Following tools and equipment shall be used normally for Cable Testing after Installation on Reel. Main keywords for this article are Cable Testing after Installation. High potential test, test on medium voltage cables, 5 kv megger tested, potential test on medium voltage.
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT
- Cable cutter
- Knife
- Diagonal cutting pliers
- Side cutting pliers
- Screw drivers
- Measuring tape
- Hack saw
- Multi-meter/ Continuity tester
- Insulation Resistance Tool (Megger, etc.)
- Wire stripper
- Crimping tool
- Other Relevant Tools
Cable Testing after Installation
- Low voltage (600, 450/750, or 600/1000 V rated) cables, including splices to existing cables, shall be 1000 V DC megger tested after installation and prior to placing in service (during commissioning).
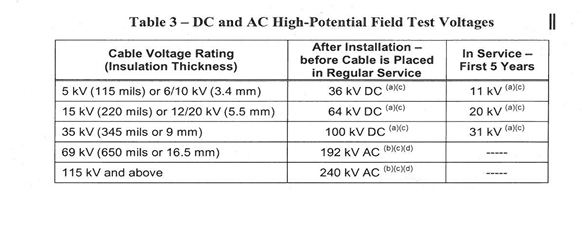
- Medium voltage cables (5 kV through 35 kV) shall be tested as follows:
a) New installations of cable and splices shall be 5 kV megger tested before and after backfilling and then DC high-potential tested after installation and prior to placing in service (during commissioning) at voltage levels specified in 15-SAMSS-502 or 15-SAMSS-503 and listed in Table 3.
b) New cables to be spliced to existing cables shall be megger tested and DC high-potential tested prior to splicing per (a) above. After splicing, the new and existing cable combination shall be 5 kV megger tested. In addition, if the existing cable has been in service for less than five years, the new and existing cable combination shall be high-potential tested to the voltage listed in Table 3.
c) Routine periodic testing of cables is not recommended. Under special circumstances, as determined by the cable Proponent, the cable may be 5 kV megger tested, and, if it has been in service for less than five years, it may be high-potential tested to the voltage listed in Table 3. Other test method such as Very Low Frequency (VLF) test may be applied to determine the condition of old cables. DC high-potential testing shall not be performed on cables that have been in service for more than five years.
d) The high potential test on medium voltage cables may be performed after mounting or forming the terminations, provided: (i) terminations have creepage distances per Section 6.12; (ii) terminations are not connected to equipment, unless the equipment can also be tested at the same voltage; and (iii) there are sufficient clearances from enclosures and other adjacent objects.
e) If separable connectors (elbows) conforming to ANSI/IEEE 386 are used, the high potential test on medium voltage cables may, at the request of the cable Proponent, be performed after installation of the elbows. In this case: (i) the test must be performed with the elbows plugged into insulated parking bushings; and (ii) test voltage shall be the lesser of the ICEA cable test voltage listed in Table 3 and the ANSI/IEEE 386 DC withstand voltage.
Commentary Notes:
A) For new 15 kV cable, when tested with elbows, the test voltage is reduced from 64 kV to 53 kV DC; for 35 kV cable it remains unchanged at 100 kV DC (the ICEA cable test value);
B) If 200 A elbows are installed on both ends of the cable, a feed-thru bushing instead of one of the two parking bushings may be used to apply the test voltage;
C) In most cases, it is chosen to test the cables without the elbows.