This article is about “float charge” in the battery system like VRLA (Valve-Regulated Lead Acid) batteries and their role in backup power systems. More will explain the roles of floating charge, the principle of float voltage, float voltage temperature compensation, and the function, voltage, and frequency of equalizing charge in the context of VRLA (Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid) batteries. Let’s break down the key points.
What is Float Charge?
- Float Charge: Float charge is a type of charging mode used for maintaining the state of charge in a battery. In a float charge system, the battery is continuously connected to a charger, which supplies a constant voltage to the battery. This voltage is set just high enough to maintain the battery’s full charge but not high enough to overcharge it. Float charging is commonly used in applications where batteries are needed for backup power.
- VRLA Batteries: VRLA batteries are a type of lead-acid battery that is sealed and maintenance-free. They are often used in applications where maintenance of the battery is difficult or impractical.
- Float Work System: In the VRLA batteries, a float work system refers to the mode of operation where the batteries are connected to a load circuit device and are kept in a state of float charge. This means that the batteries are continuously connected to the charger and provide backup power to the load as needed.
- Battery Bank: A battery bank is a collection of multiple batteries connected together to provide a larger capacity and longer backup power duration.
- Characteristics of Floating Work:
- The battery bank usually remains in a charged state (float charge) and does not discharge under normal operating conditions.
- The load current is primarily supplied by the rectifier, which is a device that converts AC (alternating current) to DC (direct current) and charges the batteries while providing power to the connected load.
- In actual operation, there may be partial discharge of the battery if the load unexpectedly increases suddenly. This means that if the demand for backup power exceeds the capacity of the rectifier, the batteries may discharge to support the load until the rectifier can catch up.
Float work in the context of VRLA batteries refers to a mode of operation where the batteries are continuously charged by a rectifier and are ready to provide backup power to a connected load in the event of a power outage or sudden increase in load demand. This mode is ideal for applications where a reliable backup power source is essential.
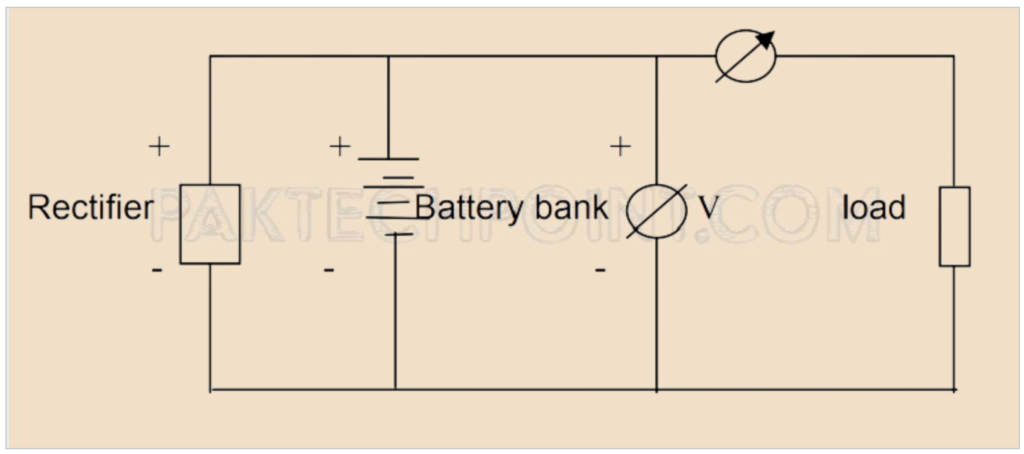
Role of Floating Charge:
- When Utility Power Fails: The battery bank in a floating work system serves as a backup power source when the utility power fails or if there is a rectifier failure. This ensures that critical communication systems are not interrupted during power outages.
- Smoothing Effect: The battery, similar to a capacitor, has a charging and discharging effect, which helps smooth out variations in AC current. This reduces ripple components in the load, ensuring that sensitive equipment receives stable voltage.
Principle of Float Voltage:
- Compensate for Self-Discharge Losses: The float current compensates for the self-discharge losses in the battery, ensuring that it remains charged even when not in use.
- Quick Replenishment: When the battery is discharged, it can quickly replenish the lost charge during float charging, preparing it for the next discharge.
- Protect Grid from Corrosion: A selected charging voltage results in the production of denser PbO2 (lead dioxide) at the battery plate, protecting the grid from rapid corrosion.
- Minimize O2 and H2 Precipitation: Float voltage selection also minimizes the precipitation of oxygen (O2) and hydrogen (H2) gases and reduces negative salinization.
Float Voltage Temperature Compensation:
- Float voltage is typically specified at 25°C ambient temperature. However, as ambient temperature changes, the float voltage needs to be adjusted according to the temperature compensation coefficient.
- Different manufacturers may have different temperature compensation coefficients, so it’s essential to consult the manufacturer’s instructions or documentation for guidance.
Function, Voltage, and Frequency of Equalize Charge:
- Equalize charge is used when the battery’s float voltage is low, when a discharged battery needs recharging, or when the battery’s capacity is low.
- The charging voltage and frequency for equalizing charge are critical for ensuring battery longevity.
- It’s important to note that equalizing charge should not be used in normal operation because it can lead to battery dehydration and premature failure.
- The recommended charging voltage for equalizing charge may vary with ambient temperature and is typically around 2.35V or 2.30V per cell at 25°C ambient temperature.
- Temperature compensation coefficients are used to adjust the equalizing charge voltage based on temperature changes.
We recommend performing an equalizing charge every six months for VRLA batteries to maintain their health and capacity. It mentions specific charging methods, such as “limiting current limiting voltage” or “constant voltage limiting current,” for recharging discharged batteries.
Overall, these principles and practices are important for managing VRLA batteries in various applications, especially in systems where backup power is critical. Proper maintenance and monitoring of battery parameters are essential to ensure their reliable performance over time.