Fossil fuels are like buried treasures from the past. They’re made from ancient plants and animals that lived millions of years ago. These plants and animals got their energy from the sun, just like we do today. Over time, their remains got buried under layers of rock and dirt. As the years passed, the pressure and heat from the Earth turned these remains into fossil fuels.
We rely on fossil fuels for a lot of things in our modern lives. They power our cars, light up our homes, and heat our buildings. But without them, we’d have a hard time doing these things.
It’s important to know that fossil fuels aren’t just from big dinosaurs. Most of them actually come from tiny plants and animals that lived long ago.
![What are Fossil Fuels? Types, Formation, Chemistry Behind [PDF]](https://paktechpoint.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/image-98-1024x799.png)
Types of Fossil Fuels
The three main types of fossil fuels are:
- Coal: Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock formed from the remains of plants that grew in swamps millions of years ago. Over time, the plant material was buried and subjected to heat and pressure, resulting in the formation of coal. Coal is primarily used for electricity generation and industrial processes.
- Oil (Petroleum): Petroleum is a liquid fossil fuel composed of hydrocarbon compounds found beneath the Earth’s surface. It is formed from the remains of marine plants and animals that lived in ancient oceans. Petroleum is extracted from underground reservoirs through drilling and is refined into various products such as gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel.
- Natural Gas: Natural gas is a gaseous fossil fuel primarily composed of methane (CH4) with small amounts of other hydrocarbons. It is formed alongside petroleum during the decomposition of organic matter and is often found in underground reservoirs. Natural gas is used for heating, electricity generation, and as a fuel for vehicles.
Why it is called fossil fuels?
The term “fossil fuels” is derived from the fact that these energy resources are formed from the fossilized remains of plants and animals that lived millions of years ago. As organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, accumulates and becomes buried under layers of sediment over time, it undergoes a process called diagenesis. This process involves the decomposition and transformation of organic material into fossil fuels due to the combination of heat, pressure, and geological processes.
The term “fossil” refers to the remains or traces of ancient organisms preserved in rocks or sediment. Since coal, oil, and natural gas are derived from the fossilized remains of ancient organic matter, they are referred to as fossil fuels.
Coal, for example, forms from the remains of plants that lived in ancient swamps. Over millions of years, the plant material accumulates and is buried under layers of sediment. The heat and pressure from overlying layers cause the organic material to undergo chemical and physical changes, ultimately transforming into coal.
Similarly, oil and natural gas are formed from the remains of marine plants and animals that lived in ancient oceans. As these organisms die and sink to the ocean floor, they become buried and subjected to heat and pressure, leading to the formation of oil and natural gas reservoirs over geological time scales.
Therefore, the term “fossil fuels” accurately reflects the origin of these energy resources from the fossilized remains of ancient life forms.
The Formation of Fossil Fuels
What is sedimentary rock?
Sedimentary rock is like a puzzle made up of many pieces. These pieces, called sediments, are tiny bits of broken rock. They form layers at the bottom of valleys and seas. Over time, more and more layers pile up on top of each other, squeezing the sediments together.
As these layers build up, the pressure on the bottom layers increases. This pressure squishes the sediments, pressing them tightly together. Then, water seeps through these compacted sediments. This water contains minerals, which stick to the sediments.
Eventually, these minerals act like glue, holding all the bits of rock together. This process forms new rock, known as sedimentary rock.
But not all sedimentary rocks form in the same way. There are different processes that create them, which you’ll learn about in other articles here.
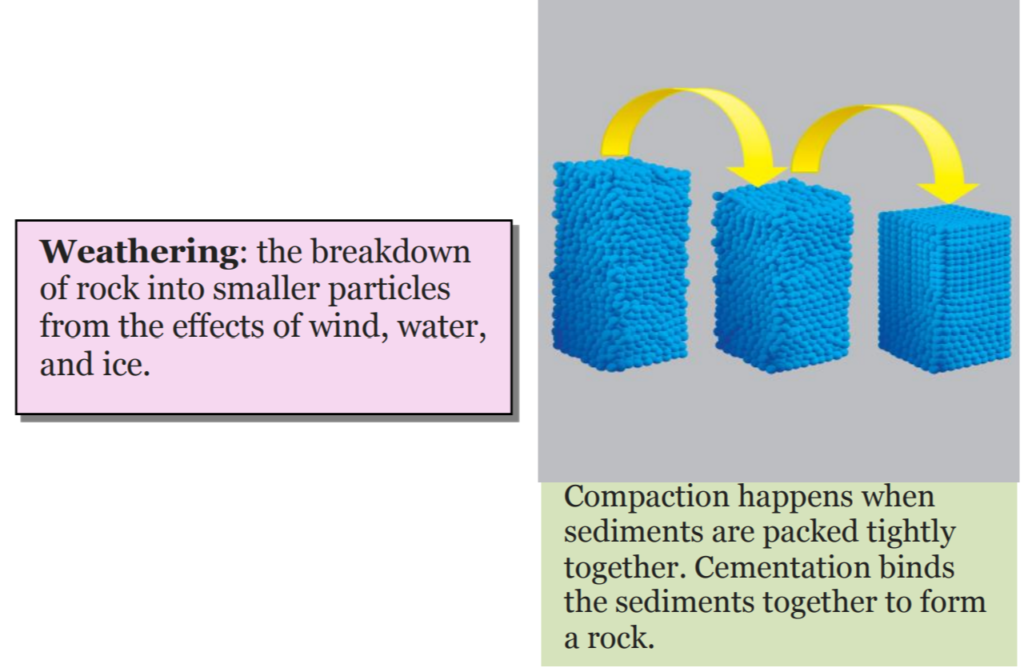
How is sedimentary rock involved in the formation of fossil fuels? How long does this process take?
Sedimentary rocks play a crucial role in the formation of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. This process takes an incredibly long time—millions of years.
Coal forms from dead plants that accumulate at the bottom of swamps. Over time, these plant remains are buried under layers of sediment. Under the weight of these sediments, the organic matter gradually transforms into a substance called peat. If more sediment piles on top, the peat undergoes further changes and eventually becomes coal. There are different types of coal, and the ones subjected to greater pressure contain more energy.
While some consider coal to be a type of sedimentary rock, oil and natural gas are not rocks at all. They originate from microscopic animals that lived in ancient seas. When these tiny organisms died, their remains sank to the ocean floor and were buried under layers of sediment. Over millions of years, the pressure from these sediments caused some of the organic matter to change into oil, also known as petroleum. With sufficient pressure, organic matter can also transform into natural gas.

Can we run out of fossil fuels?
Absolutely, we can indeed run out of fossil fuels. Fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and natural gas, are nonrenewable resources, meaning they are finite and cannot be replenished on a human timescale. These resources take millions of years to form through geological processes involving the decomposition of organic matter buried deep within the Earth’s crust.
However, human activities, particularly industrialization and rapid economic growth, have led to a significant increase in the consumption of fossil fuels. As a result, we are depleting these resources much faster than they can naturally replenish. If this trend continues unchecked, we will eventually exhaust our reserves of fossil fuels.
Moreover, the extraction, processing, and burning of fossil fuels have severe environmental consequences, including air and water pollution, habitat destruction, and greenhouse gas emissions contributing to climate change. Therefore, it is imperative that we transition to alternative sources of energy, such as renewable energy (e.g., solar, wind, hydroelectric), which are sustainable and do not harm the environment.
By reducing our dependence on fossil fuels and embracing cleaner, renewable energy sources, we can mitigate the negative impacts of fossil fuel consumption, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and ensure a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Characteristics of Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and natural gas, share several key characteristics:
- Nonrenewable: Fossil fuels are finite resources that take millions of years to form through geological processes involving the decomposition of organic matter buried deep within the Earth’s crust. Once extracted and consumed, they cannot be replenished on a human timescale.
- Energy-dense: Fossil fuels contain high concentrations of energy per unit of mass, making them highly efficient sources of energy. This energy density allows for the production of large amounts of energy with relatively small quantities of fuel.
- Combustible: Fossil fuels release energy when burned or combusted. This energy can be harnessed for various purposes, including electricity generation, transportation, heating, and industrial processes.
- Greenhouse gas emissions: Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These emissions contribute to global warming and climate change by trapping heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to adverse environmental impacts such as rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and sea-level rise.
- Environmental impact: The extraction, processing, and combustion of fossil fuels have significant environmental consequences, including air and water pollution, habitat destruction, soil degradation, and biodiversity loss. These environmental impacts pose risks to ecosystems, human health, and the overall well-being of the planet.
- Economic importance: Fossil fuels play a central role in global energy systems and economies, providing the majority of the world’s primary energy supply. They are essential for electricity generation, transportation, manufacturing, agriculture, and numerous other sectors. The fossil fuel industry also generates significant revenue and employment opportunities worldwide.
- Geographical distribution: Fossil fuel deposits are found in various regions around the world, with some countries possessing larger reserves than others. The distribution of fossil fuels influences global energy geopolitics and can impact international relations, trade, and geopolitical stability.
Interesting Fossil Fuel Facts:
Here are some interesting facts about fossil fuels:
- Fossil fuels take millions of years to develop through geological processes.
- The fossil fuels we use today began forming during the Carboniferous Period, which predates the existence of dinosaurs on Earth.
- Oil, also known as petroleum, is extracted from underground reservoirs and can be refined into various products such as gasoline and electricity.
- Natural gas, another fossil fuel, is often found underground, usually above oil reservoirs. It is commonly used for cooking and heating in homes.
- Coal, a fossil fuel found closer to the Earth’s surface, is extensively used for generating electricity.
- While fossil fuels are primarily used for electricity generation, they are also utilized to power vehicles, airplanes, and other machines.
- Fossil fuels are non-renewable resources, meaning they cannot be replenished on human timescales.
- Fossil fuels must be burned to release their energy, which is then converted into electricity.
- Burning fossil fuels emits harmful toxins and pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and climate change.
- Approximately 90% of the world’s energy comes from fossil fuels.
- The energy stored in fossil fuels originally comes from the sun, as it was captured by plants and organisms during photosynthesis.
- Natural gas mainly consists of methane, a highly flammable gas.
- Natural gas is odorless, so a chemical called mercaptan is added to give it a distinctive smell for easy detection of leaks.
- Natural gas is transported to homes through underground pipelines connected directly to the gas source.
- Despite the availability of renewable energy sources, fossil fuels are still widely used due to their ease of access and established infrastructure.
Fossil Fuels Advantages and Disadvantages
Here’s a comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of using fossil fuels:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Large amounts of electricity can be generated. | Fossil fuels are non-renewable and will eventually run out. |
| in one place using coal, at a fairly cheap cost. | Fossil fuels release carbon dioxide when burned, contributing to global warming. |
| Transporting oil and gas to power stations is. | Coal and oil release sulfur dioxide when burned, causing breathing problems and acid rain. |
| easy. | Mining coal can be dangerous and destructive to landscapes. |
| Gas-fired power stations are highly efficient. | Coal-fired power stations require huge amounts of fuel and extensive reserves, impacting landscapes. |