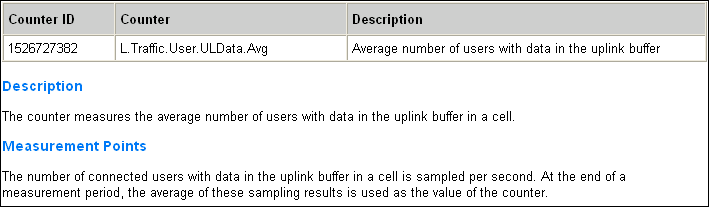
- AvgUserNumber ULData
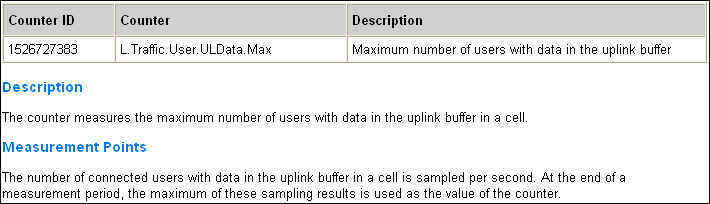
5. Maximum User Number.
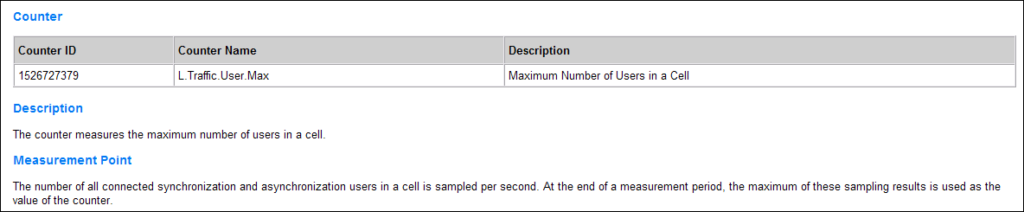
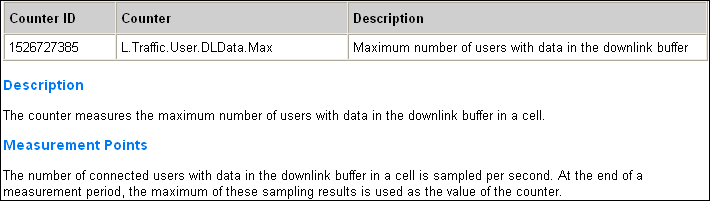
This KPI measures the maximum number of users in RRC_Connected mode in a cell during a specific period. It is calculated based on samples taken every second by the eNodeB, which records the number of users in the cell and then calculates the maximum value of these samples over the measurement period.
The Maximum User Number KPI is detailed in Table above, with its formula mapped to corresponding counters.
- MaxUserNumber.
- MaxUserNumber DLData.
- MaxUserNumber ULData.



By closely monitoring these KPIs, network operators can ensure optimal performance, manage network resources effectively, and address any issues that may impact user experience.