OSHA stands for the Occupational Safety and Health Administration. In this article you will learn in details about What is OSHA?. It is a federal agency in the United States under the Department of Labor. OSHA’s mission is to ensure safe and healthful working conditions for workers by setting and enforcing standards, providing training, outreach, education, and assistance. OSHA regulations apply to most private sector employers and their workers, as well as some public sector employers and workers in the United States.
Why is OSHA Important to You?
OSHA, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, is crucial for several reasons:
- Worker Safety: OSHA’s primary goal is to ensure that workers have a safe and healthful workplace. With thousands of workers being killed on the job each year and millions more suffering serious injuries and illnesses, OSHA’s regulations and enforcement efforts play a vital role in preventing workplace accidents and fatalities.
- Prevention of Injuries and Illnesses: By setting and enforcing safety and health standards, OSHA helps to prevent workplace injuries, illnesses, and fatalities. This not only protects workers from harm but also reduces the financial and human costs associated with workplace accidents.
- Protection for Vulnerable Workers: OSHA’s regulations help to protect vulnerable workers, including immigrant workers and workers in high-risk industries such as construction and agriculture. By ensuring that employers provide safe working conditions and comply with safety standards, OSHA helps to reduce the disproportionate risk faced by these workers.
- Worker Rights: OSHA gives workers the right to a safe workplace and the right to report unsafe conditions without fear of retaliation. This empowers workers to speak up about safety concerns and helps to ensure that employers address hazards promptly.
- Enforcement and Accountability: OSHA conducts inspections of workplaces to ensure compliance with safety and health standards. Employers found to be in violation of OSHA regulations may face fines and other penalties, which helps to hold employers accountable for providing safe working conditions.
Overall, OSHA is important because it saves lives, prevents injuries and illnesses, protects worker rights, and promotes accountability for employers. By ensuring that employers provide safe and healthful workplaces, OSHA plays a critical role in protecting the well-being of workers across the United States.
How OSHA Makes a Difference?
OSHA’s impact on workplace safety and health is significant and measurable:
- Reduction in Worker Deaths: Since its inception in 1970, OSHA has contributed to a notable decrease in worker fatalities in the United States. On average, the number of worker deaths per day has decreased from approximately 38 in 1970 to 12 in 2013. This reduction reflects OSHA’s efforts in enforcing safety standards and promoting a culture of workplace safety.
- Decrease in Worker Injuries and Illnesses: OSHA’s regulations and enforcement activities have also led to a decline in the rate of workplace injuries and illnesses. In 1972, there were about 10.9 incidents of work-related injuries and illnesses per 100 workers. By 2012, this rate had decreased to 3.0 per 100 workers. This improvement demonstrates the effectiveness of OSHA’s efforts in preventing workplace hazards and promoting safer work environments.
History of OSHA
OSHA, or the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, is a crucial agency within the U.S. Department of Labor. It is primarily responsible for enhancing worker safety and health protections across various industries.
The foundation of OSHA dates back to December 29, 1970, when President Nixon signed the Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSH Act) into law. This landmark legislation established OSHA as the overseeing agency tasked with enforcing workplace safety and health regulations. Following the enactment of the OSH Act, OSHA officially began its operations on April 28, 1971, marking the formal establishment of the agency.
OSHA’s Mission
OSHA, or the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, is dedicated to ensuring safe and healthy working conditions for employees across various industries. Its mission encompasses setting and enforcing standards while also providing training, outreach, education, and assistance.
To fulfill its mission, OSHA engages in several key activities:
- Developing occupational safety and health standards to regulate workplace conditions.
- Enforcing these standards through regular worksite inspections to ensure compliance.
- Offering comprehensive training programs aimed at increasing awareness and understanding of occupational safety and health practices among workers and employers alike.
What Rights Do You Have Under OSHA?
Under OSHA, workers are entitled to various rights to ensure their safety and well-being in the workplace. These rights include:
- A safe and healthful workplace: Employees have the right to work in an environment that is free from hazards and risks to their health and safety.
- Knowledge about hazardous chemicals: Workers have the right to be informed about any hazardous chemicals present in their workplace and the associated risks.
- Report injury to employer: Employees have the right to report any work-related injuries or illnesses to their employer without fear of retaliation.
- Complain or request hazard correction from employer: Workers can voice concerns or request corrective actions regarding workplace hazards or unsafe conditions.
- Training: Employees have the right to receive training and instruction on safety procedures and protocols relevant to their job duties.
- Access to hazard exposure and medical records: Workers have the right to access records related to their exposure to workplace hazards and any medical records resulting from workplace injuries or illnesses.
- File a complaint with OSHA: Employees have the right to file a complaint with OSHA if they believe their workplace is unsafe or if their employer is not complying with OSHA standards.
- Participate in an OSHA inspection: Workers have the right to participate in OSHA inspections of their workplace and to accompany OSHA inspectors during the inspection process.
- Be free from retaliation: Employees have the right to exercise their safety and health rights without fear of retaliation or discrimination from their employer. This includes reporting hazards, filing complaints, or participating in OSHA inspections.
Worker Rights
1. Safe and Healthful Workplace
Worker protection is mandated by law through the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 (OSH Act). OSHA, established by this act, ensures that workers have the fundamental right to a safe and healthful workplace. Employers bear the responsibility of providing work environments that are devoid of known hazards capable of endangering their employees.
The OSH Act grants workers significant rights, empowering them to engage in activities aimed at safeguarding themselves from job-related hazards. This includes the right to voice concerns about workplace safety and participate in initiatives to mitigate risks to their health and well-being.
Know about hazardous chemical
Employers are required to establish a comprehensive hazard communication program, documented in writing, which encompasses several crucial components:
- Container labeling: Containers holding hazardous substances must be clearly labeled to convey information about the contents and associated hazards.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDSs): Employers must maintain Safety Data Sheets for all hazardous chemicals present in the workplace. These sheets provide detailed information on the properties and hazards of the chemicals.
- Worker training: Employers are responsible for providing adequate training to workers regarding the physical and health hazards posed by the chemicals they may encounter. This training should also cover protective measures that workers can take to safeguard themselves from these hazards.

Information about injuries and illnesses
Under OSHA’s Recordkeeping rule, most employers with more than 10 workers are obligated to maintain a log of all work-related injuries and illnesses. Workers retain the right to report any injuries they suffer and to review the current log of injuries and illnesses kept by their employer.
Additionally, employees have the right to access and review the annually posted summary of injuries and illnesses, known as OSHA Form 300A. This summary provides a snapshot of workplace safety and helps workers stay informed about the health and safety conditions in their workplace.

Complain or Request Corrections
Workers have the right to raise safety and health concerns in the workplace to their employers without fear of retaliation, discharge, or discrimination. OSHA rules specifically protect workers who voice concerns about unsafe or unhealthy conditions either to their employer directly or to OSHA itself. This protection ensures that employees can advocate for their own safety and that of their colleagues without facing negative consequences from their employer.
Training
Workers have the right to receive training from their employers on various health and safety hazards as well as the standards that employers must adhere to. This training is essential for ensuring that workers are equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to protect themselves and their colleagues in the workplace. Required training topics may include chemical hazards, equipment hazards, noise, confined spaces, fall hazards in construction, personal protective equipment, and other relevant subjects. Importantly, this training must be conducted in a language and vocabulary that workers can understand, ensuring effective communication and comprehension.

Examine Exposure and Medical Records
According to OSHA’s 1910.1020 standard, workers have the right to examine and copy records related to toxic substances and harmful physical agents present in their workplace. Examples of such substances and agents include metals like lead, cadmium, and silica, as well as biological agents such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Additionally, physical stressors like noise, heat, cold, vibration, repetitive motion, and both ionizing and non-ionizing radiation are considered harmful and fall under this category. This provision empowers workers to access information crucial for understanding and addressing potential health and safety risks in their work environment.
File a complain with OSHA
Workers have the right to file a confidential complaint with OSHA if they suspect a violation of safety or health standards, or if they believe there is an imminent danger situation in their workplace. They may request that their name be kept confidential from the employer during the process. If a worker files a complaint, they are entitled to learn about OSHA’s response to the complaint and request a review if an inspection is not conducted as a result. This ensures that workers can raise concerns about workplace safety without fear of reprisal and can have confidence that their complaints are being addressed by the appropriate authorities.

Participate in an OSHA Inspection
Employees have the right to have a representative accompany an OSHA inspector during workplace inspections. This representative can be a worker chosen by the employees or a union representative if the workplace is unionized. During the inspection, workers can speak privately with the inspector, pointing out hazards, describing any injuries, illnesses, or near misses resulting from those hazards, and expressing any concerns about safety or health issues. Additionally, workers have the right to learn about the results of the inspection, the measures being taken to address any violations found, and they can object to the deadlines set for correcting violations if necessary. This ensures that workers have a voice in the inspection process and can actively participate in ensuring a safe and healthy work environment.
Be Free From Retaliation
Workers have the fundamental right to be protected from retaliation for exercising their safety and health rights in the workplace. This means that workers should be able to seek safety and health protections on the job without fearing any form of punishment or reprisal from their employer. This right is explicitly outlined in Section 11(c) of the Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSH Act). If workers believe they have faced retaliation for exercising their safety and health rights, they have the option to contact OSHA within 30 days to report the issue and seek resolution. This provision ensures that workers are empowered to speak up and advocate for their own safety and well-being in the workplace.
What responsibilities does your employer have under OSHA?
Employers have a range of responsibilities to ensure workplace safety and comply with OSHA standards:
- Provide a workplace free from recognized hazards and adhere to OSHA standards to ensure the safety and health of workers.
- Offer the necessary training as required by OSHA standards to equip workers with the knowledge and skills to perform their jobs safely.
- Maintain records of injuries and illnesses occurring in the workplace as mandated by OSHA regulations.
- Arrange for medical examinations when required by OSHA standards and grant workers access to their exposure and medical records.
- Refrain from discriminating against workers who exercise their rights under the OSH Act, as outlined in Section 11(c).
- Display OSHA citations and notices related to hazard corrections in prominent locations within the workplace.
- Provide and cover the cost of most personal protective equipment (PPE) needed to ensure worker safety and health.
By fulfilling these obligations, employers contribute to creating a safe and healthy work environment, fostering employee well-being, and complying with regulatory requirements.
Employer Responsibilities
To ensure compliance with reporting and recording requirements, employers should adhere to the following checklist:
- Report Worker Fatalities: Promptly report each worker death to OSHA.
- Report Severe Injuries: Report any work-related hospitalization, amputation, or loss of an eye to OSHA.
- Maintain Records: Maintain accurate records of injuries and illnesses as required by OSHA regulations.
- Inform Workers: Inform workers about the process for reporting an injury or illness to the employer.
- Provide Access: Make injury and illness records available to workers upon request.
- Grant OSHA Access: Allow OSHA inspectors access to relevant records during inspections.
- Post Annual Summary: Post the annual summary of injuries and illnesses in a visible location for workers to review.
By adhering to these guidelines, employers can fulfill their obligations regarding reporting and recording workplace incidents, promote transparency, and ensure compliance with OSHA regulations.
What are OSHA Standards?
OSHA standards serve as comprehensive guidelines that outline the specific methods and practices employers must implement to safeguard their employees from various workplace hazards. These standards are meticulously designed to ensure the protection of workers across different industries and job roles. They cover a wide array of potential risks and dangers present in the workplace environment.
The primary objectives of OSHA standards are to establish clear protocols and procedures aimed at minimizing or eliminating occupational hazards, thereby promoting a safe and healthy work environment for all employees. Compliance with OSHA standards is mandatory for employers and is enforced through inspections and penalties for violations.
Furthermore, OSHA standards play a crucial role in fulfilling the General Duty Clause of the Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSH Act), which requires employers to provide workplaces that are free from recognized hazards that are causing or likely to cause death or serious physical harm to their employees. By adhering to OSHA standards, employers demonstrate their commitment to prioritizing the safety and well-being of their workforce.

OSHA standards not only specify protective measures but also set limits on workers’ exposure to hazards like chemicals and noise. They require safe work practices, appropriate equipment, and monitoring of hazards. Employers must also keep records of workplace injuries and illnesses to ensure compliance.
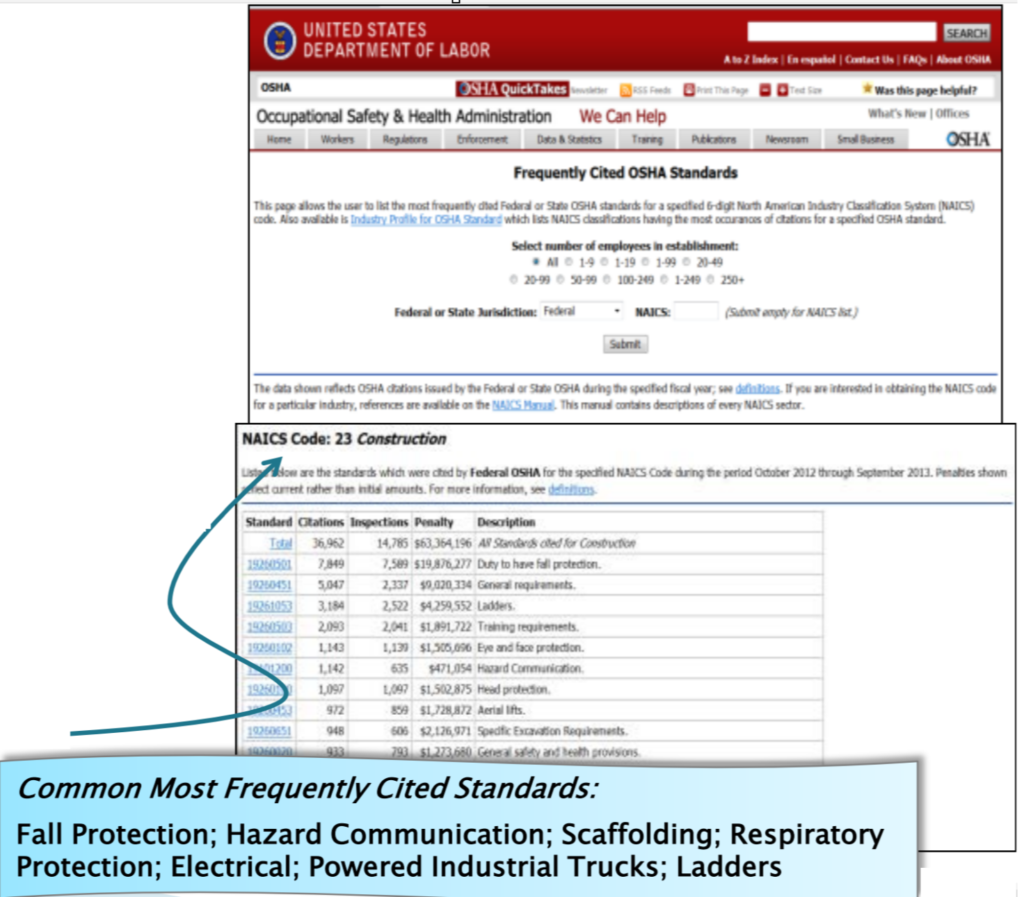
Most Frequently Cited OSHA Standards
Visit OSHA’s website to access information on the most frequently cited standards. You can filter the data by the number of employees, jurisdiction (Federal or State), and industry classification (NAICS code). This tool helps you understand common violations and prioritize safety measures accordingly.
How are OSHA Inspection Conducted?
Under the OSH Act, OSHA compliance safety and health officers (CSHOs) are authorized to conduct workplace inspections at reasonable times. Inspections typically occur without advance notice, except in rare circumstances such as imminent danger situations. It’s important to note that informing an employer about an upcoming OSHA inspection in advance can lead to fines and even legal consequences, including potential jail time.
Different Types of OSHA Inspection
OSHA inspections can occur for various reasons, including:
- Imminent danger situations where there is a threat of serious harm or death.
- Incidents involving fatalities, hospitalizations, or other serious injuries.
- Worker complaints or referrals regarding workplace safety concerns.
- Targeted inspections as part of Local Emphasis Programs (LEPs), National Emphasis Programs (NEPs), or specific hazards or industries identified for scrutiny.
- Follow-up inspections to ensure compliance with previously cited violations or to verify corrective actions have been taken.

Citation and Penalties
Sure, here’s the information presented in a table format:
| Violation Type | Definition | Penalty |
|---|---|---|
| Willful | A violation where the employer intentionally and knowingly commits a violation, or commits a violation with plain indifference to the law. | Up to $70,000 for each willful violation, with a minimum penalty of $5,000 for each willful violation. |
| Serious | A violation where there is a substantial probability that death or serious physical harm could result, and the employer knew or should have known of the hazard. | Mandatory penalty of up to $7,000. |
| Other-Than-Serious | A violation that has a direct relationship to safety and health but probably would not cause death or serious physical harm. | Up to $7,000 for each other-than-serious violation. |
| Repeated | A violation that is the same or similar to a previous violation. | Up to $70,000 for each repeated violation. |
This table summarizes the different types of violations defined by OSHA along with their respective definitions and penalties.
Where can you go for help?
1. Sources within the workplace/worksite.
These sources within the workplace/worksite can provide valuable information regarding safety procedures, hazards, and precautions:
- Employer or Supervisor: They can provide guidance on workplace safety protocols, emergency procedures, and specific hazards relevant to the job.
- Co-workers: Experienced colleagues can share firsthand knowledge about workplace hazards, safe work practices, and tips for staying safe on the job.
- Union Representatives: They may offer insight into safety concerns raised by employees, advocate for improved safety measures, and provide resources for addressing workplace hazards.
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): SDS provides detailed information about the properties and potential hazards of chemicals used in the workplace, as well as guidance on safe handling, storage, and disposal.
- Labels and Warning Signs: These provide immediate visual cues about potential hazards, safety precautions, and necessary protective equipment in specific areas or when handling certain materials.
- Employee Orientation Manuals or Training Materials: These resources typically outline workplace safety policies, procedures, and expectations, ensuring new employees are aware of potential hazards and proper safety protocols from the outset.
- Work Tasks and Procedures Instructions: Detailed instructions for carrying out job tasks can include safety measures, equipment usage guidelines, and steps to mitigate risks associated with specific activities.
By utilizing and referencing these sources, employees can stay informed about workplace hazards and safety practices, helping to prevent accidents and promote a safe working environment.
2. Sources outside the workplace/worksite.
These sources outside the workplace/worksite offer valuable information and assistance regarding workplace safety and health:
- OSHA Website: OSHA’s official website provides a wealth of resources, including safety standards, regulations, educational materials, and tools for promoting workplace safety.
- OSHA Offices: Local OSHA offices offer assistance and guidance on safety regulations, compliance, and workplace safety issues. You can contact them via phone or in writing for inquiries or assistance.
- Compliance Assistance Specialists: These specialists, available in area offices, offer guidance and support to employers and employees regarding OSHA standards, compliance assistance, and training programs.
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH): As OSHA’s sister agency, NIOSH conducts research, provides recommendations, and offers resources to improve workplace safety and health.
- OSHA Training Institute Education Centers: These centers provide training courses and resources to enhance workplace safety knowledge and skills for employers, employees, and safety professionals.
- Healthcare Providers: Doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals can offer guidance on occupational health issues, injury prevention, and treatment of work-related illnesses or injuries.
- Public Libraries: Libraries may offer access to resources such as books, journals, and online databases containing information on workplace safety, health regulations, and related topics.
- Local, Community-Based Resources: Community organizations, non-profits, and labor unions may provide workshops, seminars, or educational materials on workplace safety and health tailored to specific industries or demographics.
By utilizing these external sources, employers and employees can access information, support, and training to promote a safe and healthy work environment.
3. How to file an OSHA complaint?
To file an OSHA complaint, follow these steps:
- Identify Safety and Health Problems: Review provided handouts or discuss with colleagues to identify workplace hazards or safety concerns.
- Download OSHA Complaint Form: Visit OSHA’s website and download the complaint form. This form can be filled out and submitted online.
- File Complaint Online: Complete the complaint form online. Both workers and worker representatives have the option to file a complaint using this method.
- Contact Local OSHA Offices: Alternatively, you can contact local regional or area offices by telephone or in person to discuss your concerns.
- Provide Detailed Information: When completing the form, be specific and include relevant details about the identified safety or health issues.
- Maintain Anonymity (Optional): Workers have the choice to remain anonymous when filing a complaint. OSHA will keep the complainant’s identity confidential during the investigation process.
- OSHA Inspection Determination: OSHA will review the complaint and decide whether an inspection is necessary based on the information provided.
For the Construction and Maritime industries, the process for filing an OSHA complaint is similar to the general process outlined earlier. However, since these industries have their own unique hazards and safety concerns, it’s essential for groups to tailor their complaints accordingly. Here’s how the discussion and complaint formulation might unfold for each industry:
Construction:
- Review Handout: Each group reviews the handout detailing construction industry-specific scenarios, which may include hazards like falls, electrical hazards, or hazardous materials.
- Identify Important Information: Groups discuss what specific hazards or safety issues are present in the scenario and determine what information is crucial to include in their complaint. This might involve detailing specific hazards encountered on the construction site, inadequate safety equipment provided, or lack of proper training.
- Group Discussion: After completing the exercise, the class discusses each group’s results. They can share what hazards were included in the complaint and any additional details or concerns that were added to address the specific construction-related risks.
Maritime Industry:
- Review Handout: Similarly, each group reviews the handout outlining scenarios specific to the maritime industry, such as hazards related to working aboard ships, confined spaces, or maritime equipment.
- Identify Important Information: Groups discuss the unique hazards present in the maritime industry scenario and determine what information is essential to include in their complaint. This might involve addressing issues like inadequate safety procedures for working at sea, lack of proper equipment maintenance, or insufficient emergency response protocols.
- Group Discussion: The class then discusses each group’s findings, sharing what hazards were included in the complaint and any additional details added to address the specific safety concerns of the maritime industry.
In both cases, the goal is to ensure that the complaints are comprehensive and address the specific hazards and safety challenges inherent in each industry. This exercise helps students understand the importance of industry-specific safety considerations and how to effectively communicate these concerns to OSHA.
Give an example of a reason why OSHA would
conduct an inspection at your workplace?
What are the types of OSHA violations?
Willful Violations: These are the most severe violations where an employer intentionally or knowingly commits a violation, or shows plain indifference to the law. Penalties for willful violations can be up to $70,000 per violation.
Serious Violations: These violations involve hazards where there’s a substantial probability that death or serious physical harm could occur, and the employer knew or should have known about the hazard. Penalties for serious violations can be up to $7,000 per violation.
Other-Than-Serious Violations: These violations are related to safety and health but are not likely to cause death or serious physical harm. Penalties for other-than-serious violations can be up to $7,000 per violation.
Repeated Violations: These are violations that are the same or similar to previous violations. Penalties for repeated violations can be up to $70,000 per violation.
Failure to Abate Prior Violation: If an employer fails to correct a previously cited violation within the prescribed timeframe, they may face additional penalties of up to $7,000 per day until the violation is abated.
Understanding these types of violations helps employers prioritize workplace safety and compliance with OSHA standards to ensure the well-being of their employees.
What are some resources inside the workplace that will help you find information on safety and health issues?
Employee Orientation Manuals
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
Labels and Warning Signs
Safety Training Materials
Work Tasks and Procedures Instructions
Supervisors and Managers
Co-workers
These resources provide guidance on safety protocols, hazard identification, and safe work practices, fostering a culture of safety within the organization.
What are some resources outside the workplace that will help you find information on safety and health issues?
OSHA Website (http://www.osha.gov) and local OSHA offices.
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
OSHA Training Institute Education Centers.
Healthcare Providers (doctors, nurses, etc.).
Public Libraries.
Community-Based Organizations and Nonprofits.
These resources provide access to safety standards, regulations, educational materials, and assistance in addressing workplace safety concerns, helping individuals stay informed and promote a safe working environment.