5G clock synchronization ensures the proper functioning of communication networks by aligning the timing or frequency of devices. This process prevents performance issues due to timing errors during signal transmission and reception. Clock synchronization involves both time synchronization, aligning the system clocks, and frequency synchronization, ensuring devices operate on the same frequency. This coordination is crucial for the efficient operation of 5G networks, especially in large, complex systems where precise synchronization is necessary to maintain signal quality and minimize interference.
Time Synchronization and Frequency Synchronization
Time Synchronization.
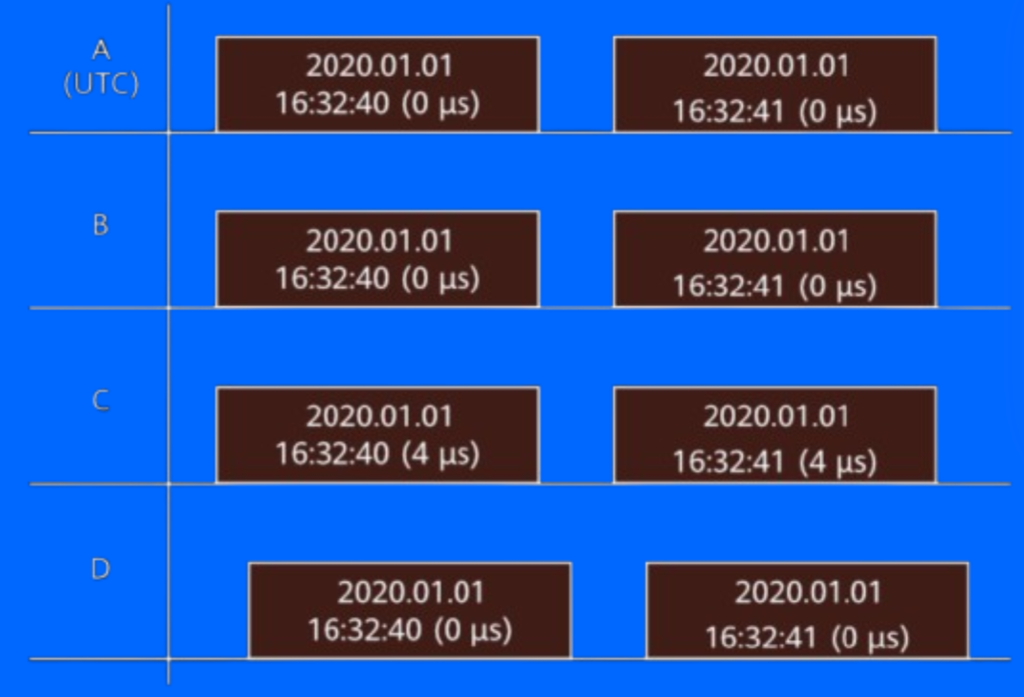
Time synchronization, also called moment synchronization, ensures that the starting time of signals across equipment matches Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). This is critical for the accurate coordination of communication systems. For example, in time synchronization, signals A and B would be synchronized to UTC, while signals A, C, and D would not. This ensures that all devices operate on the same time basis, crucial for effective signal transmission and reception in digital networks.
Figure 1 shows Time synchronization.
Frequency Synchronization.
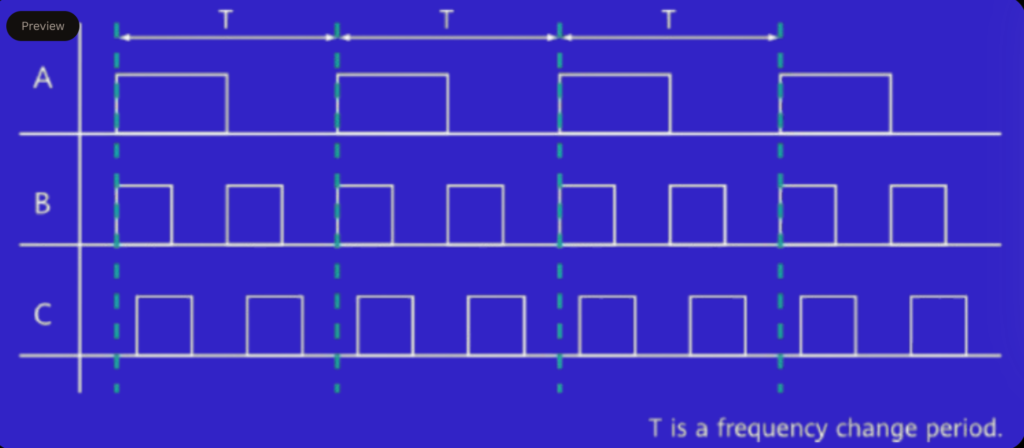
Frequency synchronization ensures that two signals change frequencies in the same manner or maintain a fixed ratio, even if their individual phases or frequencies differ. Unlike time synchronization, which aligns absolute time, frequency synchronization focuses on the consistency of frequency changes across signals. In this example, signals A, B, and C are frequency-synchronized, meaning they have the same frequency change characteristics, ensuring stable communication and minimizing errors due to discrepancies in frequency shifts.
Figure 2 shows frequency synchronization in 5G.
What are the application scenarios of time synchronization and frequency synchronization?
1. In TDD systems, including NR TDD and LTE TDD, time synchronization is critical to avoid interference between uplink and downlink slots. Proper synchronization ensures that transmission and reception slots between base stations are correctly aligned, preventing inter-base-station and inter-UE interference. Without synchronization, service quality can deteriorate, leading to negative impacts on key performance indicators (KPIs) in wireless communications.
2. In FDD (including NR FDD and LTE FDD), achieving accurate frequency or time synchronization is crucial for proper operation. Base stations must maintain synchronization to ensure that UEs can detect neighboring cells and avoid timing issues that could affect handovers. For FDD, ms-level time synchronization between base stations is essential, and either frequency or time synchronization can be employed to maintain this alignment and prevent transmission performance degradation.
- Basic FDD services rely on frequency synchronization between base stations, ensuring optimal power consumption during UE mobility. However, services like UL CoMP and CA, which require inter-base-station coordination, demand higher synchronization precision, including time synchronization.
- LTE FDD can use hybrid synchronization, where a base station is configured with both time and frequency reference clocks. These clocks can switch depending on the requirements, ensuring that both time and frequency synchronization are maintained as needed for optimal operation.
- In LTE FDD, the time reference source is preferred as the active clock, with the frequency reference source serving as a backup. If the time reference becomes unreliable—due to issues like GPS satellite loss, frequency offset, or a clock link disruption—the base station automatically switches to the frequency reference.
- Once the time reference is restored, the base station switches back to it during off-peak hours to ensure accurate synchronization.
Prerequisites for this article are:
- What synchronization precision is required in 5G?
- What are the Mainstream Clock Sources in 5G?
- How do we deploy clocks for multimode base stations in 5G?
- How do we detect clock deviations in 5G?