We are going to discuss bolting for flanged joints in a piping system and technical requirements in industry.
What is Flange Bolting?
Flange bolting refers to the process of attaching two flanges together in a piping system using bolts and nuts. Flanges are the components that are designed to connect sections of pipe, valves, or other equipment to create a leak-tight seal in a piping system. The flanges have holes for bolts, and when two flanges are aligned with each other and brought into contact, bolts are inserted through these holes, and nuts are tightened onto the bolts. This compresses a gasket (usually made of rubber or other sealing material) between the flange faces, creating a secure and sealed connection.
Bolting Selection:
- Bolting for flanged joints should be selected following the guidelines provided in industry standards such as ASME B16.5 or ASME B16.47 as a minimum requirement.
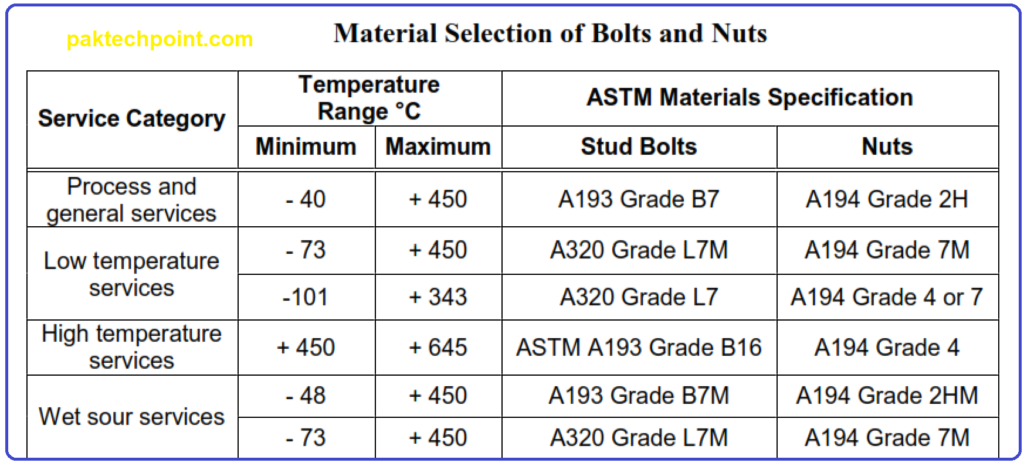
Bolting Materials:
- The material specification for stud bolts and nuts should align with Table, which is based on the design temperature range and service conditions.
- Specific restrictions and requirements for certain services and applications mentioned in applicable codes must be considered.
- If the temperature or service condition isn’t listed in Table below, approval from the Chairman of the Piping Standards Committee is necessary for material selection.
- Low-temperature bolting material should be chosen for flanges exposed to auto-refrigeration during flange leakage.
- Stud bolts and nuts should be specified for wet sour services only if they are directly exposed or potentially exposed to the fluid service. Potential exposures could include buried, insulated, or shielded flanges.
Bolting Material Protection:
- Bolting material installed in aggressive external environments like offshore or underground piping systems should be protected in one of the following ways:
a) Applying a ceramic-fluoropolymer coating following the guidelines provided in document 09-SAMSS-107.
b) Using corrosion-resistant alloys.
c) Painting the exposed portions of the bolts and sealing the gap between flange faces.
d) Encapsulating the bolted flange connection with heat shrinkable tubing.
Washers:
- Flat washers beneath the nuts are generally required for specific cases, such as insulating flanges or when nuts bear against plastic flanges.
- Belleville washers may be necessary for severe cyclic service or when bolt service temperatures exceed 450°C. In such cases, review by the Chairman of the Piping Standards Committee in CSD is necessary for approval.
These guidelines help ensure that the bolting materials and their protection are appropriate for the specific conditions and services in a piping system, considering factors like temperature, environment, and exposure to fluid services.
Purpose of Flange Bolting
The purpose of flange bolting is to:
- Create a Leak-Tight Seal: The gasket, when compressed between the flange faces, prevents the leakage of fluids, gases, or other substances from the joint, ensuring that the piping system remains leak-free.
- Provide Structural Integrity: The bolts and nuts hold the flanges together, providing structural integrity to the joint. This is important, especially in high-pressure or high-temperature applications.
- Allow for Easy Assembly and Disassembly: Flange connections can be easily assembled and disassembled, which is beneficial for maintenance, repairs, and modifications of piping systems.
The selection of bolts and nuts for flange bolting depends on factors such as the material and size of the flanges, the operating conditions (pressure and temperature), and the type of fluid being transported in the piping system. Bolting materials are typically chosen to withstand the mechanical and environmental stresses to which they will be subjected.
In summary, flange bolting is a critical aspect of creating secure and sealed connections in piping systems, ensuring their safe and efficient operation.