In LTE (Long-Term Evolution) networks, RSRQ, or Reference Signal Received Quality, is a UE measurement metric used to assess the quality of the received signal. It plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient network performance, especially in challenging scenarios such as at the cell edge. Understanding RSRQ helps in optimizing the user experience by helping in the decision-making process for handovers and network resource allocation.
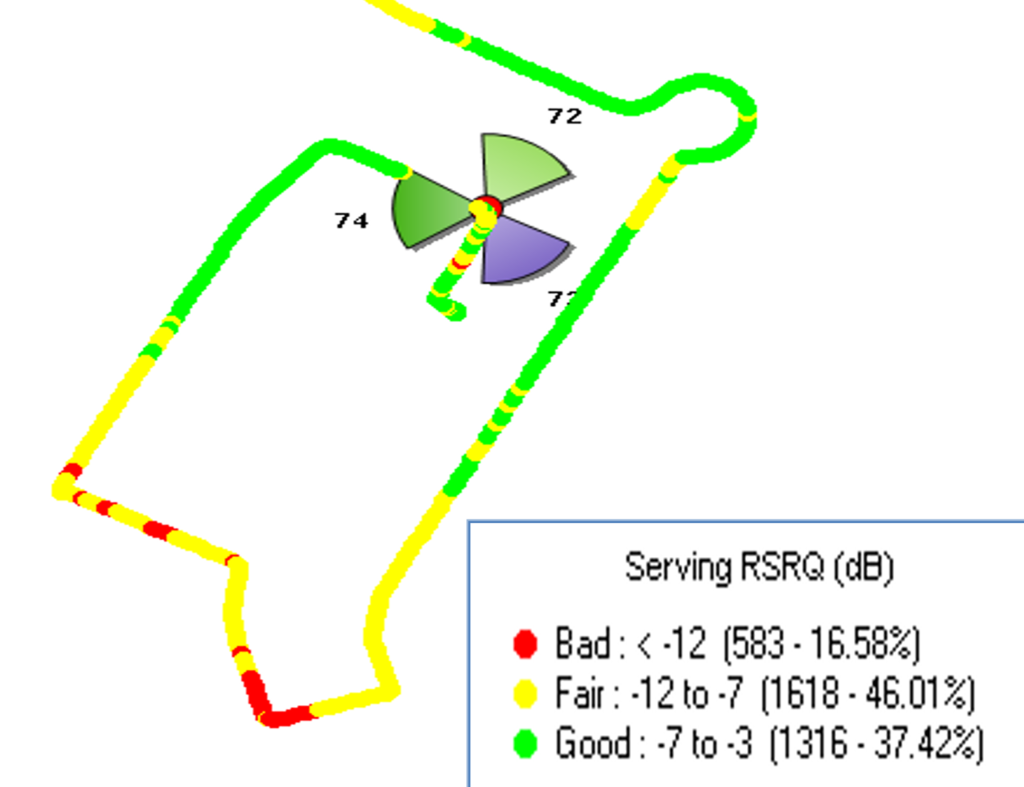
Below picture shows RSRQ Plot & Threshold and value ranges.
RSRQ Definition and Calculation.
RSRQ is a measure of the quality of the reference signal received by the User Equipment (UE). It takes into account not only the signal strength but also the level of interference and noise present in the received signal. The formula to calculate RSRQ is:
RSRQ = RSRP / (RSSI / N)
- RSRP (Reference Signal Received Power): The power level of the LTE reference signals.
- RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator): The total received power including all the interference and noise.
- N: The number of Resource Blocks (RBs) over which the RSSI is measured.
Importance of RSRQ.
RSRQ provides an indication of signal quality, which is crucial for maintaining a reliable and efficient connection. Its significance lies in the following aspects:
- Signal Quality Assessment: RSRQ is a direct measure of the quality of the received signal, taking into account both the signal strength and the level of interference.
- Handover Decisions: RSRQ is particularly important near the cell edge. Even if the RSRP is low, a high RSRQ value can indicate good signal quality, influencing the decision to handover to a neighboring cell.
- Network Performance: By providing a comprehensive measure of signal quality, RSRQ helps in optimizing network performance and resource allocation.
RSRQ Measurement Range.
The typical range of RSRQ values is from -3 dB to -19.5 dB:
- -3 dB: Represents excellent signal quality with minimal interference.
- -19.5 dB: Indicates poor signal quality, typically at the cell edge or in areas with high interference.
RSRQ vs. Ec/No.
In 3G networks, a similar concept to RSRQ is Ec/No (Energy per Chip to Noise Ratio). While both measurements serve the same purpose of indicating signal quality, RSRQ is specific to LTE networks and Ec/No to UMTS (3G) networks.
Usage of RSRQ.
RSRQ is primarily used by the UE during connected states:
- Connected State: The UE continuously measures RSRQ to maintain a robust connection. It helps in making informed decisions regarding handovers, ensuring that the UE is connected to the cell with the best possible signal quality.
RSRQ Measurement in LTE.
RSRQ (Reference Signal Received Quality) is similar to RSRP in its use for determining the best cell for an LTE radio connection at a specific geographic location. However, while RSRP measures the absolute strength of the reference radio signals, RSRQ measures the signal-to-noise ratio. Both metrics can be used for initial cell selection or handover.
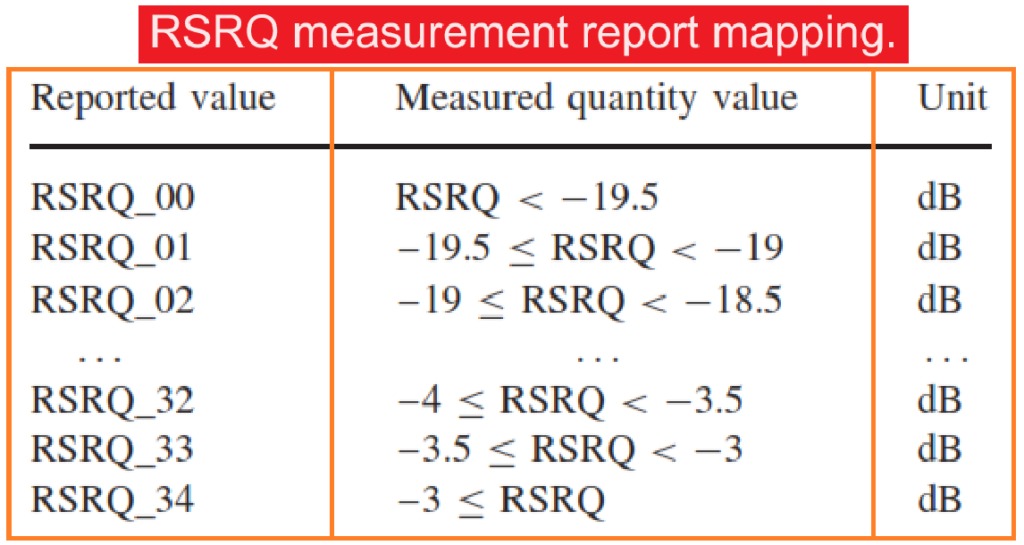
Reporting Range and Interpretation.
The reporting range of RSRQ is defined from -19.5 to -3 dB with a 0.5 dB resolution. When comparing RSRQ and RSRP measurements taken at the same location (identified by the same timestamp in a protocol trace), it’s possible to diagnose coverage or interference issues.
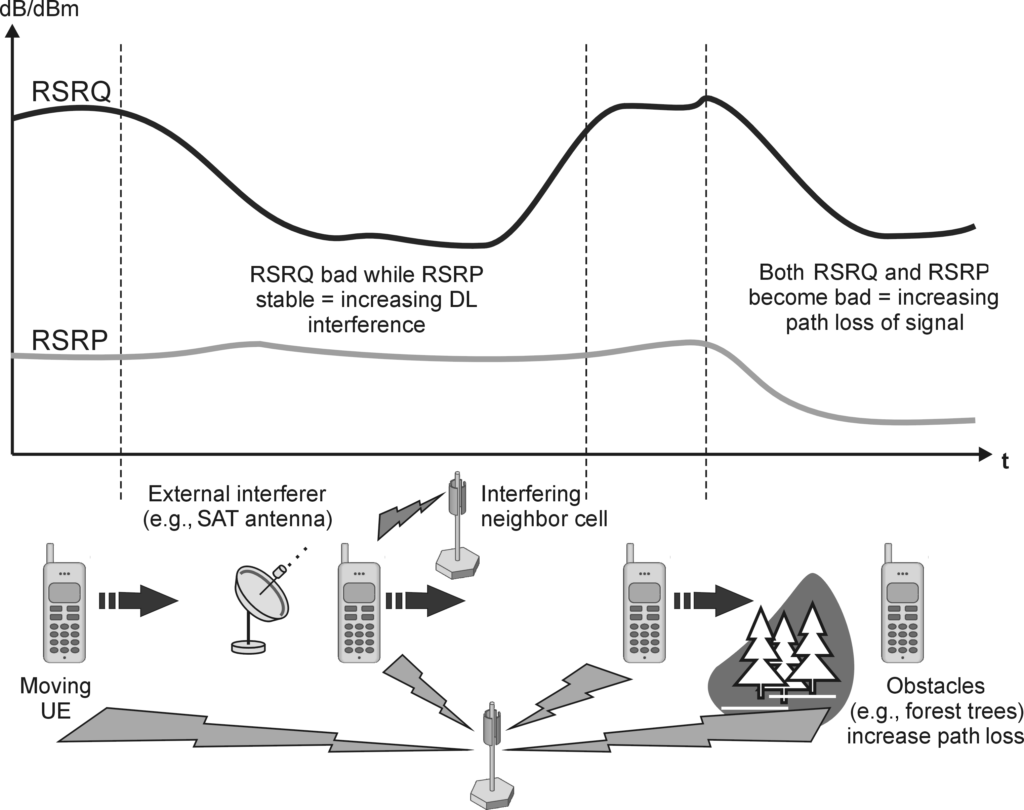
- Stable RSRP with Declining RSRQ: Indicates rising interference, as the signal strength remains the same or improves, but the signal quality worsens.
- Declining RSRP and RSRQ: Indicates an area with weak coverage, as both signal strength and quality degrade simultaneously.
This type of analysis is crucial for identifying the root causes of call drops due to radio problems.
Quality Ranges of RSRQ.
Like RSRP, RSRQ can also be categorized into three quality ranges, though the exact values are still uncertain due to limited data from field trials:
- RSRQ > -9 dB: Provides the best subscriber experience with high quality.
- RSRQ between -9 and -12 dB: Indicates a neutral range with slight QoS degradation, but overall fair customer experience.
- RSRQ < -13 dB: Significantly declines throughput and increases the risk of call drops, indicating poor quality.
Understanding these ranges helps in evaluating network performance and ensuring optimal user experience by addressing both coverage and interference issues.
Conclusion
RSRQ is a critical measurement in LTE networks, providing essential information about signal quality. It plays a vital role in network optimization, handover decisions, and ensuring reliable connectivity for users. By understanding and leveraging RSRQ, network operators can enhance the performance and coverage of LTE networks, delivering a better user experience.