This article is about 5G NR Frequency Bands and frequency ranges FR1 and FR2 and duplexing methods are discussed for 5G NR.
5G NR Frequency Bands.
5G New Radio (NR) technology, the global standard for a more capable 5G wireless air interface, operates across two primary frequency ranges: Frequency Range 1 (FR1) and Frequency Range 2 (FR2). These ranges support various applications by balancing coverage, capacity, and latency requirements.
Frequency Range 1 (FR1).
FR1 covers 5G NR frequency bands between 450 MHz and 7.125 GHz, offering channel bandwidths from 5 MHz to 100 MHz. These frequencies, encompassing many traditional 4G LTE bands and new sub-6 GHz bands, provide extensive coverage and better penetration through obstacles, making them suitable for widespread deployment and ensuring indoor coverage.
Below is the list of FR1 5G NR Frequency Bands:
- n77 (3300–4200 MHz): TDD, 10–100 MHz
- n78 (3300–3800 MHz): TDD, 10–100 MHz
- n79 (4400–5000 MHz): TDD, 40–100 MHz
- n80 (1710–1785 MHz): SUL, 5–30 MHz
- n81 (880–915 MHz): SUL, 5–20 MHz
- n82 (832–862 MHz): SUL, 5–20 MHz
- n83 (703–748 MHz): SUL, 5–20 MHz
- n84 (1920–1980 MHz): SUL, 5–20 MHz
- n86 (1710–1780 MHz): SUL, 5–40 MHz
- n90 (2496–2690 MHz): TDD, 10–100 MHz
Frequency Range 2 (FR2).
FR2 spans from 22.450 GHz to 52.600 GHz, encompassing the millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum. This range supports channel bandwidths from 50 MHz to 400 MHz, enabling extremely high data rates and capacity. However, FR2 bands have limited range and poor penetration through obstacles, making them ideal for dense urban environments and specific high-capacity applications.
Below is the list of FR2 5G NR Frequency Bands:
- n257 (26.5–29.5 GHz): TDD, 50–400 MHz
- n258 (24.25–27.5 GHz): TDD, 50–400 MHz
- n259 (39.5–43.5 GHz): TDD, 50–400 MHz
- n260 (37–40 GHz): TDD, 50–400 MHz
- n261 (27.5–28.35 GHz): TDD, 50–400 MHz
Duplexing Methods.
5G NR supports various duplexing methods to share the communication channel between downlink (DL) and uplink (UL) transmissions.
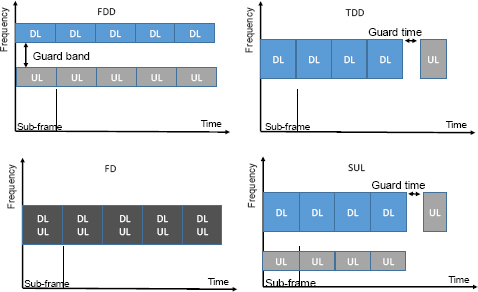
FDD (Frequency Division Duplexing): Uses paired frequency bands for separate DL and UL transmissions, separated by a frequency guard band.
- TDD (Time Division Duplexing): Uses the same frequency band for both DL and UL transmissions, separated by time intervals. TDD can dynamically allocate more time for DL or UL as needed.
- FD (Full Duplex) Spatial Duplexing: Allows simultaneous DL and UL transmissions in the same frequency band using spatial diversity of antennas.
- SUL (Supplementary Uplink) Mode: Uses an additional frequency band exclusively for UL, paired with any DL band. This mode improves UL coverage and reduces latency.
Duplexing Support by Frequency Range.
- FR1: Supports TDD, FDD, and SUL.
- FR2: Supports only TDD.
Conclusion.
The dual frequency ranges (FR1 and FR2) and various duplexing methods in 5G NR provide a versatile framework for next-generation wireless communication. FR1 ensures broad coverage and indoor penetration, while FR2 offers high capacity and data rates for dense urban areas. The combination of these elements allows 5G networks to meet diverse requirements, including enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), massive machine-type communications (mMTC), and ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC).