A Traffic Collision Avoidance System TCAS Resolution Advisory (RA) is a guidance issued by the TCAS to pilots to assist in avoiding potential collisions with other aircraft. When TCAS detects a risk of collision between two aircraft, it issues Resolution Advisories to provide instructions to pilots on how to maneuver their aircraft to safely avoid the collision.
There are two types of Resolution Advisories:
- Climb RA: If TCAS determines that an aircraft is on a collision course with another aircraft and climbing is the safest maneuver to avoid the collision, it will issue a Climb RA. In this case, the TCAS instructs the pilot to climb at a specific rate to increase vertical separation between the two aircraft.
- Descend RA: Similarly, if TCAS determines that descending is the safest maneuver to avoid a collision, it will issue a Descend RA. The TCAS instructs the pilot to descend at a specific rate to create vertical separation between the two aircraft.
What is TCAS Resolution Advisory?
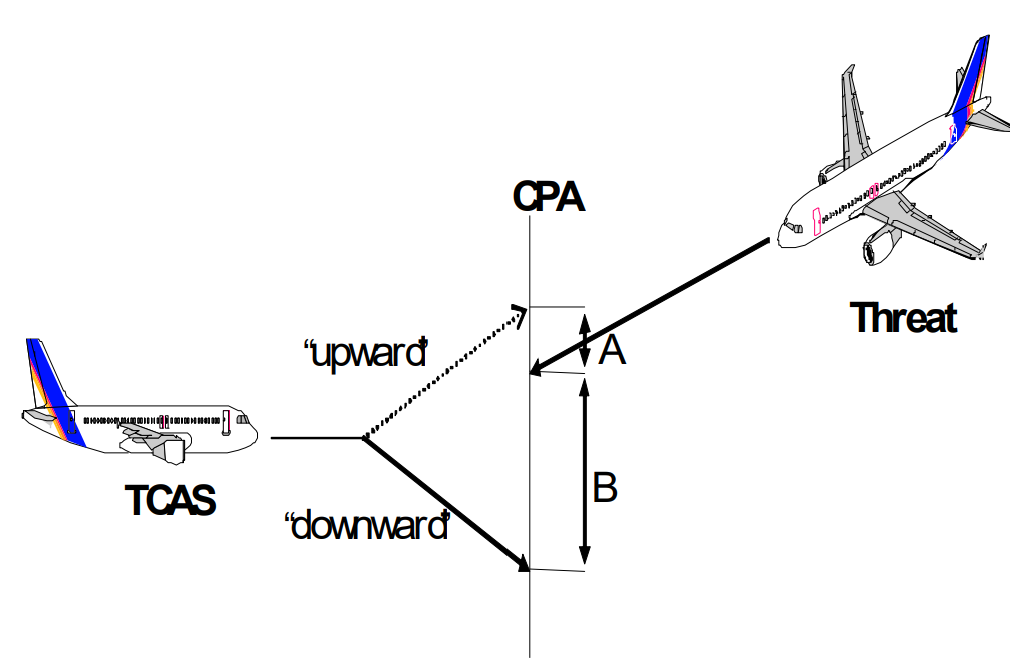
When an intruder aircraft is identified as a threat, TCAS follows a two-step process to select the appropriate Resolution Advisory (RA) based on the encounter geometry.
1. RA Sense Selection:
The first step involves determining whether the recommended maneuver for own aircraft should be upward or downward. TCAS analyzes the range and altitude tracks of the intruder aircraft to model its flight path from its current position to the Closest Point of Approach (CPA). Then, TCAS evaluates both upward and downward RA options for own aircraft to determine which maneuver would provide the most vertical separation at CPA.
2. RA Sense Determination:
In scenarios where either upward or downward maneuvers result in own aircraft crossing through the altitude of the intruder, TCAS prioritizes selecting the non-crossing sense if it still achieves the desired vertical separation at CPA. This means that if the non-crossing sense can provide at least the desired separation at CPA (known as ALIM), TCAS will select that sense even if the crossing sense offers greater separation. However, if the non-crossing sense cannot achieve the desired separation, TCAS will issue an altitude crossing RA.
Pilots are expected to respond promptly to TCAS RAs by initiating the recommended maneuver within specified timeframes to ensure effective collision avoidance. The system accounts for pilot response times and aircraft performance to optimize safety during potential collision scenarios.
In certain situations, TCAS may limit or modify the advisories it provides to pilots based on aircraft performance limitations or specific configurations. For example:
- Some climb or increase climb advisories may be inhibited at high altitudes or when certain aircraft configurations, like certain flap or landing gear settings, are in use. This inhibition can be programmed into TCAS settings or adjusted in real-time by the Flight Management System (FMS).
- TCAS is designed to limit increase descent advisories when the aircraft is below 1450 feet Above Ground Level (AGL), and descend advisories when below 1100 feet AGL. Below 1000±100 feet AGL, all advisories are typically disabled or modified to prevent unnecessary maneuvers.
- When selecting the type of advisory, TCAS aims to minimize disruption to the aircraft’s current flight path while still ensuring a safe vertical separation of at least a certain distance.
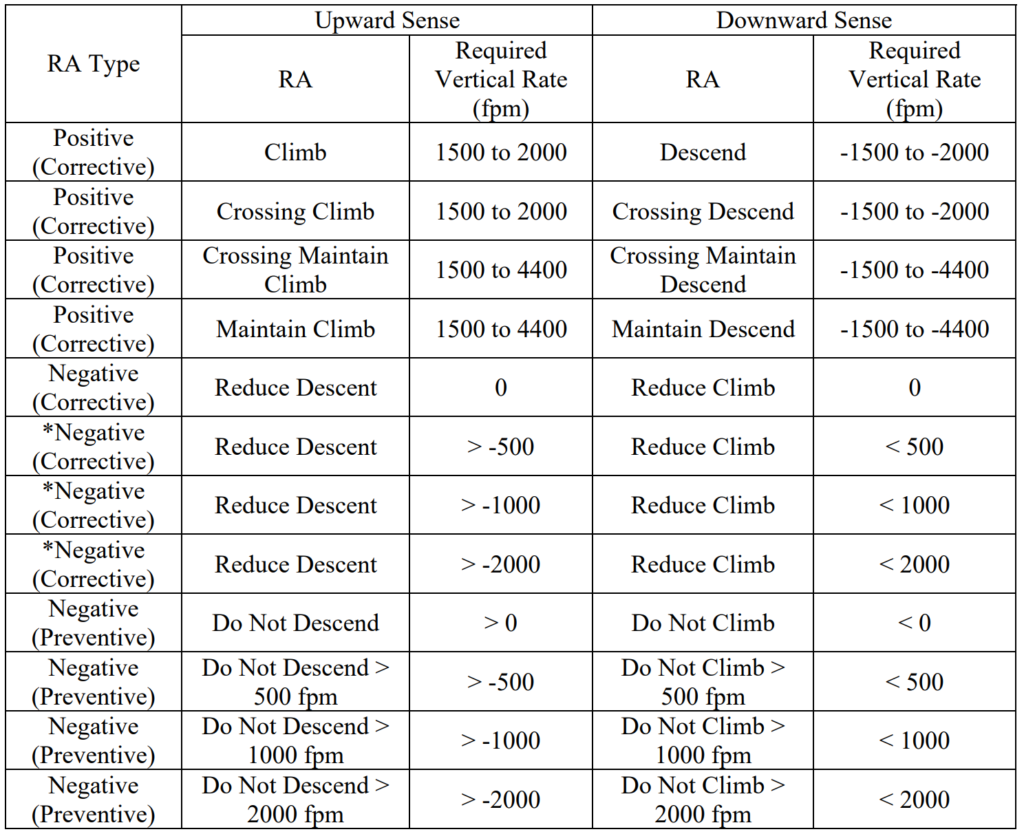
- Advisories can be either positive (e.g., climb, descend) or negative (e.g., limit climb to 0 feet per minute, limit descent to 500 feet per minute). Negative advisories restrict the aircraft’s vertical speed. Additionally, advisories can be either preventive (no change in vertical speed required) or corrective (require a change in vertical speed to maintain separation).
Strengthening Advisories
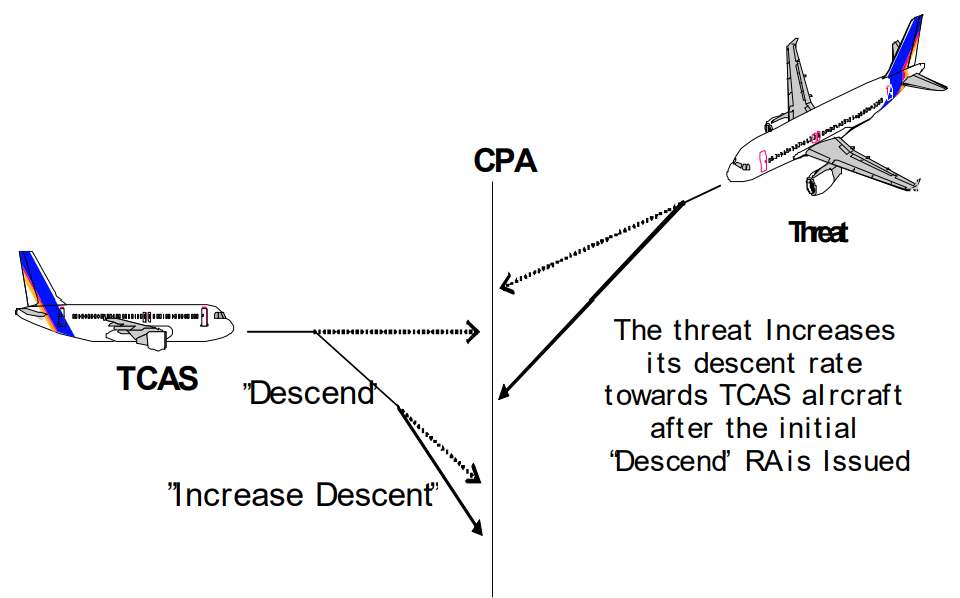
In certain situations, the initial resolution advisory (RA) issued by TCAS may not effectively maintain separation between aircraft due to the maneuvers of the intruder aircraft. In these cases, the RA may be strengthened or modified to ensure safety:
- If a Vertical Speed Limit (VSL) advisory is issued, it may be strengthened by imposing a more restrictive limit on the aircraft’s vertical speed or by changing it to a positive Climb or Descend RA.
- If a Climb or Descend RA is initially issued, it may be strengthened to an Increase Climb or Increase Descent RA. However, an Increase Climb/Descent RA can only be issued after a Climb/Descend RA has already been displayed, either as the initial advisory or as a result of strengthening a negative RA or reversing the sense of the RA.
Multiple-Threat Resolution Advisories
TCAS is equipped to manage encounters involving multiple threats, where more than one aircraft poses a potential collision risk simultaneously. In such situations, TCAS aims to resolve the encounter by selecting a single or composite resolution advisory (RA) that ensures sufficient separation from each intruding aircraft. However, it’s important to note that the chosen RA may not always guarantee the desired separation from all threats. Initially, a multi-threat RA could be any of the RAs listed in Table 3, or a combination of upward and downward sense negative RAs, such as “Do Not Climb” and “Do Not Descend.” With the introduction of version 7.0, TCAS gained enhanced capabilities in its multi-threat logic, allowing it to utilize Increase Rate RAs and RA Reversals more effectively to address such encounters.