In the world of mobile communications, the ability for users to connect to networks outside their home network, known as roaming, remains a critical feature. This capability allows users to maintain their connectivity, access services, and enjoy seamless communication even when they are outside their home country.
The Long Term Evolution (LTE) standard, along with System Architecture Evolution (SAE), provides robust support for roaming. This article explains LTE roaming architecture, explaining how it enables users to connect to Public Land Mobile Networks (PLMNs) other than their home networks, and the associated mechanisms and benefits.
Understanding LTE Roaming and PLMNs.
A network operated by a single mobile operator within a specific country is referred to as a Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN). Roaming allows users to connect to PLMNs other than their home PLMN, thereby extending the reach and usability of mobile networks globally. This is particularly beneficial for international travelers, who can use their mobile devices seamlessly across different countries without changing their SIM cards or mobile numbers.
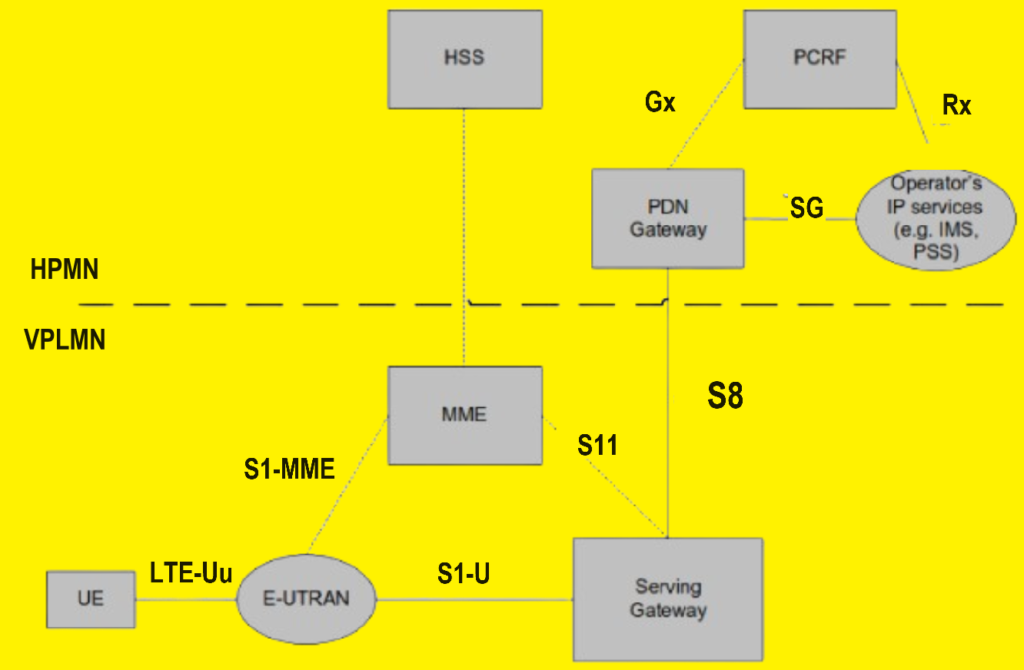
The Role of E-UTRAN, MME, S-GW, and P-GW
When a user roams into a visited LTE network, they connect to the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN), Mobility Management Entity (MME), and Serving Gateway (S-GW) of the visited network. These components play crucial roles in maintaining the user’s connection and managing their mobility within the visited network.
E-UTRAN
E-UTRAN is responsible for the radio communication between the user equipment (UE) and the network. It manages radio resources, handovers, and overall radio access performance.
MME
The MME handles the control plane functions related to subscriber mobility, session management, and security. It is pivotal in managing the user’s sessions and maintaining their connectivity as they move within the visited network.
S-GW
The S-GW serves as the data plane anchor for the user plane. It routes and forwards user data packets and acts as a mobility anchor for inter-eNodeB handovers and inter-3GPP mobility.
P-GW: Home Network vs. Visited Network
A unique feature of LTE/SAE roaming is the flexibility in selecting the Packet Data Network Gateway (P-GW). The P-GW can be located in either the home network or the visited network, each offering distinct advantages.
Home Network P-GW
Using the P-GW in the home network enables the user to access their home operator’s services even while connected to a visited network. This setup ensures that the user can utilize services like home-based billing, customer care, and value-added services provided by the home operator. The data traffic is tunneled back to the home network, maintaining consistency in the user’s experience.
Visited Network P-GW
Alternatively, a P-GW in the visited network allows for a “local breakout” to the Internet. This means that the user’s data traffic can be routed directly to the local Internet in the visited network, potentially improving data speed and reducing latency. This approach can also optimize network resources by reducing the need for data tunneling back to the home network.
Benefits of LTE Roaming
The architecture of LTE roaming offers several benefits:
- Seamless Connectivity: Users can maintain their mobile connectivity across different countries without changing their SIM cards or mobile numbers.
- Access to Home Services: Users can access services provided by their home network, ensuring a consistent and familiar user experience.
- Improved Performance: Local breakout through the visited network’s P-GW can enhance data speeds and reduce latency.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Reducing the need for data tunneling back to the home network optimizes network resources and improves overall efficiency.
Conclusion
LTE roaming architecture exemplifies the advanced capabilities of modern mobile networks, ensuring users remain connected and can access essential services wherever they are in the world. By allowing flexibility in the choice of P-GW—either in the home network or the visited network—LTE/SAE enhances user experience, optimizes network performance, and supports seamless global mobility. This architecture not only benefits users but also enables mobile operators to provide superior service quality and maintain competitive advantage in the global telecommunications market.