RSSI stands for Received Signal Strength Indicator.
- Definition: RSSI measures the total received wideband power, which includes the power from the serving cell, co-channel interference, and noise.
- Formula: RSSI=12*N*RSRP
- Here, RSSI per resource block is measured over 12 resource elements (REs).
- N: Number of resource blocks (RBs) across which RSSI is measured, depending on the bandwidth (BW).
- RSRP (Reference Signal Received Power): Measures the received power of the reference signal, which indicates the signal quality from the serving cell.
Conversion Formula in dbm:
To convert RSSI to RSRP:
RSRP (dBm) = RSSI (dBm) -10*log (12*N)
Below picture represents RSSI Plot & Threshold during LTE drive test.
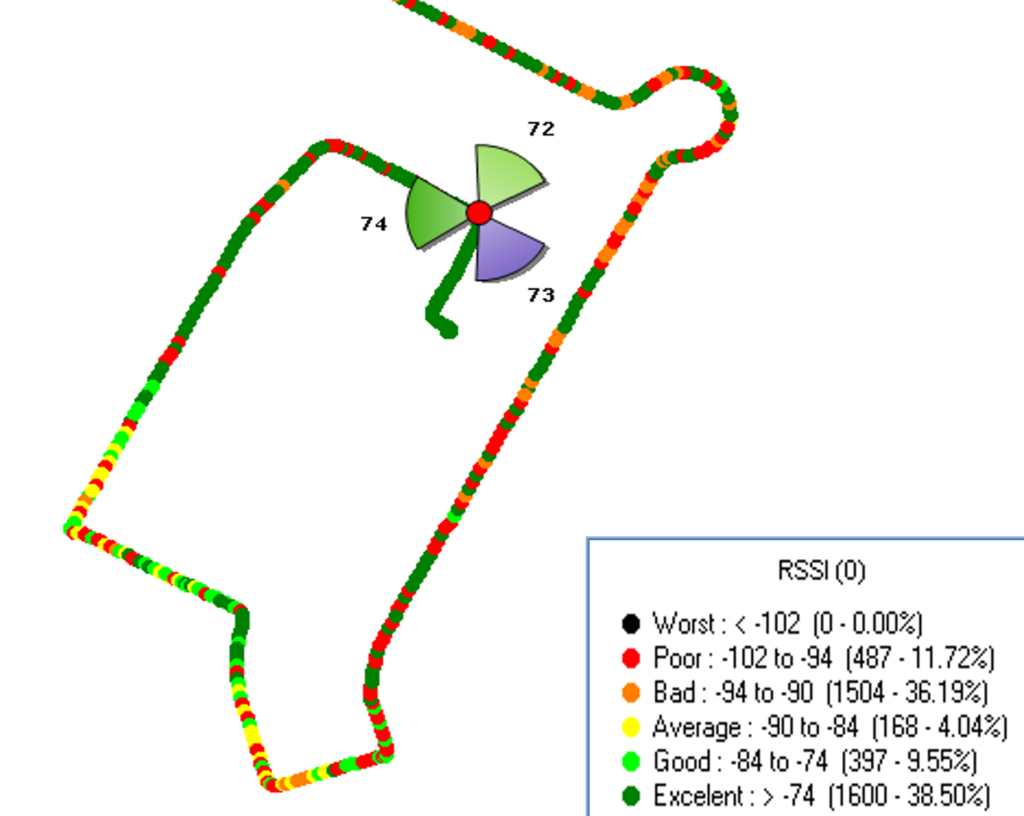
How RSSI is measured in LTE?
In LTE, measurements are performed on individual resource blocks that carry reference signals to assess the downlink (DL) signal quality. The noise floor in LTE’s DL is referred to as the E-UTRA carrier Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI). However, instead of reporting RSSI directly, the system reports the Received Signal Reference Power (RSRP). RSRP serves as a key metric for evaluating the LTE interface’s performance.
Based on the RSRP, the Received Signal Reference Quality (RSRQ) is calculated. This is similar to how Ec/No (energy per chip to noise density ratio) was calculated for the 3G Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) radio quality. Essentially, RSRQ provides a measure of the signal quality relative to the noise and interference.
In LTE, the reference signals of a particular cell can be identified by the physical cell ID. This ID functions as a scrambling code, which is quite similar to the primary scrambling code used in 3G FDD cells. This similarity aids in identifying and differentiating between various cells within the network, ensuring accurate measurements and efficient network performance analysis.
RSSI Significance:
- Overall Power Measurement: RSSI represents the total received power, encompassing the desired signal from the serving cell, interference from co-channel users, and noise. This makes it a crucial parameter for assessing the overall radio environment in LTE networks.
- Network Performance Indicator: High RSSI values generally indicate strong received signals, but they do not differentiate between useful signal and interference/noise. This is why RSRP and SINR (Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise Ratio) are often used alongside RSSI for a more detailed analysis of network performance.
Understanding RSSI is essential for optimizing network performance, managing interference, and ensuring reliable communication in LTE systems.
Read Also: What is RSRP, RSRQ, SINR?